Creating an AWS Hosted Connection for an MVE with Fortinet SD-WAN
A Hosted Connection can support one private, public, or transit virtual interface. These are dedicated connections and are recommended for production environments.
To create a Hosted Connection from an MVE to AWS
-
In the Megaport Portal, go to the Services page and select the MVE for the connection.
-
Click +Connection and click Cloud.
-
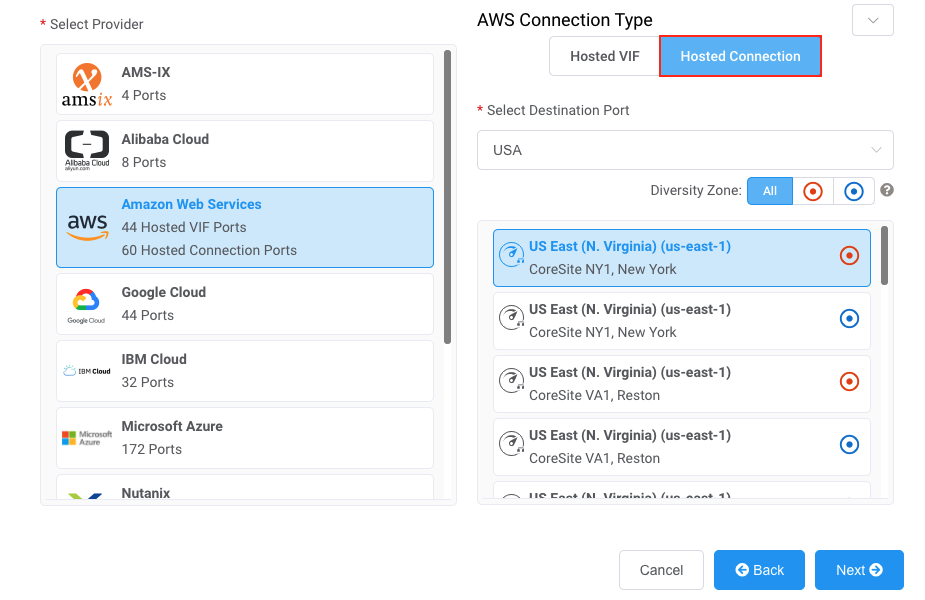
Select AWS as the service provider, select Hosted Connection as the AWS Connection Type, select the destination port, and click Next.
You can use the Country filter to narrow the selection.
Each destination port has either a blue or an red icon to indicate its diversity zone. To achieve diversity, you need to create two connections with each one in a different zone.
-
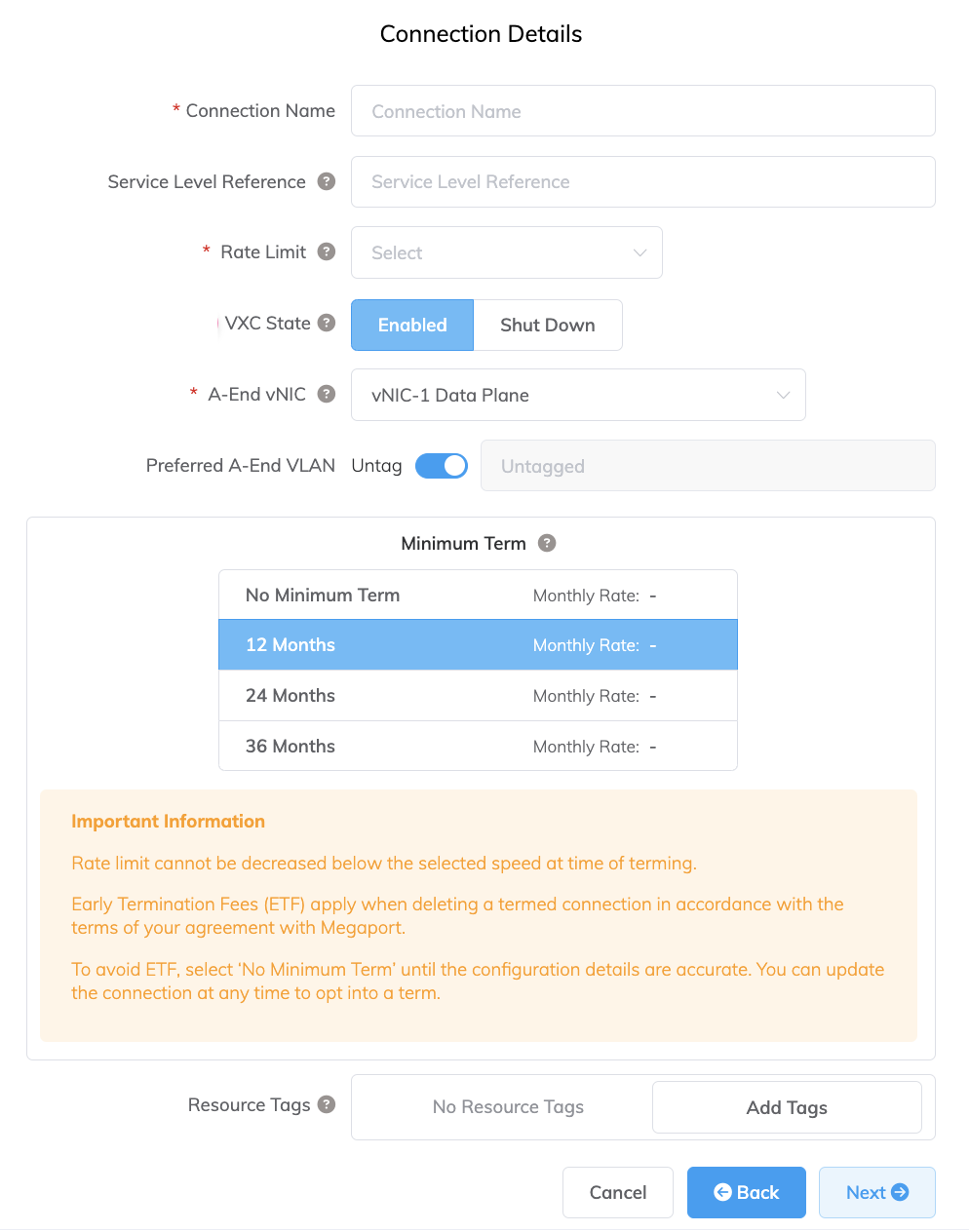
Specify the connection details:
-
Connection Name – The name of your VXC to be shown in the Megaport Portal.
-
Service Level Reference (optional) – Specify a unique identifying number for your Megaport service to be used for billing purposes, such as a cost center number, unique customer ID, or purchase order number. The service level reference number appears for each service under the Product section of the invoice. You can also edit this field for an existing service.
-
Rate Limit – The speed of your connection. This value cannot be changed after deployment. The drop-down list displays predefined rate limits available for your MVE, with speeds varying by location and service capabilities.
-
VXC State – Select Enabled or Shut Down to define the initial state of the connection. For more information, see Shutting Down a VXC for Failover Testing.
Note
If you select Shut Down, traffic will not flow through this service and it will behave as if it was down on the Megaport network. Billing for this service will remain active and you will still be charged for this connection.
-
A-End vNIC – Select an A-End vNIC from the drop-down list. For more information about vNICs, see Creating an MVE in the Megaport Portal.
-
Preferred A-End VLAN (optional) – Specify an unused VLAN ID for this connection.
This must be a unique VLAN ID on this MVE and can range from 2 to 4093. If you specify a VLAN ID that is already in use, the system displays the next available VLAN number. The VLAN ID must be unique to proceed with the order. If you don’t specify a value, Megaport will assign one. -
Minimum Term – Select No Minimum Term, 12 Months, 24 Months, or 36 Months. Longer terms result in a lower monthly rate. 12 Months is selected by default. Take note of the information on the screen to avoid early termination fees (ETF).
Enable the Minimum Term Renewal option for services with a 12, 24, or 36-month term to automatically renew the contract at the same discounted price and term length at the end of the contract. If you don’t renew the contract, at the end of the term, the contract will automatically roll over to month-to-month contract for the following billing period, at the same price, without term discounts.
For more information, see VXC Pricing and Contract Terms and VXC, Megaport Internet, and IX Billing.
-
Resource Tags – You can use resource tags to add your own reference metadata to a Megaport service.
To add a tag:- Click Add Tags.
- Click Add New Tag.
- Enter details into the fields:
- Key – string maximum length 128. Valid values are a-z 0-9 _ : . / \ -
- Value – string maximum length 256. Valid values are a-z A-Z 0-9 _ : . @ / + \ - (space)
- Click Save.
If you already have resource tags for that service, you can manage them by clicking Manage Tags.
Warning
Never include sensitive information in a resource tag. Sensitive information includes commands that return existing tag definitions and information that will identify a person or company.
-
-
Click Next.
-
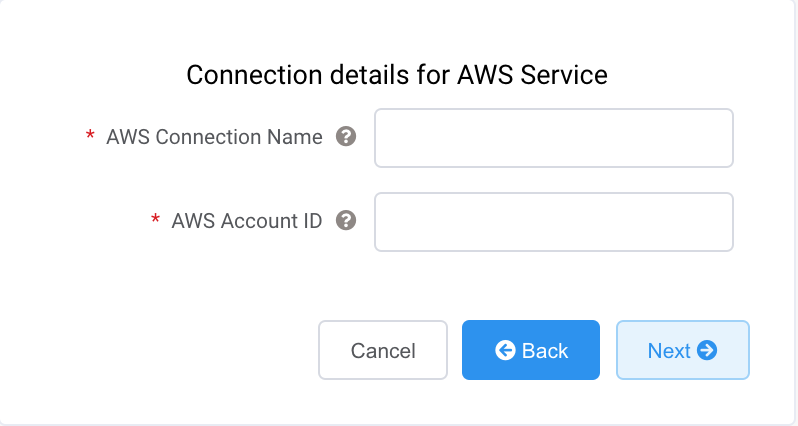
Specify the connection details for the AWS service.
-
AWS Connection Name – This is a text field and will be the name of your virtual interface that appears in the AWS console. The AWS Connection Name is automatically populated with the name specified in a previous step.
-
AWS Account ID – This is the ID of the account you want to connect. You can find this value in the management section of your AWS console.
-
-
Click Next to proceed to the connection detail summary, click Add VXC, and order the connection.
Once the VXC connection is deployed successfully, it appears on the Megaport Portal Services page and is associated with the MVE. Click the VXC title to display the details of this connection. Note that the service status (Layer 2) is up but BGP (Layer 3) will be down because the configuration does not exist yet.
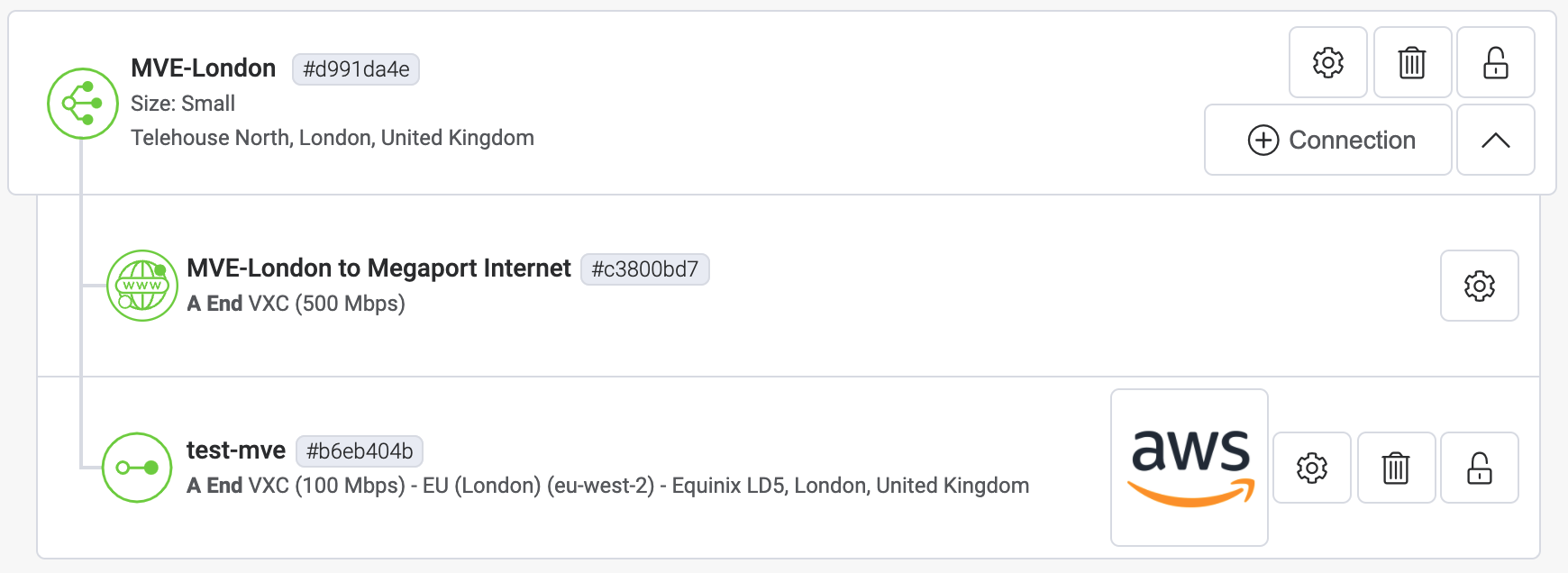
Once deployed in the Megaport Portal, you need to accept the connection in the AWS console and create a Virtual Interface for the connection:
To accept a Hosted Connection
-
In AWS, go to Services > AWS Direct Connect > Connections and click the connection name.
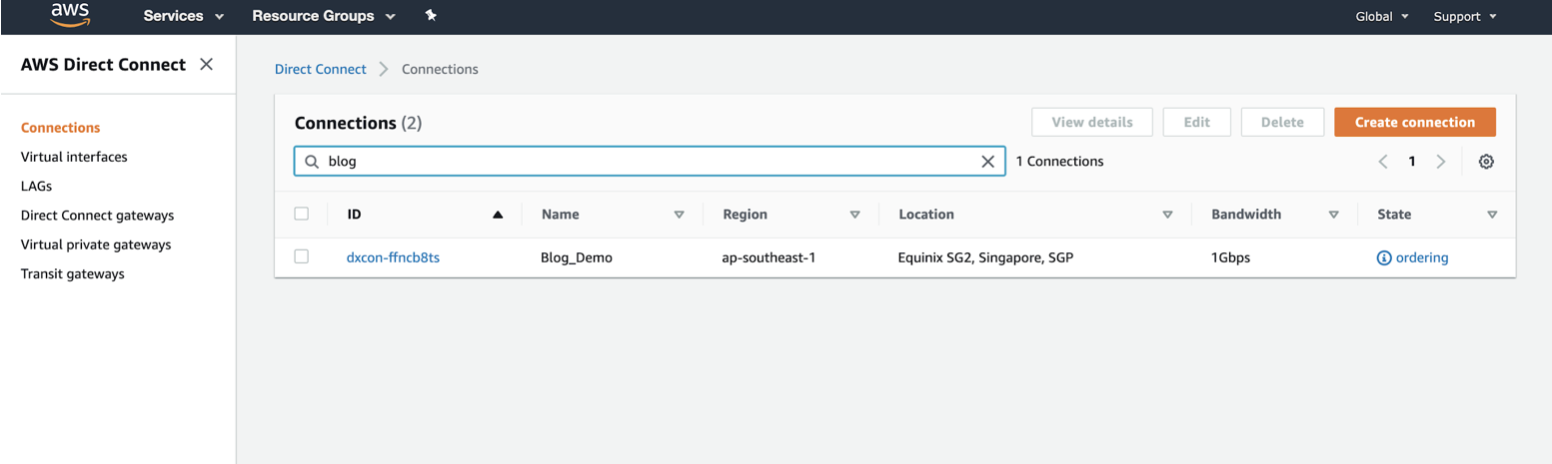
-
Click Accept at the top right of the window.
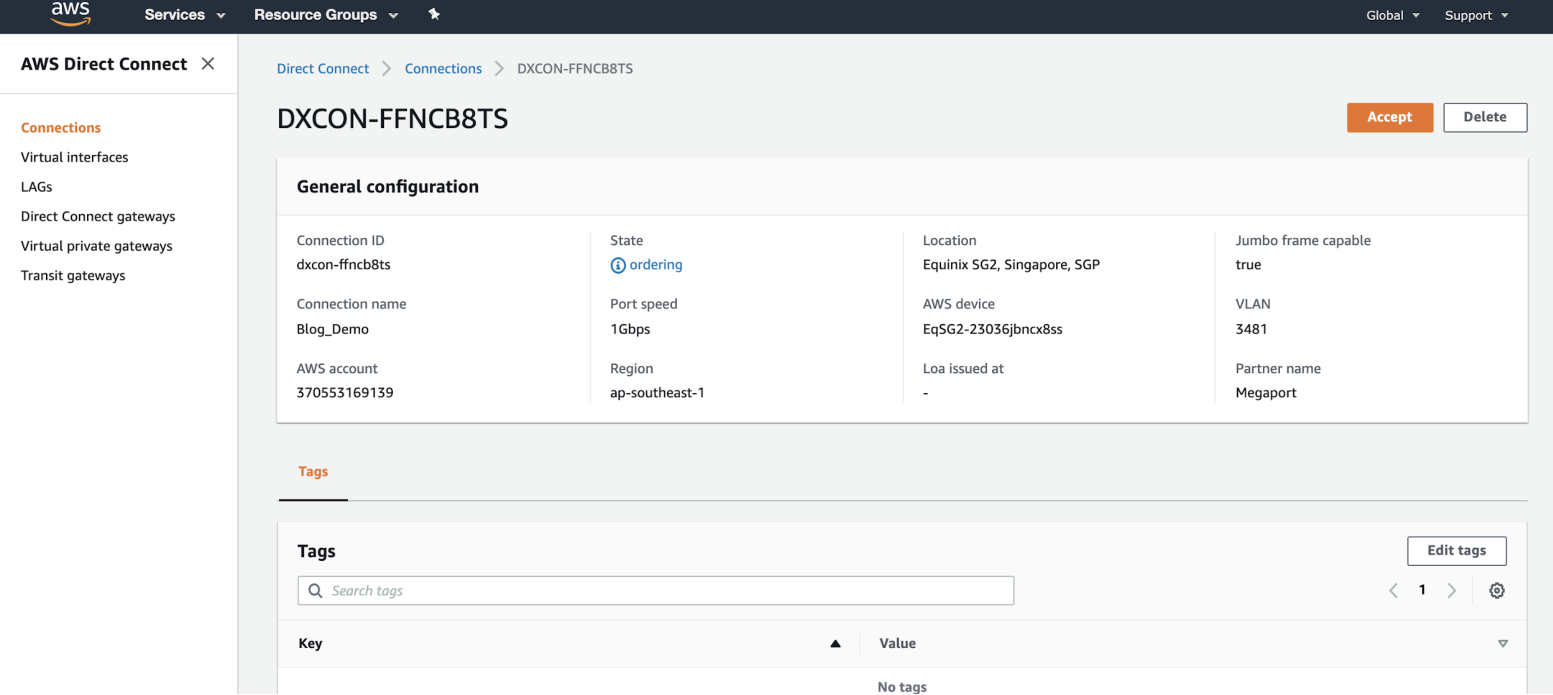
The state will be pending for a few minutes while AWS deploys the connection. After it is deployed, the state changes from ordering to available.
The connection is now available, however you need to create a VIF to connect to AWS services.
Tip
For more information about accepting AWS connections, see the AWS documentation.
Creating a virtual interface
Once you have created and accepted a Hosted Connection, create a VIF and attach the Hosted Connection to a gateway.
Tip
AWS provides detailed instructions for creating Public, Private, and Transit interfaces.
To create and attach a VIF
-
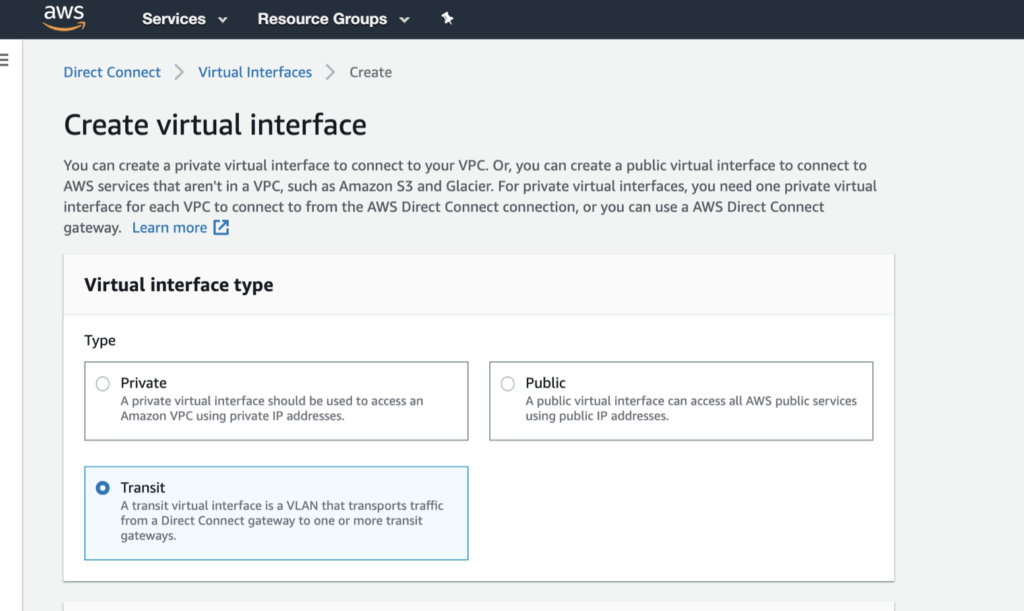
In the AWS console, click Create Virtual Interface.
-
Select the interface type.
The type will vary depending on the type of service you need to access.
- Private – Access resources running into a VPC using their private IP addresses. You can choose to terminate a private virtual interface on a private virtual gateway (to access a single VPC) or to a Direct Connect gateway (and map up to 10 VPCs to the VIF).
- Public – Access all AWS public endpoints, as well as all AWS resources that are reachable by a public IP address.
- Transit – Transport traffic from a Direct Connect gateway to one or more transit gateways.

-
Specify the configuration details:
- Virtual interface name – Enter a name for the virtual interface.
- Connection – The physical connection where you want this virtual interface to be provisioned. The name you provided for the Hosted Connection in the Megaport Portal appears here.
- Virtual interface owner – The account that will own the virtual interface. Select My AWS account.
- Direct Connect gateway – Select the Direct Connect gateway to attach this virtual interface to. A transit VIF is not directly attached to a Transit gateway, but to a Direct Connect gateway.
- VLAN – The VLAN assigned to the virtual interface. Leave this value as is. The VLAN address is populated and appears to be editable; however, you will get an error if you try to change it.
- BGP ASN – Enter the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) autonomous system number (ASN) for the MVE side of the BGP session.
The following BGP details can be filled out or left blank. When left blank, they are auto-populated by AWS.
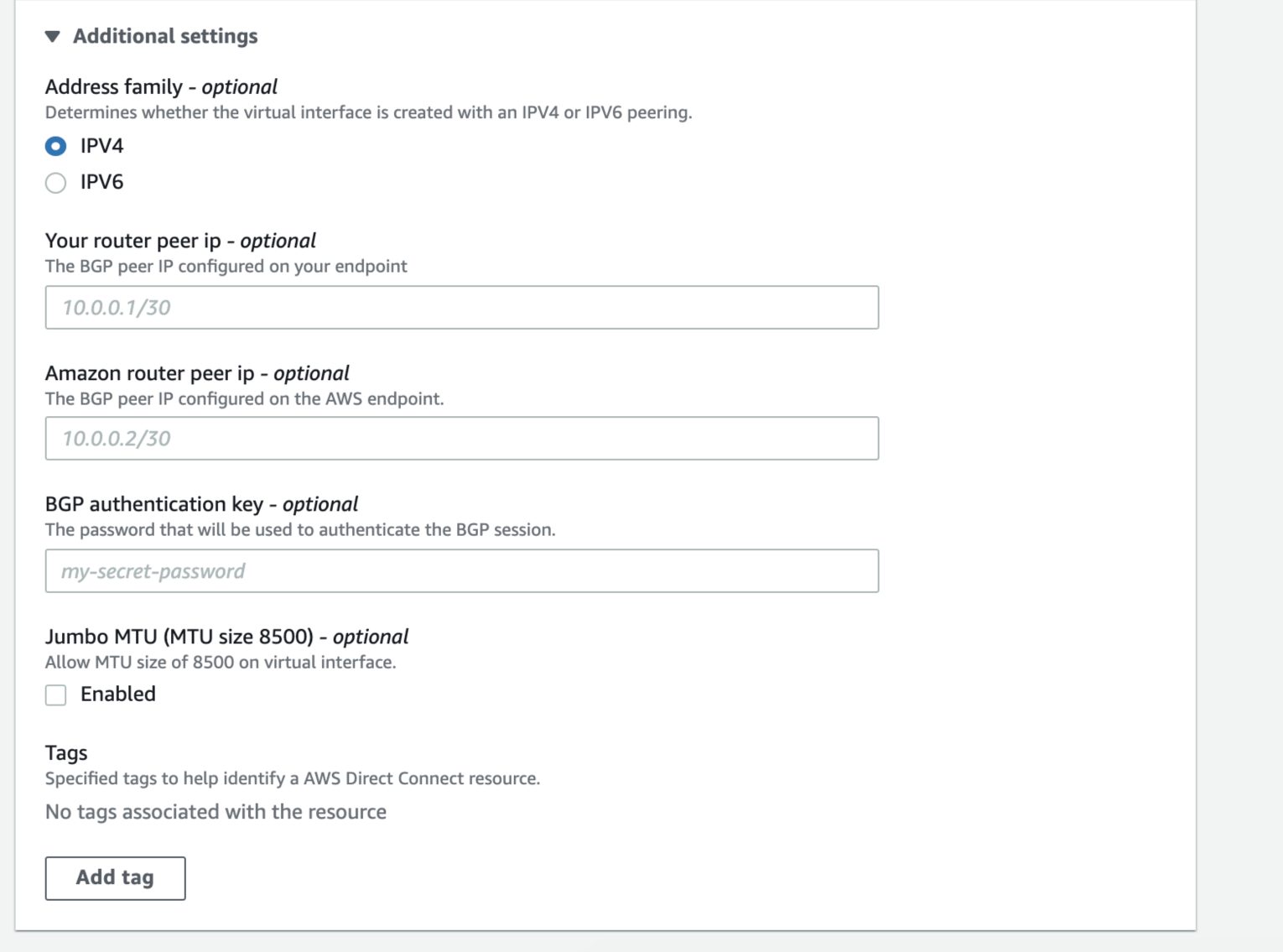
You can also choose whether you want the virtual interface to support Jumbo frames. Enable Jumbo MTU to support an Ethernet packet of 8500 bytes.
-
Click Create virtual interface.
To view the VIF details and state, navigate to Services > AWS Direct Connect > Connections > Name of the Megaport-Created-Hosted Connection.
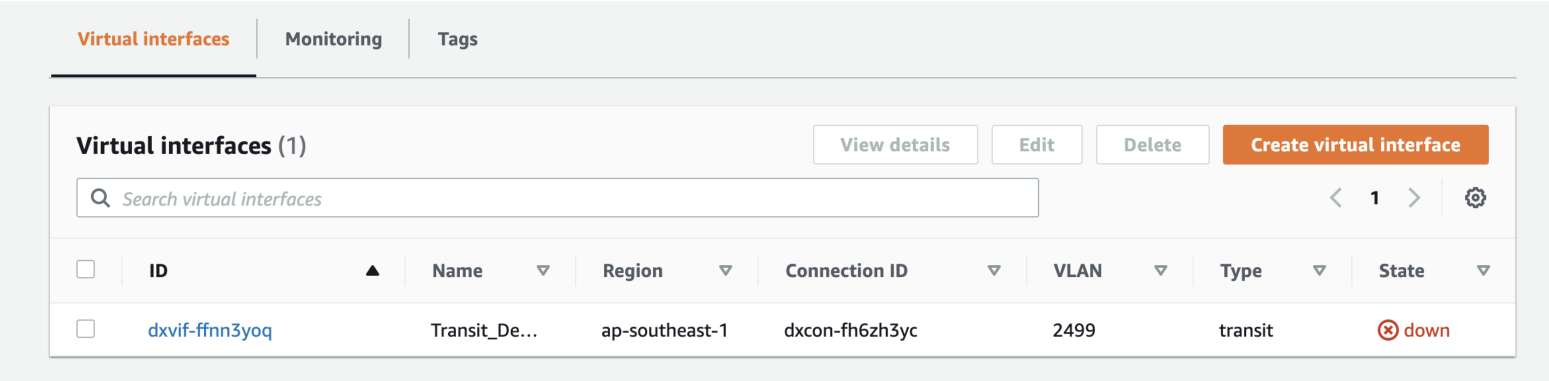
BGP hasn’t been configured, so the interface state appears as down.
Once you accept the connection and create the VIF in AWS, the VXC state changes to configured in the Megaport Portal.
Adding AWS connection details to FortiManager
After you create the connection from your MVE to AWS and set up the connection in the AWS console, you need to configure it in FortiManager. This involves creating an interface and configuring BGP settings, ASNs, VLANs, and MD5 values.
To add the AWS connection in FortiManager
-
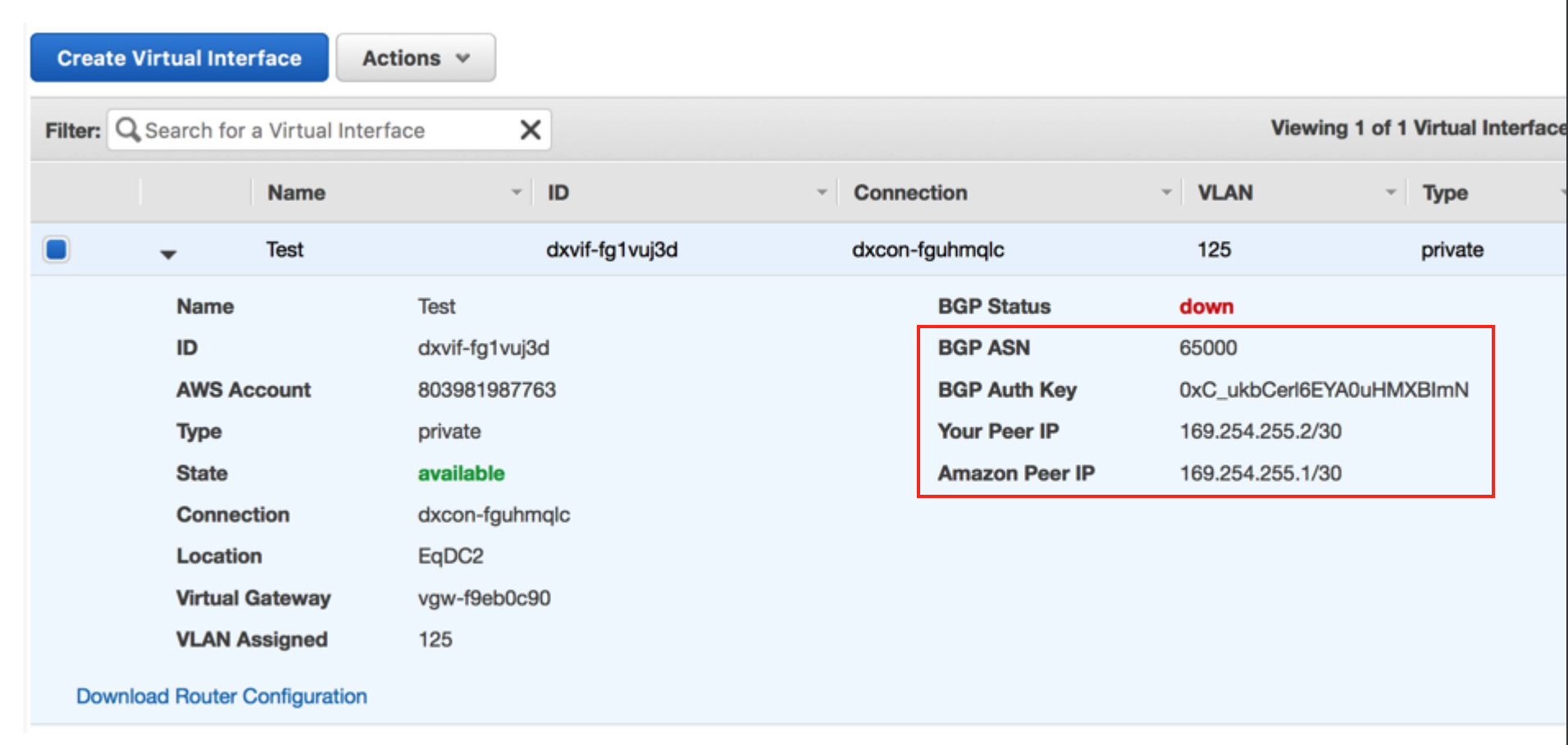
Collect the connection details from the AWS console.
Display the details of the Virtual Interface you created in AWS for this Hosted Connection. Note the values for the BGP ASN, BGP Auth Key, Your Peer IP, and Amazon Peer IP.
-
Collect the connection details from the Megaport Portal.
Click the gear icon for the AWS connection from your MVE then click the Details view. Note the value for the A-End VLAN. -
Log in to the FortiManager.
Note
You can also log in on your MVE instance: https://<mve-ip-address>
-
From your managed device, go to the System menu and choose Interface.
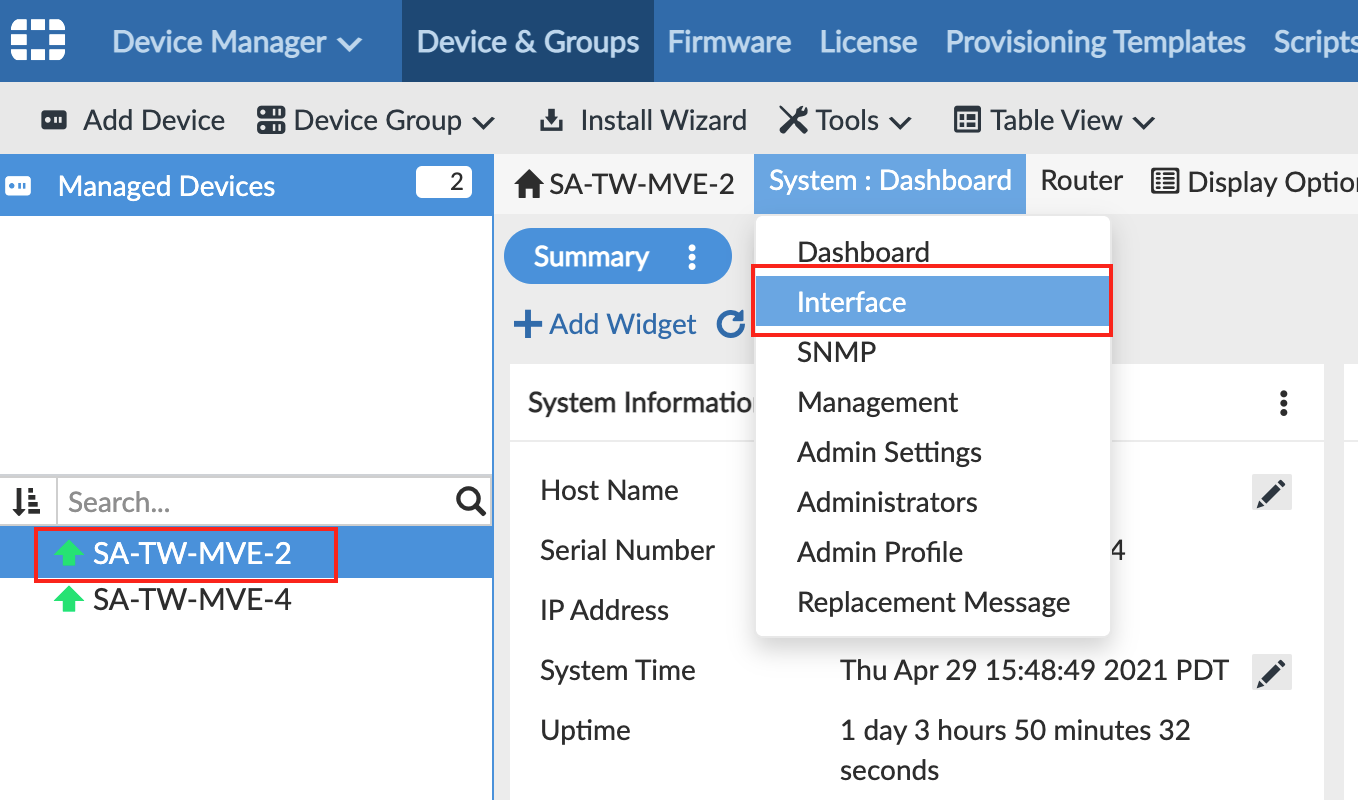
The page displays port1 as your physical interface. -
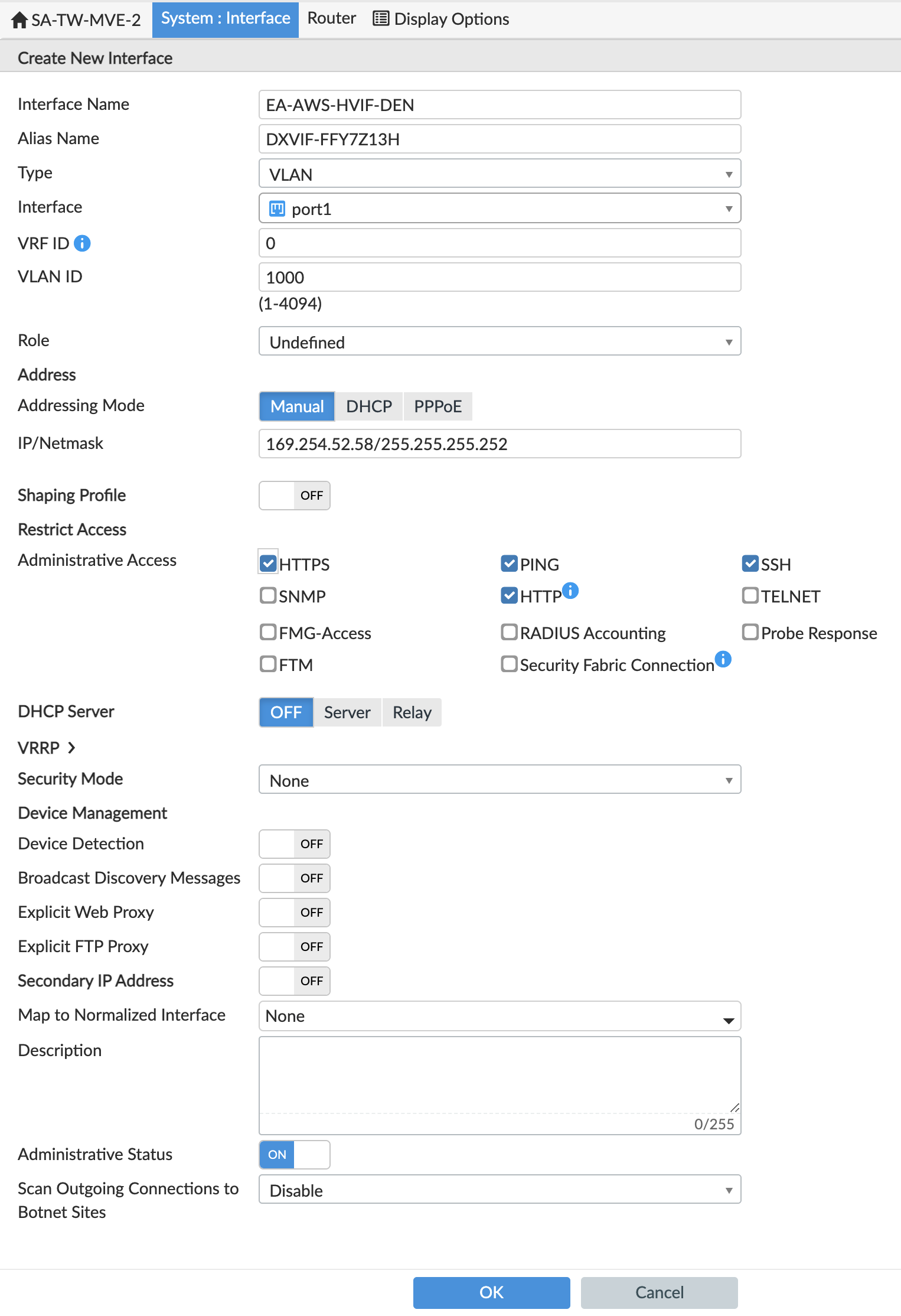
Click +Create New > Interface and provide this information:
- Interface Name – Specify a meaningful name for the interface.
- Alias Name (optional) – Enter an alternate name. For easy reference, use the AWS Virtual Interface ID for this connection as the alias.
- Type – Choose VLAN.
- Interface – Choose the parent interface:
port1. - VLAN ID – Specify the A-End VLAN listed for this AWS Connection in the Megaport Portal.
- Role – Choose Undefined.
- Addressing Mode – Select Manual.
- IP/Netmask – These values are available in the virtual interface details in the AWS console. The IP address and netmask appear in the Your Peer IP field.
- Administrative Access - Specify how you want to access this interface, such as HTTPS, PING, and SSH.
- DHCP Server - Click OFF.
-
Click OK.
The new VLAN interface appears with yourport1physical interface.
You can run an execute ping command from FortiOS to verify the connection.
Note
You need to push the configuration to the MVE, which happens when you have AutoUpdate configured. If you cannot successfully ping the connection, go to Manage Devices in FortiManager, select the MVE, and choose Refresh Device from the More menu. If prompted, select AutoUpdate for the Config Status.
At this point, we have created the interface and next we need to create the BGP session.
-
In FortiManager, go to Router > BGP.
-
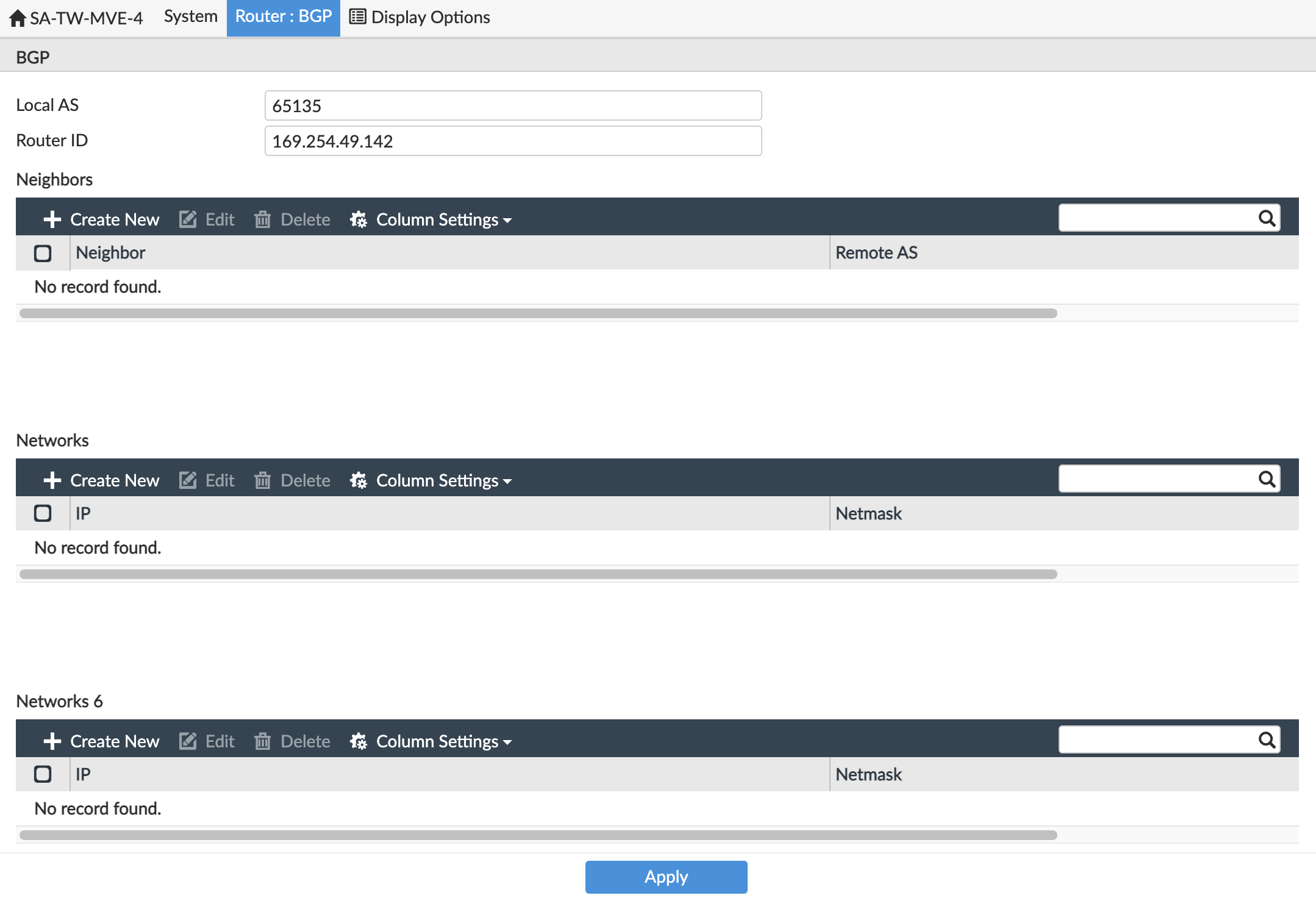
Provide this information:
- Local AS – Provide the ASN for the MVE connection. Use the BGP ASN from the virtual interface details in the AWS console.
- Router ID – Enter the IP address that appears in the Your Peer IP field for the virtual interface details in the AWS console.
-
In Neighbors, click +Create New.
- For the neighbor IP, add the Amazon Peer IP from the virtual interface details in the AWS console.
-
For Remote ASN, enter the Amazon-side ASN.
By default this is 64512. -
Click OK.
-
Click Apply.
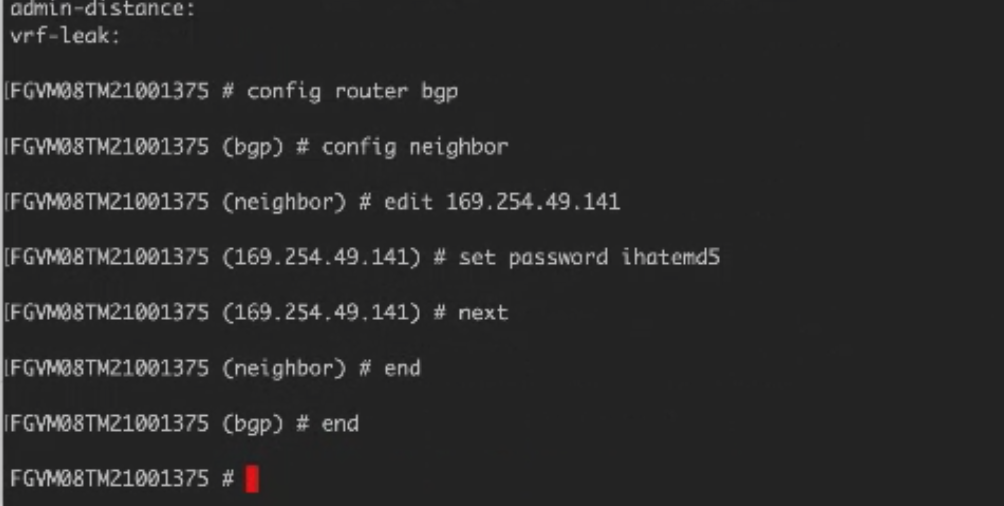
The neighbor is configured but we need to add the BGP Auth information. The web interface does not let you define this and you need to use the command line to add the BGP details. -
SSH to the MVE instance using your private key file.
For example
ssh -i ~/.ssh/megaport-mve-instance-1-2048 admin@162.43.143.XX -
Use these commands to add a password for the BGP neighbor.
Validating your AWS connection
You can review connection details, including the connection state, from the CLI with these commands:
get system interface– Displays configuration details and current status for the device interfaces.get router info bgp neighbor <ip-address>– Displays configuration details and current status for the BGP neighbors.