Troubleshooting MCR When a BGP Session is Down
When a BGP session on Megaport Cloud Router (MCR) is down, step through these troubleshooting actions.
Troubleshooting actions
| Action | Steps |
|---|---|
| Verify the BGPBorder Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a standardized routing protocol designed to exchange route and reachability information among autonomous systems (AS) on the internet. configuration |
Check the ASNAn autonomous system (AS) is a collection of connected Internet Protocol (IP) routing prefixes under the control of one or more network operators on behalf of a single administrative entity or domain. ASN refers to autonomous system number and is a unique numerical ID allocated to each AS for use in BGP routing. , BGP IP address, and subnet mask:
|
| Verify access to TCP port 179 | BGP neighborsMCR uses Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to exchange network reachability information with adjacent BGP systems, known as neighbors, or peers. By default, once the BGP neighbors are connected, they share routing information with each other. establish a TCP session using TCP port 179.
|
| Verify the route filtering | The MCR Looking Glass displays the routes received or sent after applying route filtering. For more information, see Viewing Traffic Routing Through MCR Looking Glass.
|
| Check the BGP neighbor state | When BGP is configured with a neighbor IP address, it goes through several stages before it reaches the Established state. The BGP Neighbor States are Idle, Connect, Active, OpenSent, OpenConfirm, and Established.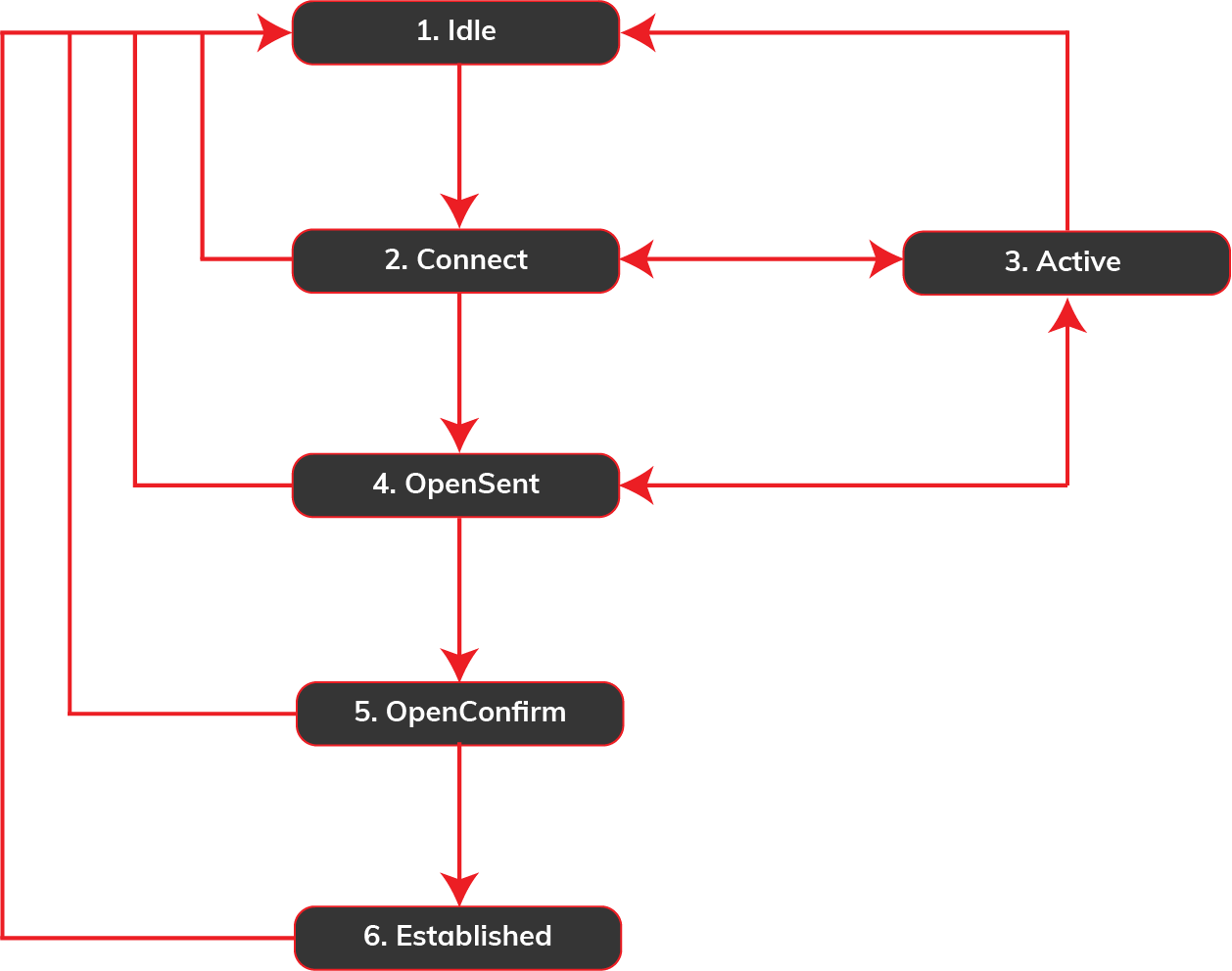 |
| Check the BGP message type | BGP packets use these message types:
|
| Verify the MD5Sometimes known as an MD5 hash or BGP key. The message-digest (MD5) algorithm is a widely used cryptographic function producing a string of 32 hexadecimal digits. This is used as a password or key between routers exchanging BGP information. authentication |
|
| Run connectivity tests |
|
| Find error conditions in BGP logs | The BGP protocol sends a notification message when it detects an error with the BGP session such as: an expiring hold timer, a change to neighbor capabilities, or a request to reset a BGP session. When an error is detected, the BGP session is closed. For example, enter show log %BGP-xxxxx |
Next steps
If the troubleshooting actions do not resolve your issue, contact support. Before contacting support for assistance, collect the following information.
- Note the date, time, and time zone in which the issue started.
- Is the BGP session down?
- Is the BGP session flapping? For example, does the peering establish, then drop, re-establish, and then drop? Try to pinpoint where the problem might be in the network using ping.
- Is there a BGP routing issue?
Note
For more information about when a field service technician is needed onsite at the data center, see Customer Field Services.
Collect essential troubleshooting data
BGP configuration information
- Interface settings, including VLAN number
- BGP IP address and subnet mask
- BGP ASN
- BGP network addresses to be advertised
- BGP neighbor IP address and subnet mask
- BGP neighbor ASN
- BGP neighbor network addresses to be received
- BGP authentication between BGP peers
- BGP route filtering and manipulation, if any
BGP command output and packet capture information
- Examine the BGP neighbor table and BGP state using the show IP BGP summary command
- Examine the BGP neighbor details using the show IP BGP neighbors command
- Logs that show BGP-related messages (output from the show log %BGP-xxxxx command)
- BGP routing table entries that have BGP routing issues (output from the show IP BGP command)
- BGP advertised routes (output from the show IP BGP neighbors <neighbor-ip-address> advertised-routes command)
- BGP received routes (output from the show IP BGP neighbors <neighbor-ip-address> routes command)
- Routing table (output from the show IP route <ip-address> command)
- Traceroute logs between source and destination host
- Packet capture logs, if possible (file size can be up to 10 M)