Introducing MVE
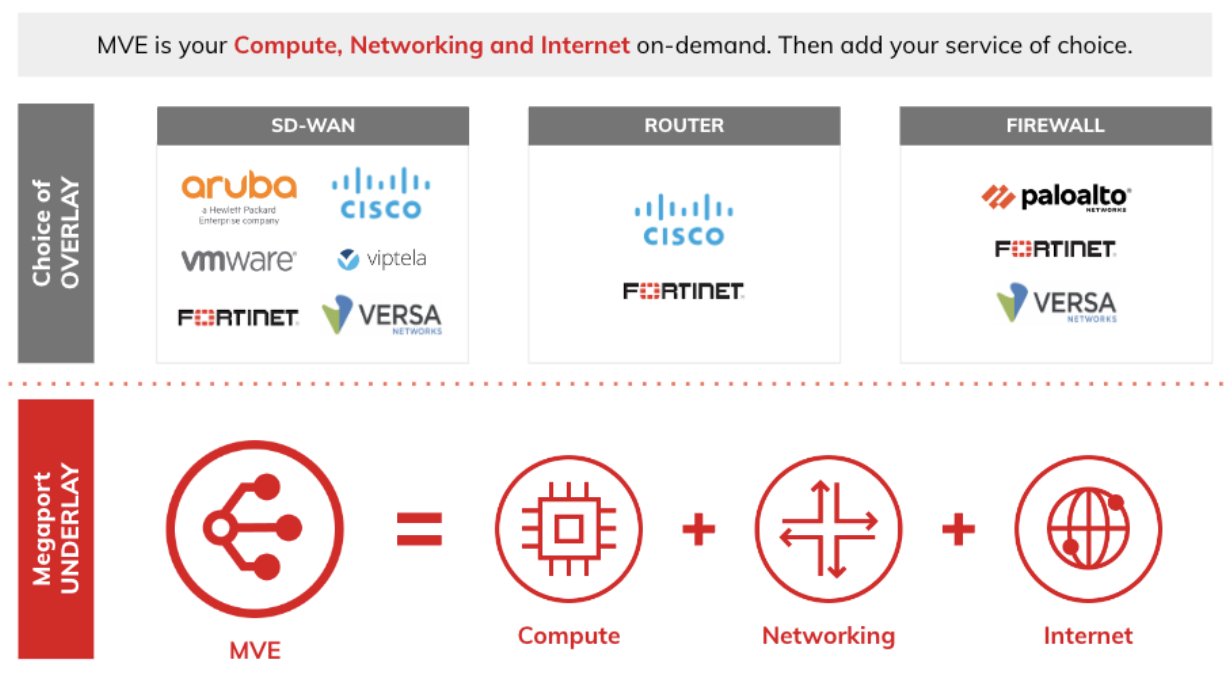
The MVE is an on-demand, vendor-neutral Network Function Virtualization (NFV) platform that provides virtual infrastructure for network services at the edge of Megaport’s global software-defined network (SDN). Network technologies such as SD-WAN and NGFW are hosted directly on Megaport’s global network via Megaport Virtual Edge.
MVE modernizes network connectivity and enables customers to deploy NGFWs, SD-WAN gateways, virtual routers, and integrated transit gateways in minutes. Users of MVE can seamlessly extend their network services closer to the end user without the need for hardware. MVE improves the performance of these virtual network devices by connecting them to Megaport’s global, private network, providing secure, dedicated, and highly reliable connectivity to branches, remote sites, public clouds, private clouds, and other mission-critical digital infrastructure.
What is SD-WAN?
A software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) provides enterprise customers with centralized control over multiple network endpoints such as branch offices, hubs, data centers, point-of-sale locations, and home offices. The virtualized network design allows flexibility in the choice of transport services, including public internet over broadband, satellite, MPLS, and mobile 4G/5G networks by decoupling the network software controls from the WAN connections.
SD-WAN simplifies the setup and management of WAN solutions using a management control console that an enterprise network manager can use to apply routing decisions, automate business policies, and monitor network usage and performance in real time.
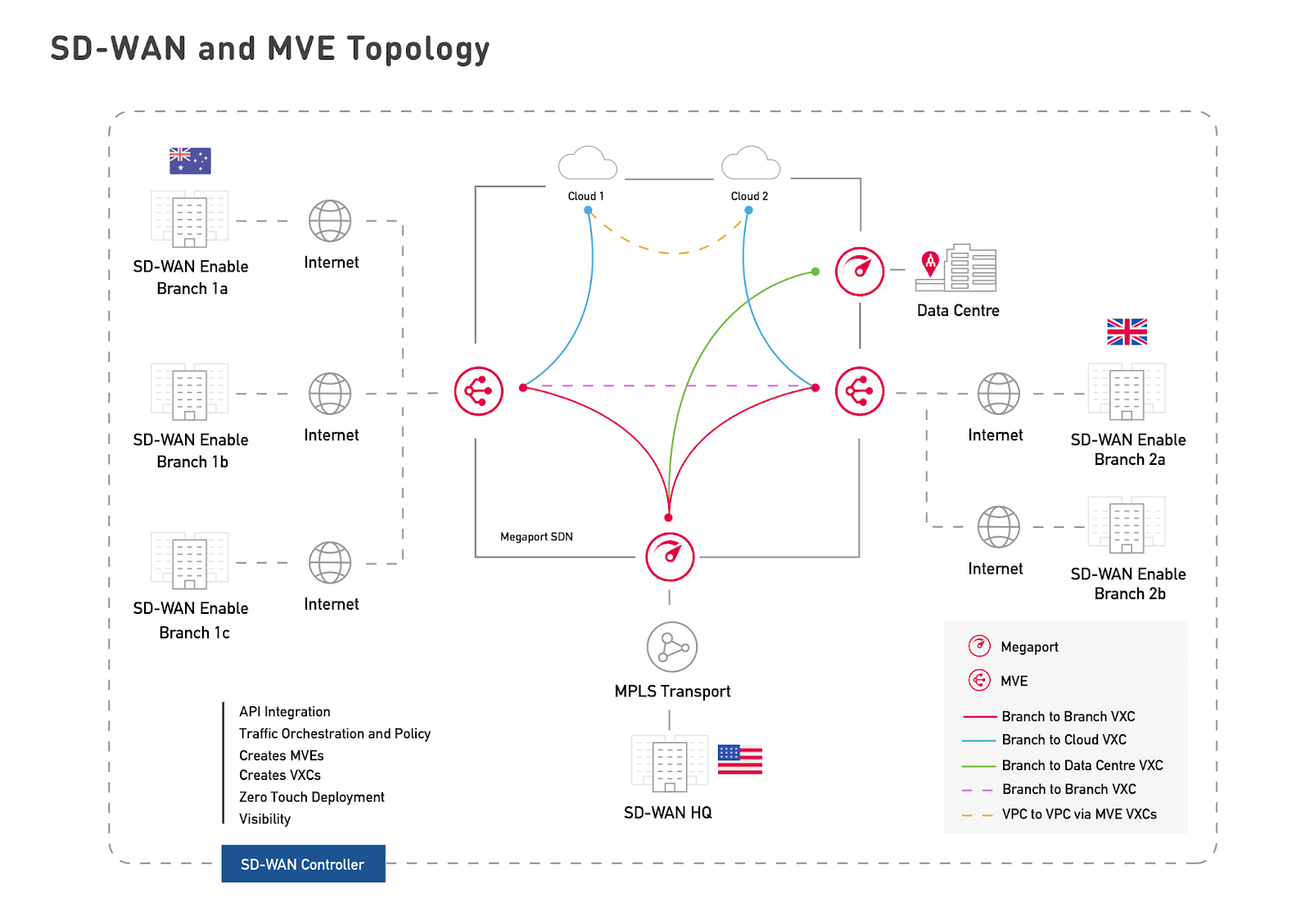
SD-WAN with Megaport
The Megaport SDN is a private network that does not provide connectivity to the public. MVE is connected to the Megaport Internet Gateways so that SD-WAN appliances can reach the Megaport private network via the internet. But internet dependency is reduced, because MVE makes use of transit IP connectivity to the public internet only as a bridge to the Megaport private network. The public internet portion of the end-to-end connectivity is limited to only one-hop or a few-hops to the Megaport SDN. Terminating traffic to the nearest MVE reduces internet hops. The internet acts as the first mile, and Megaport acts as the middle and last mile.
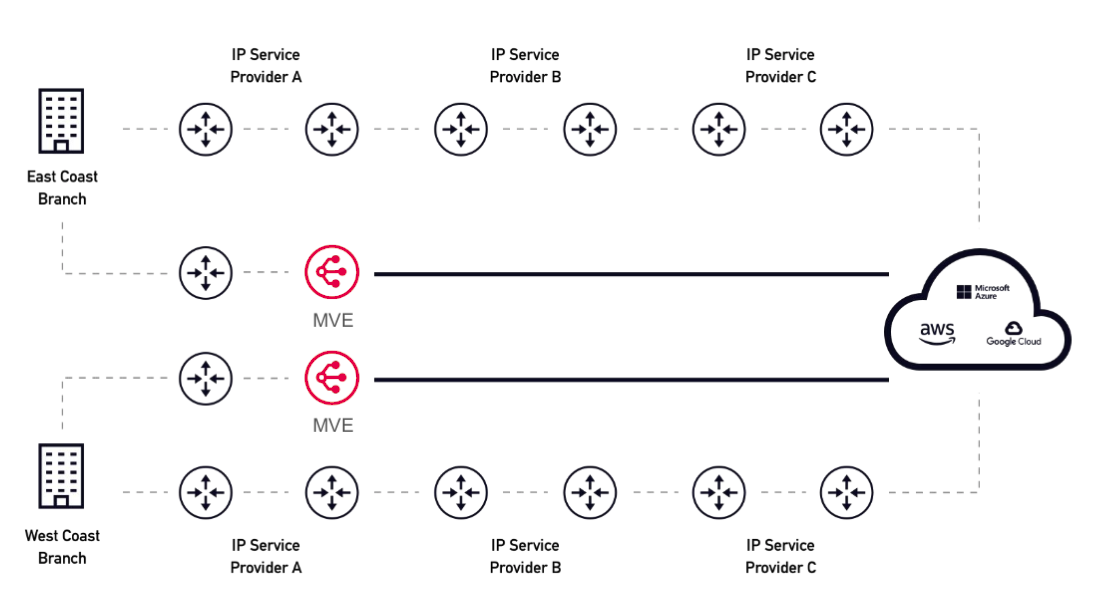
The internet connection is used only to bridge connectivity from the customer SD-WAN on-premises devices into the Megaport SDN. The internet connection terminates at the Megaport MVE. Other than the initial connection between the customer on-premises devices and MVE to enter the Megaport SDN, once the connection is made, all traffic remains within the Megaport network.
Note
The internet-facing interface on an MVE can reach the internet-facing interface on another MVE over the public internet. That is, you can exchange traffic from MVE to MVE in different metros over the internet. The basic connection model consists of an MVE at one metro connecting via a Megaport Internet connection to an MVE at another metro. Connectivity consists of a customer/SD-WAN partner-managed connection, not Megaport managed. For more information, see Megaport Internet Overview.
SD-WAN and next generation firewall partners
MVE is integrated with these providers:
- Aruba EdgeConnect SD-WAN – See Aruba EdgeConnect SD-WAN with Megaport MVE
- Aviatrix – See Aviatrix with Megaport Virtual Edge
- Cisco – See Cisco with MVE
- Fortinet FortiGate – See Fortinet FortiGate with Megaport MVE
- Palo Alto Networks VM-Series Next Generation Firewall – See Palo Alto Networks VM-Series NGFW
- Versa Secure SD-WAN – See Versa Secure SD-WAN with Megaport MVE
- VMware SD-WAN – See VMware SD-WAN with Megaport MVE
The SD-WAN providers create the private overlay network and manage the network connections and network policies. The provider’s SD-WAN fabric acts as the overlay, and the Megaport SDN acts as the underlay.
Key features
The SD-WAN and MVE solutions include these key features and benefits:
- Flexible connections countrywide – You can use MVE to hop onto important high-speed networks without provisioning a private circuit for access. Although a country area covers a larger area than a LAN, MVE treats a country area as one big LAN, keeping data traffic local.
- SD-WAN termination – MVE instances are preconfigured in essential metro areas as edge points across the Megaport platform. Connections are terminated from branch and on-premises locations to the nearest MVE metro hub to localize traffic. Remote sites are connected to MVE, so anything on the internet or the Megaport SDN is treated as though it is present on the edge. You can connect to MVE directly, through a cross-connect in a data center, or by using the public internet.
- Direct on-ramps – MVE provides direct access to any service within a cloud service provider (CSP). You can also use MVE to connect to any SaaS or IaaS provider within the Megaport Marketplace, or your own data center and branch locations.
- Subscription-based, pay-as-you-go pricing models – Your subscription includes a public IP address, internet access, and a connection to the internet that terminates the tunnel between the MVE and customer-provided equipment at the branch.
- Secure the network edge with SASE – In addition to the Network Function Virtualization (NFV) services that MVE provides, Megaport’s Fortinet and Versa SD-WAN partners offer Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) services. Both Versa and FortiGate VMs on MVE natively support SASE and SD-WAN services. For more information, see Securing the Network with SASE.
- Simple online provisioning – You order and configure MVE through the Megaport Portal or through Cisco’s SD-WAN vManage NMS console. You then order and provision up to 25 Virtual Cross Connects (VXCs). You can also create VXCs from existing Ports and CSPs into MVE to enable meshed network access, as shown in this image: