Connecting MVEs Integrated with Aruba EdgeConnect SD-WAN
This topic describes how to connect a Megaport Virtual Edge (MVE) integrated with Aruba EdgeConnect SD-WAN to another MVE.
This deployment uses the Megaport private software defined network (SDN) to reduce reliance on the internet and connect enterprise branch locations.
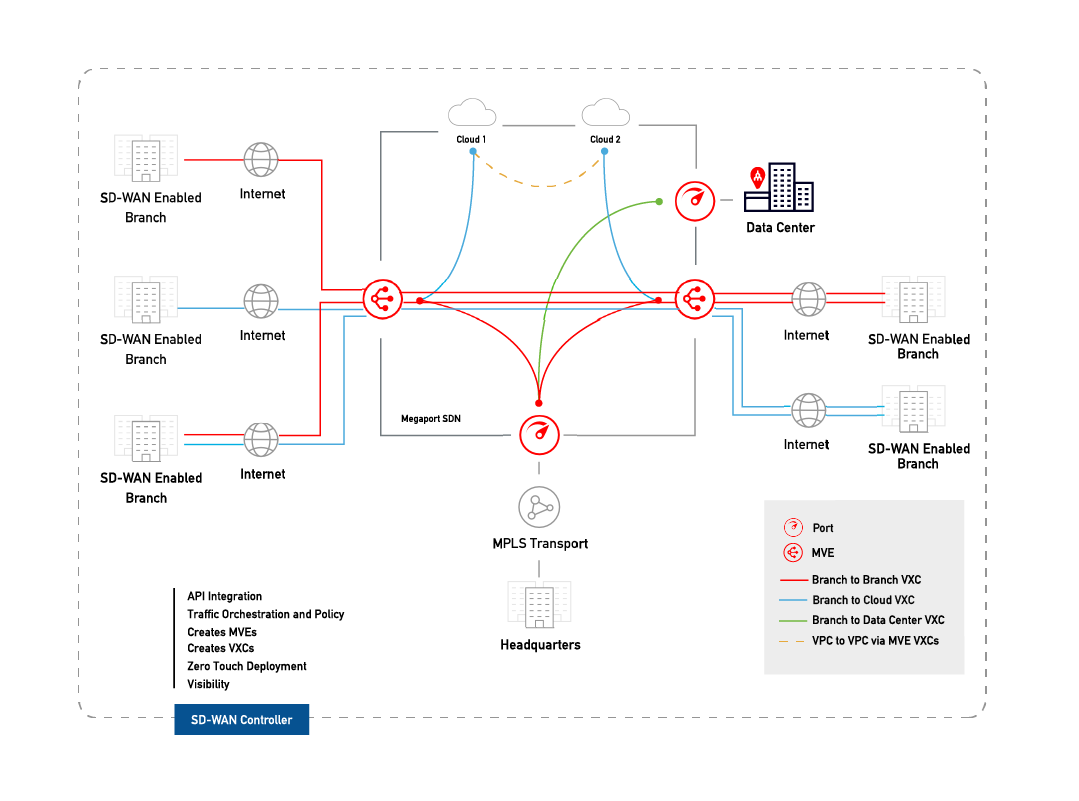
With two MVEs configured, you can create a private VXC to connect them on the Megaport network without the need for any physical infrastructure. A VXC is essentially a private point-to-point Ethernet connection between an A-End MVE and a B-End MVE.
Note
The internet-facing interface on an MVE can reach the internet-facing interface on another MVE over the public internet. That is, you can exchange traffic from MVE to MVE in different metros over the internet. The basic connection model consists of an MVE at one metro connecting via a Megaport Internet connection to an MVE at another metro. Connectivity consists of a customer/SD-WAN partner-managed connection, not Megaport managed. For more information, see Megaport Internet Overview.
Before you begin
Provision two MVEs in different locations. If you haven’t already created MVEs, see Creating an MVE in Aruba.
Creating a VXC between two MVEs
A private VXC deployment between two MVEs integrated with Aruba starts in the Megaport Portal. To complete the configuration, you use the Aruba Orchestrator console.
To create a VXC
-
In the Megaport Portal, go to the Services page and click +Connection next to the originating A-End MVE.
-
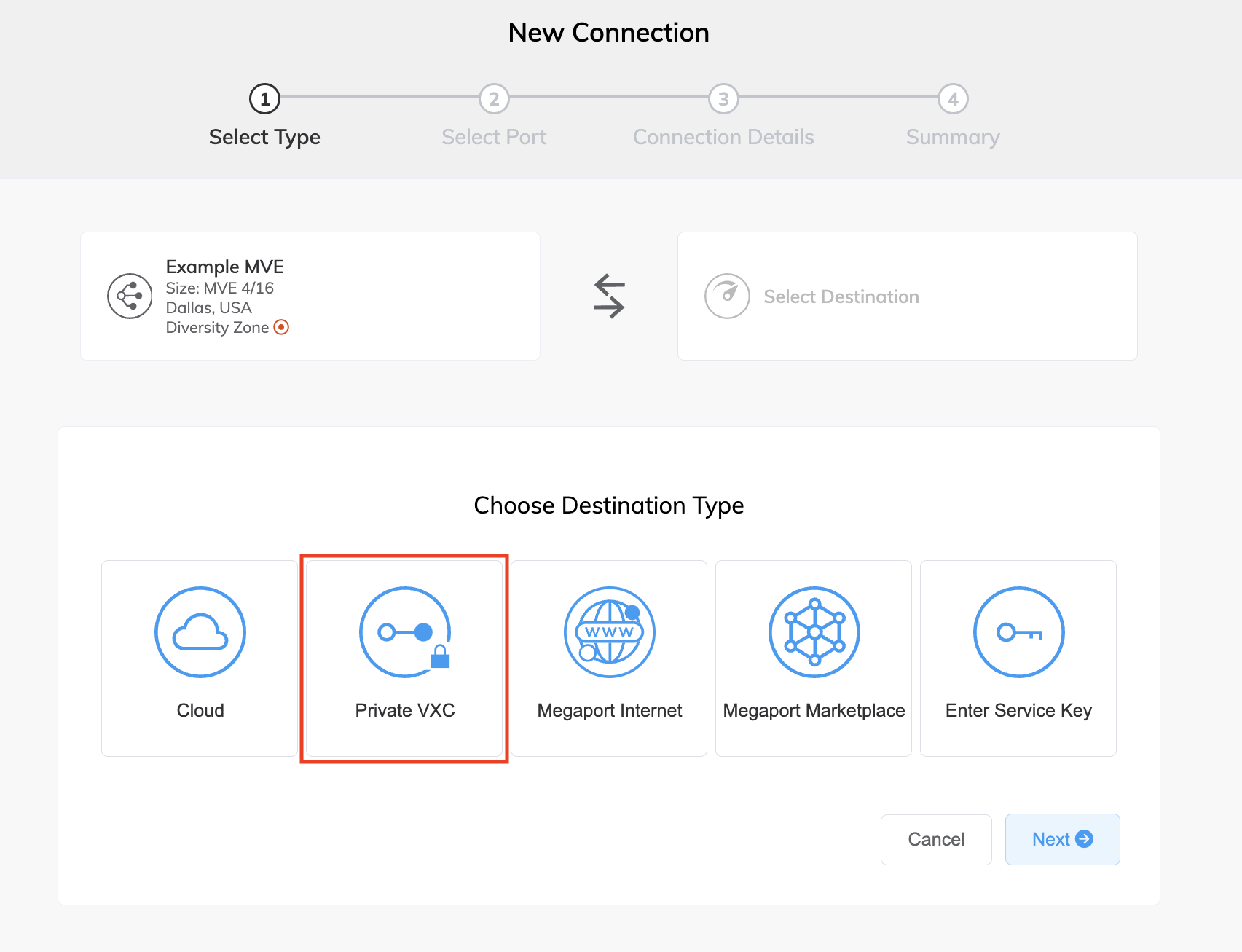
Select Private VXC.
-
Select the destination B-End MVE and location.
Use the Country filter to narrow the selection. -
Click Next.
-
Specify the connection details:
-
Connection Name – The name of your VXC to be shown in the Megaport Portal. Specify a name for the VXC that is easily identifiable, for example, LA MVE 2 to Dallas MVE 4. You can change the name later, if you like.
-
Service Level Reference (optional) – Specify a unique identifying number for the VXC to be used for billing purposes, such as a cost center number or a unique customer ID. The service level reference number appears for each service under the Product section of the invoice. You can also edit this field for an existing service.
-
Rate Limit – The speed of your connection in Mbps. The maximum speed is displayed. Although the rate limit for a VXC can be up to 10 Gbps, the compute capacity of the A-End or B-End MVE can influence the circuit throughput. Consult Aruba’s documentation for more information.
-
VXC State – Select Enabled or Shut Down to define the initial state of the connection. For more information, see Shutting Down a VXC for Failover Testing.
Note
If you select Shut Down, traffic will not flow through this service and it will behave as if it was down on the Megaport network. Billing for this service will remain active and you will still be charged for this connection.
-
vNIC selection – Depending on the definition of the MVEs you are using, you might have to specify A-End and B-End vNICs.
-
A-End vNIC – Specify a vNIC by using the pre-populated default, or select from the drop-down list.
-
B-End vNIC – Specify a vNIC by using the pre-populated default, or select from the drop-down list.
For more information on vNIC selection when connecting MVEs with different services, see Types of vNIC Connections.
-
-
Preferred A-End VLAN – Specify the 802.1q VLAN tag for this connection for the A-End.
Each VXC is delivered as a separate VLAN on the MVE. The VLAN ID must be unique on this MVE and can range from 2 to 4093. If you specify a VLAN ID that is already in use, the system displays the next available VLAN number. The VLAN ID must be unique to proceed with the order. If you don’t specify a value, Megaport will assign one. -
Preferred B-End VLAN – Specify the 802.1q VLAN tag for this connection that you will receive through the B-End VLAN.
-
Minimum Term – Select No Minimum Term, 12 Months, 24 Months, or 36 Months. Longer terms result in a lower monthly rate. 12 Months is selected by default.
Take note of the information on the screen to avoid early termination fees (ETF). For more information, see VXC Pricing and Contract Terms and VXC, Megaport Internet, and IX Billing. -
Resource Tags – You can use resource tags to add your own reference metadata to a Megaport service.
To add a tag:- Click Add Tags.
- Click Add New Tag.
- Enter details into the fields:
- Key - string maximum length 128. Valid values are a-z 0-9 _ : . / \ -
- Value - string maximum length 256. Valid values are a-z A-Z 0-9 _ : . @ / + \ - (space)
- Click Save.
If you already have resource tags for that service, you can manage them by clicking Manage Tags.
Warning
Never include sensitive information in a resource tag. Sensitive information includes commands that return existing tag definitions and information that will identify a person or company.
-
-
Click Next to view the Summary page.
-
Confirm the configuration and click Add VXC.
-
Click Order to proceed through the checkout process.
Once the VXC is deployed, you can view it in the Megaport Portal Services page. The Services page displays the VXC under the A-End MVE and the B-End MVE. Note that the service identifier number is the same for the VXC at both ends of the connection.
The next step is to configure the A-End and B-End MVEs in Aruba Orchestrator.
Note
The next procedure configures IP connectivity with BGP, providing just one solution out of many. Consult your SD-WAN vendor documentation for specific network design and configuration options before configuring interfaces for the MVEs.
Configuring the A-End MVE in Orchestrator
After you create the VXC between your MVEs, you need to configure it in Orchestrator. This involves configuring LAN interfaces.
To configure the A-End appliance
-
Log in to your enterprise Aruba Orchestrator system.
-
Choose Configuration > Discovery | Discovered Appliances or click Appliances Discovered on the upper right of the screen.
-
Select the A-End MVE.
-
Go to the System menu and choose Interface.
-
Choose Configuration > Networking | Deployment.
-
Locate the appliance by the hostname and click the Edit (pencil) icon.
-
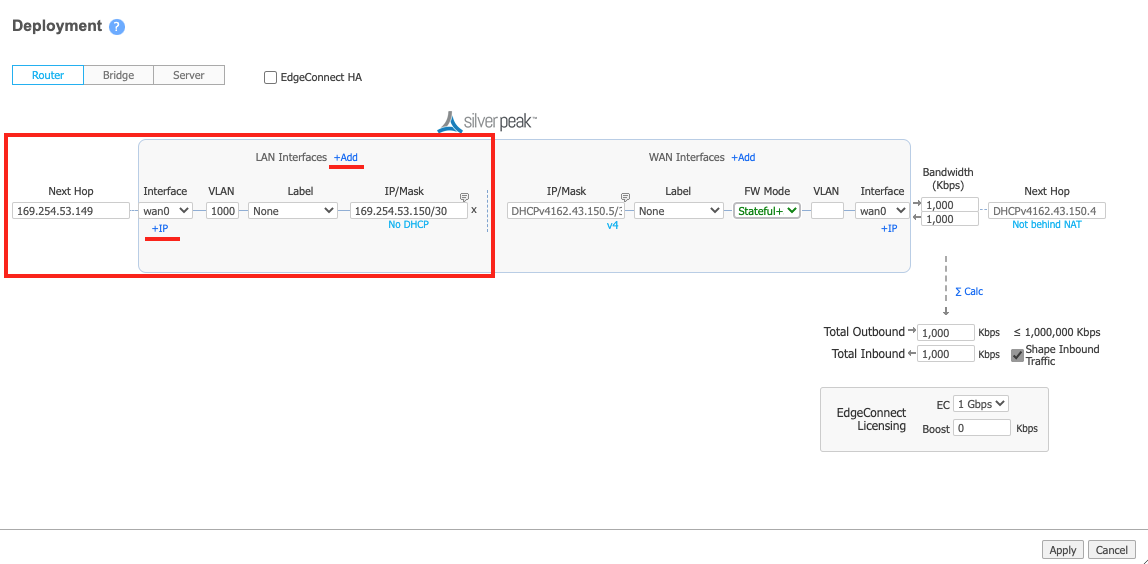
Add a new LAN side interface: Click +Add next to LAN Interfaces.
Note
If this is the first LAN side service connection, click +Add. If you already have a LAN interface, click +IP under the Interface drop-down list to add a new configuration.
Here is a screen with sample values.
-
In the Interface drop-down menu, choose wan0.
-
In the VLAN field, enter the A-End VLAN value for this connection from the Megaport Portal.
Click the Details icon for the connection in the Megaport Portal to find this value. Note that it might be different from the B-End VLAN ID. - (Optional) Select a preconfigured Label or select None.
- In the IP/Mask field, enter the A-End interface IP Address and subnet mask as required for your network.
- For the Next Hop, enter the B-End IP address.
- Specify in and out bandwidth values.
The bandwidth must be equal to or less than the MVE bandwidth limit. - Click Apply.
- If prompted, reboot the appliance.
At this point, the A-End interface is created. Once the device is reachable from Orchestrator, you can configure a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) session.
To set up the MVEs to exchange routing information, follow the steps in To configure BGP in Orchestrator.
Configuring the B-End MVE in Orchestrator
-
Log in to your enterprise Aruba Orchestrator system.
-
Choose Configuration > Discovery | Discovered Appliances or click Appliances Discovered on the upper right of the screen.
-
Select the B-End MVE.
-
Go to the System menu and choose Interface.
-
Choose Configuration > Networking | Deployment.
-
Locate the appliance by the hostname and click the Edit (pencil) icon.

-
Add a new LAN side Interface: Click +Add next to LAN Interfaces.
Note
If this is the first LAN side service connection, click +Add. If you already have a LAN interface, click +IP under the Interface drop-down list to add a new configuration.
Here is a screen with sample values.

-
In the Interface drop-down menu, choose wan0.
-
In the VLAN field, enter the B-End VLAN value for this connection from the Megaport Portal.
Click the Details icon for the connection in the Megaport Portal to find this value. Note that it might be different from the A-End VLAN ID. - (Optional) Select a preconfigured Label or select None.
- In the IP/Mask field, enter the B-End interface IP Address and subnet mask as required for your network.
This value is the Customer Address from the AWS connection details in the Portal. - For the Next Hop, enter the A-End IP address.
- Specify in and out bandwidth values.
The bandwidth must be equal to or less than the MVE bandwidth limit. - Click Apply.
- If prompted, reboot the appliance.
A reboot is required only when adding the first LAN interface, as the system switches the appliance from server mode to router mode.
At this point, the B-End interface is created. The next step is to optionally create a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) session.
To configure a BGP neighbor (optional)
-
In Orchestrator, go to Configuration > Networking | BGP.
-
Click the Edit (pencil) icon for the appliance.
-
Move the slider to Enable BGP.
-
Provide the local AS number.
This is the Customer ASN (your local MVE), collected in step 1. - In the Router ID field, enter a system IP as required by your network design.
You can use any IP address on the MVE, such as the loopback 0 IP specified during the initial acceptance of the appliance, the interface IP on the MVE side of the VXC, or the transit IP address.
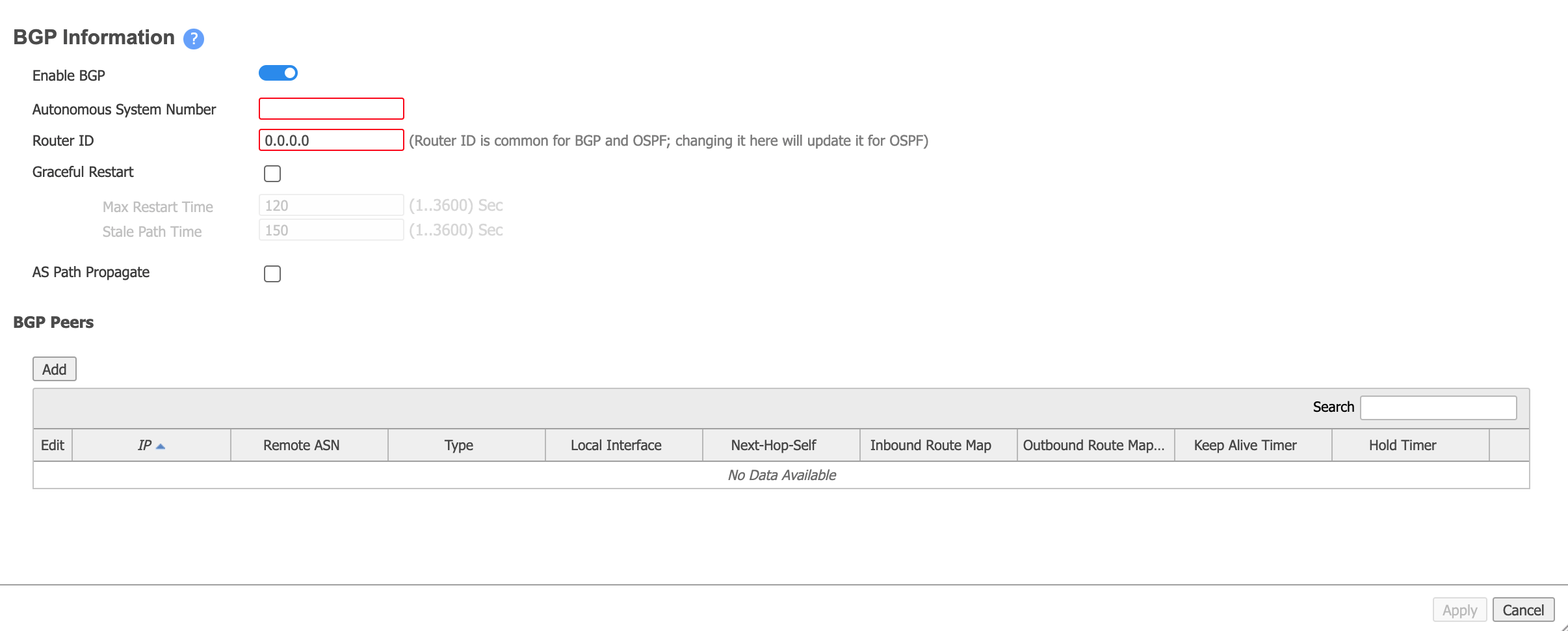
-
In the BGP Peers section, click Add and provide the following information:
- Peer IP – Enter the neighbor/peer IP address.
- Local Interface – Choose the associated LAN interface (the interface is in the format wan0.{VLAN ID}).
- Peer ASN – Enter the peer ASN.
- Peer Type – Choose Branch.
- Enable MD5Sometimes known as an MD5 hash or BGP key. The message-digest (MD5) algorithm is a widely used cryptographic function producing a string of 32 hexadecimal digits. This is used as a password or key between routers exchanging BGP information.
Password – If required, select this and then enter and confirm your MD5 password.
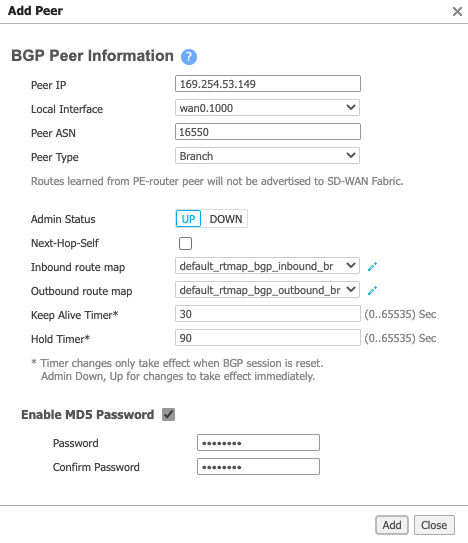
-
Click Add.
- Click Apply.
It takes several seconds for the configuration to be pushed to the appliance. Click the refresh icon to update the data from the appliance.
When successful, the Peer State indicates Established:
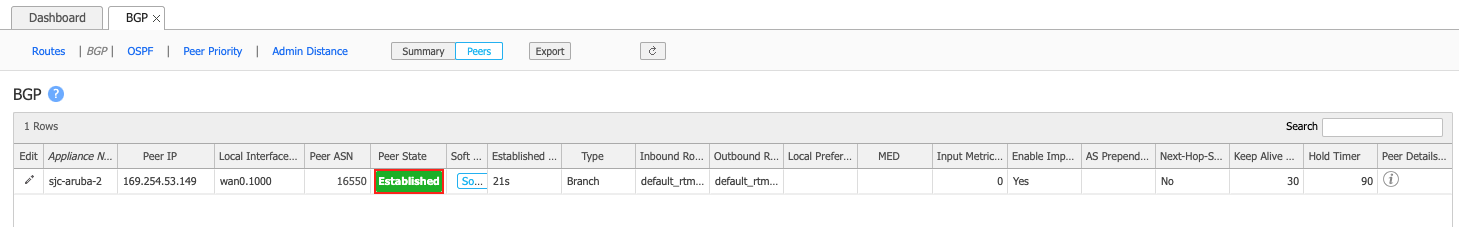
Validating your connection
You can review connection details, including the connection state, from the CLI with these commands:
show interface wan0.<subinterface id>– Displays configuration details and current status for the appliances.show bgp neighborsorshow bgp summary– Displays configuration details and current status for the BGP neighbors.
To start a CLI session from Orchestrator
-
In Orchestrator, use the mouse to hover over the appliance and click the Appliance Menu icon to the right of the appliance name.
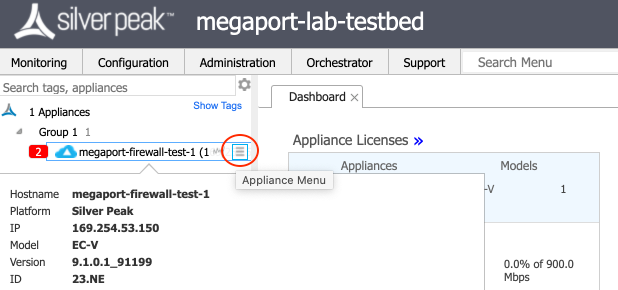
-
Select CLI Session from the menu.
-
Enter enable mode to use the recommended CLI commands to display configuration details.