Internet Exchange Overview
Megaport owns and operates a series of Internet peering exchanges (IXs) in the majority of our global networks. IXs provide greater efficiency between networks and allow traffic to be exchanged directly, reducing latency and bandwidth usage on client internet connections.
There are two main types of IX peering arrangements:
- multilateral - Multilateral peering (MLPA) is the default when you connect to MegaIX. With multilateral peering, you use BGP to peer with both route servers (RS1 and RS2) for an IX market, you advertise your routes to the route servers, and all routes available from all other multilaterally peered connections are advertised to your peer from the route servers.
- bilateral - The second type of peering is bilateral peering (BLPA). This method is required for peers that do not participate in multilateral peering through the route servers and establishes a direct peering relationship with another entity on the exchange. You can participate in both multilateral and bilateral peering across the Megaport IX infrastructure.
If you are connecting to an AMS-IX location, see AMS-IX Connectivity.
IX requirements
Before configuring your IX connection, ensure that you meet these requirements:
-
Permitted traffic types – All frames forwarded to the Internet Exchange must be Ethernet II (DIX), using ARP (0x0806), IPv4 (0x0800), or IPv6 (0x86DD) Ethertypes.
-
First ASN – In a standard BGP configuration the first ASN in the path will match the peer ASN. In multi-lateral peering, the first ASN is the downstream peer that provides the routes. This reduces AS path lengths for correct routing decisions. To permit multi-lateral peering, configure your devices so they do not enforce the first AS requirement. For example, on a Cisco router the command is no bgp enforce-first-as.
Recommendation
To avoid any unneeded layer 2 frames towards the IX, a VLAN tagged MegaIX service is recommended.
Note
To prevent members from sending all the internet routes to Megaport, we limit the number of prefixes (MaxPFX) that Megaport can receive. The default limit is 1000 IPv4 routes and 100 IPv6 routes. Exceeding this value results in ending the session, however you can contact Megaport support if you require a reset.
Illegal traffic types
The following frames are not permitted on the Internet Exchange:
-
Multiple MAC addresses – MegaIX operates on the principle of one router per port, meaning that frames must have the same source MAC address behind each port in each VLAN. Some members connect through intermediate switches or use a Layer 2/Layer 3 hybrid device. If these devices are not configured properly they can cause forwarding loops, STP instabilities, and unwanted traffic on the Exchange.
-
Multicast and broadcast (with the exception of ARP and IPv6 neighbor discovery) – Only exchange unicast routes over your BGP sessions in the Peering LANs. Multicast traffic is not permitted on (unicast) Peering LANs.
-
Frames from Proxy ARP – Peering VLAN traffic is exchanged based on BGP routes, so it is unnecessary to answer ARP queries for any IP addresses other than those configured on your MegaIX interface. Some vendors enable Proxy ARP by default, which can lead to unwanted traffic on your network. If you have Proxy ARP enabled at MegaIX, it is likely to be enabled at other peering points, which allows parties on both sides to use you as a transit.
-
LLC/SNAP (Subnetwork Access Protocol) frames – LLC/SNAP encapsulation (802.2) is not permitted because the IX infrastructure is based on the Ethernet II standard.
-
STP (Spanning Tree) – Devices connected to the MegaIX port are not permitted to be visible as Layer 2 bridges, and should not use STP or any other proprietary L2-specific protocol.
-
Vendor discovery protocols (CDP, EDP, FDP, MNDP) – Some vendors (e.g. Cisco and Extreme Networks) run discovery protocols by default. Running discovery protocols should be avoided as it can cause unwanted broadcast or multicast traffic.
-
Internal routing protocols (OSPF, EIGRP, IGRP, and ISIS) – BGP is the only routing protocol permitted on the Peering VLANs. Interior routing protocols only cause unnecessary multicast and broadcast traffic.
-
Cisco Layer 2 keepalives – By default, Cisco routers and switches periodically test their Ethernet links by sending out loopback frames (Ethertype 0x9000) addressed to themselves. In a switched environment, this tests the functionality of the switch and keeps the router’s MAC address in the switch’s address table. In the MegaIX environment, this is not useful because MAC timeouts are longer than the typical BGP or ARP timeouts.
-
Non-unicast IPv6 (IPv6 ND-RA) – IPv6 hosts on the MegaIX are not autoconfigured, and can cause IPv6 router advertisements to generate unnecessary traffic.
-
Non-unicast IPv4 (IGMP, DHCP, TFTP) – Do not configure multicast on the MegaIX interface. The Peering LAN is for unicast IP traffic only. The only permitted non-unicast traffic is an ARP query.
-
Trunking protocols – On Cisco Layer 2 devices such as the 2900 and 3500 series, disable VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol), DTP (Dynamic Trunking Protocol), LLDP, and UDLD.
-
Non-IP protocols – Some vendors enable protocols other than IP by default. For example, in some versions of IOS Cisco enables MOP (Maintenance Operation Protocol). Non-IP traffic is not appropriate for the MegaIX environment.
Important
Megaport imposes a set of restrictions to ensure smooth operation of the MegaIX. Megaport reserves the right to temporarily disable offending services in order to maintain the health and stability of the MegaIX.
Exceptions
Link-local protocols ARP and IPv6 ND (Neighbor Discovery) are exceptions, and are permitted.
Additional considerations
There are some considerations when thinking about configuring an IX peering arrangement:
-
MegaIX route servers do not recognize the BGP community attribute no-export. This community attribute is passed transparently to the other peers connected to the route server.
-
Multiple Exit Discriminator (MED) values are considered in the route selection rules only when the advertising ASN is the same for candidate routes. MED values are not modified by the route servers. Values advertised to the route servers are passed unaltered to other peers.
-
All routes on the IX are given equal local preference by the route servers. The route servers do not compare the BGP router ID for best route selection, instead preferring the oldest route when all other attributes are equal.
-
Do not configure “network 194.146.118.0/24” or any of the other peering LANs in your router’s BGP configuration.
Joining an IX
You can join an Internet Exchange for Megaport and MegaIX locations.
Before joining an IX, ensure that you can meet the requirements.
To join an Internet Exchange for Megaport and MegaIX locations
- In the Megaport Portal, go to the Services page and select the Port you want to use.
If you haven’t already created a Port, see Creating a Port. -
Add an IX connection for the Port.
Click +Connection, click Internet Exchange, then click Next.
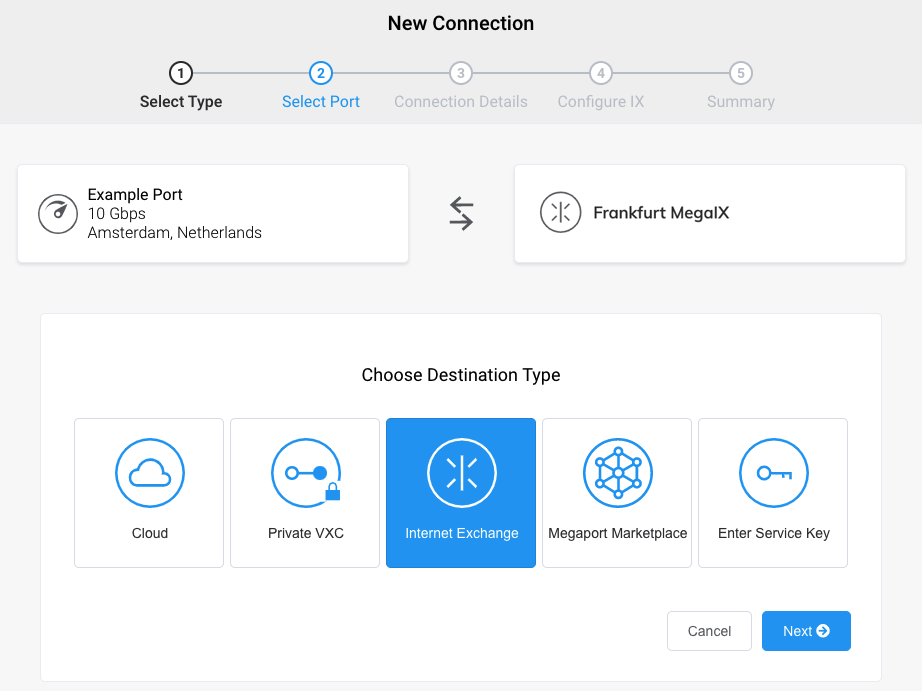
-
Select the IX location and click Next.
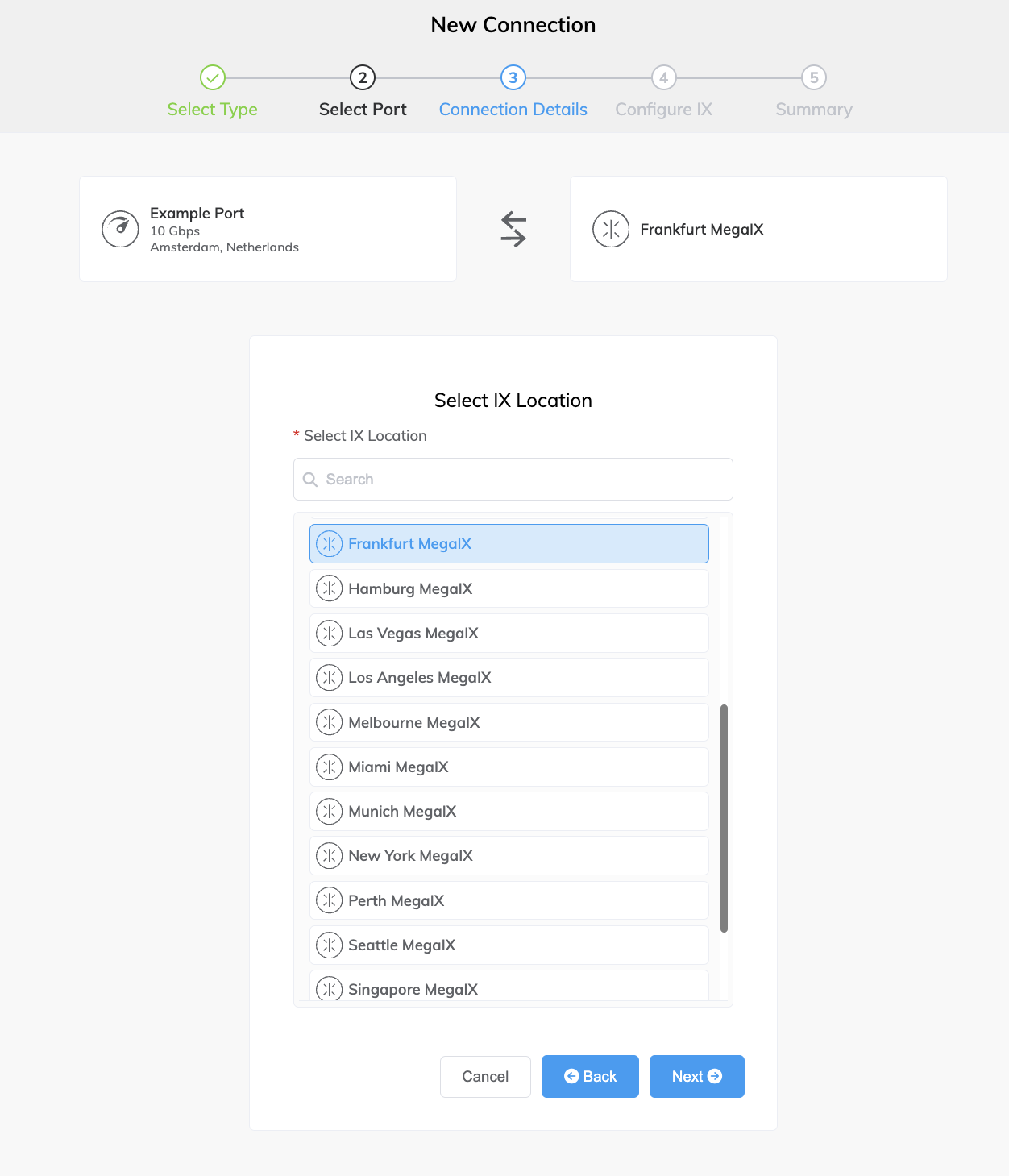
-
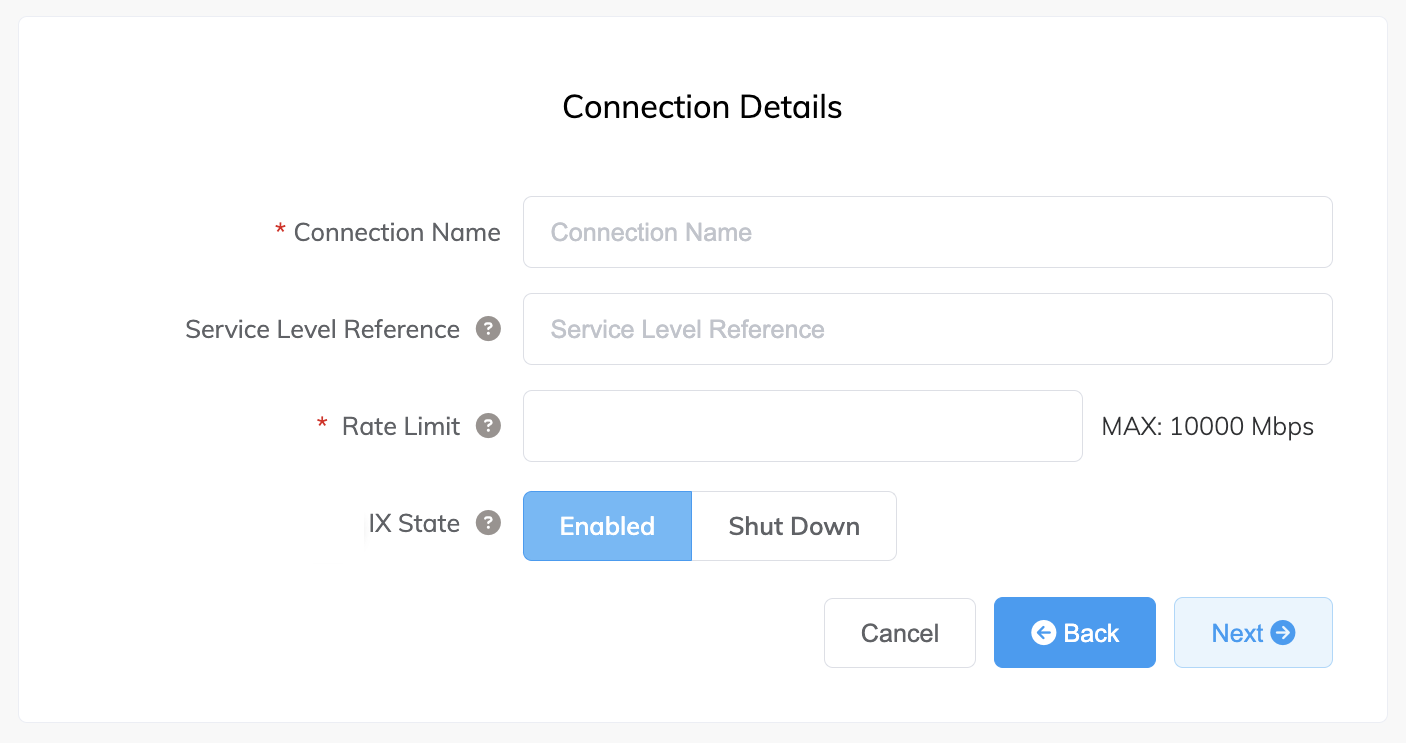
Specify the connection details:
-
Connection Name – The name of your VXC to be shown in the Megaport Portal.
Note
Partner-managed accounts can apply a Partner Deal to a service. For more information, see Associating a Deal With a Service.
-
Service Level Reference (optional) – Specify a unique identifying number for the VXC to be used for billing purposes, such as a cost center number or a unique customer ID. The service level reference number appears for each service under the Product section of the invoice. You can also edit this field for an existing service.
-
Rate Limit – The speed of your connection in Mbps.
For metro connections, the rate limit for an IX cannot exceed the aggregate port speed. For non-metro connections, the maximum rate is dynamically calculated based on network routes used to deliver the service. The calculation uses the Ports at each end and bases calculations on the lowest rate. The rate cannot exceed the speed of the physical interface on which it resides. -
IX State – Select Enabled or Shut Down to define the initial state of the connection. For more information, see Shutting down an IX for failover testing.
Note
If you select Shut Down, traffic will not flow through this service and it will behave as if it was down on the Megaport network. Billing for this service will remain active and you will still be charged for this connection.
-
-
Click Next.
-
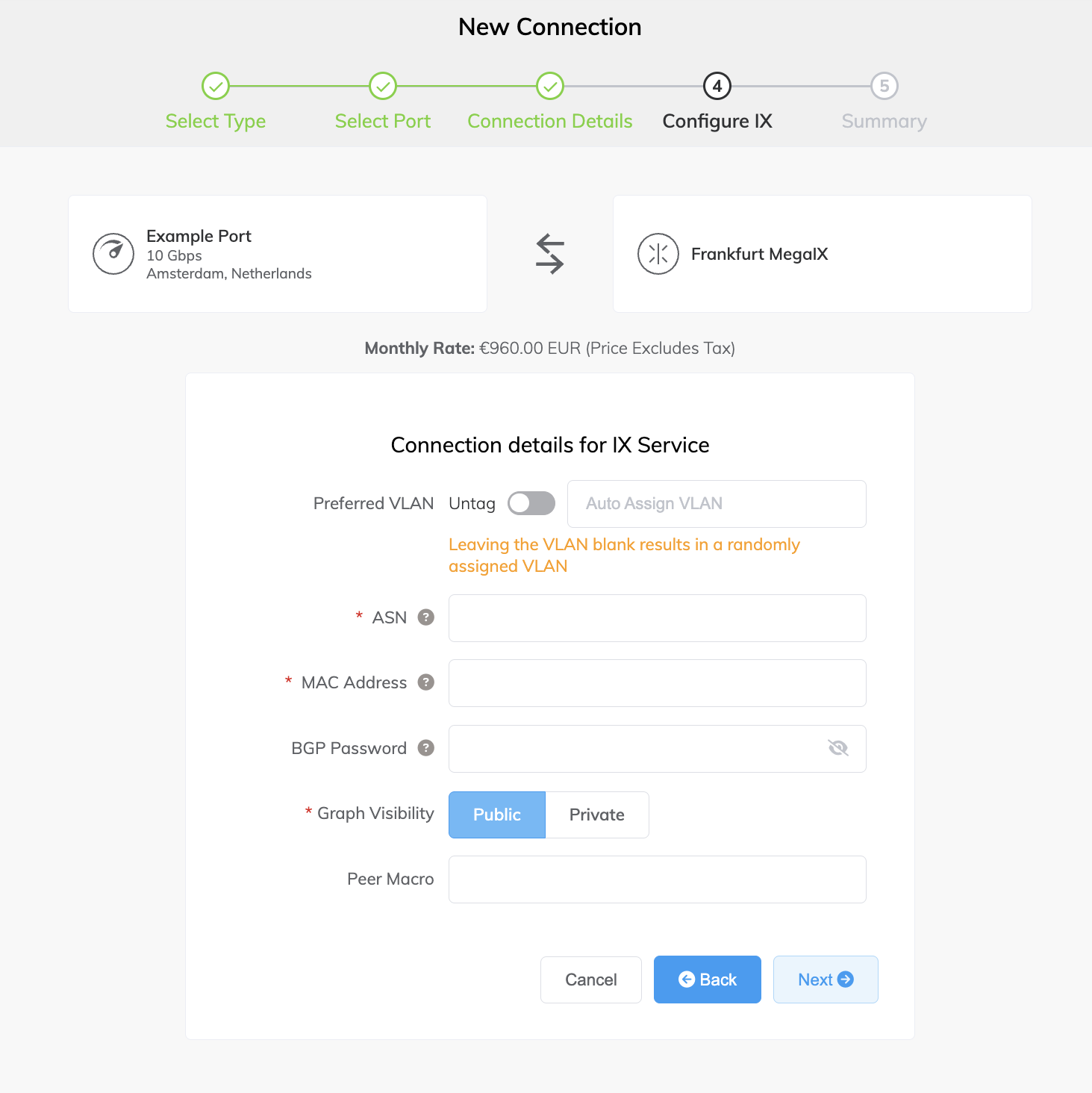
Specify the IX details:
-
Preferred VLAN (optional) – Specify an unused VLAN ID for this connection.
The VLAN ID must be unique on this Port and can range from 2 to 4093. If you specify a VLAN ID that is already in use, the system displays the next available VLAN ID. Megaport validates the VLAN ID before proceeding with the order. If you don’t specify a value, Megaport will assign one. You can also select the toggle to Untag this connection. This selection removes the VLAN tagging for this connection but limits you to only one IX (or VXC) on this Port. -
ASN – The autonomous system number (ASN) of your network. The ASN can be either a 16-bit or 32-bit ASN (2 or 4 byte) but must be a public AS.
-
MAC Address – The MAC Address of the Layer 3 device that will establish the BGP peering session with the IX. Connections to the IX on this VXC will be locked to this address for security purposes. If you do not have the correct MAC available at the time of ordering, enter a placeholder MAC (such as 00:01:00:01:12:34) as this field remains editable after deployment.
-
BGP Password (optional) – Add a BGP password to the VXC. This field can be left blank. The password length is from 1 to 25 characters. The password can include any of these characters:
a-z
A-Z
0-9
! @ # . $ % ^ & * + = - _Tip
Click the eye icon to see the password as you type. The view persists until you click the eye icon again to hide the password.
-
Graph Visibility – Specify how to display your traffic graphs in the MegaIX Looking Glass tool. Public lets other clients see your IX throughput; Private hides this information from other clients.
-
Peer Macro (optional) – The peer macro value defines the AS macro filter for the peer. Megaport uses this value to generate a list of prefixes this AS can originate, and this list filters announcements through the route server.
Another name for this field is AS-MACRO (or AS-SET) as it contains a list of AS numbers belonging to this peer.
If you don’t have a Peer Macro, you can enter your ASN in this field (You can only send routes that originate from your own AS). Invalid prefixes won’t be announced by the route server and an incorrect configuration results in the route server rejecting all your prefixes.
If not specified, your own ASN will be used in the filter and you can only send routes that originate from your own AS and prefixes registered to that AS.
-
-
Click Next.
A summary page appears that includes the monthly cost. Click Back to make changes or click Add IX to move this configuration to your cart and proceed through the checkout process.After deployment, Megaport sends an email to your registered email address with additional information on how to finish the BGP configuration.
Editing an IX
After you have joined an IX, you can edit the connection settings. You can change any of the settings defined when joining the IX, as well as the IX reverse DNS, and decide whether to shut down or enable the service.
To edit an IX
-
In the Megaport Portal, go to the Services page and locate the IX.
-
Click the gear icon next to the IX to make changes.
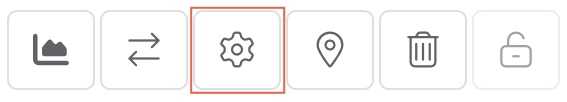
The Connection Configuration page appears.
-
You can edit any field on the Connection Configuration page. When editing an IX, you can also change the reverse DNS.
-
Reverse DNS (optional) – A reverse DNS (rDNS)Reverse DNS (rDNS) is a querying technique of the Domain Name System (DNS) to determine the domain name associated with an IP address. This is the reverse of the usual forward DNS lookup of an IP address from a domain name. The process of reverse resolving of an IP address uses PTR records.
is a Domain Name Service (DNS) lookup of a domain name from an IP address. This is the ‘reverse’ of a regular DNS request which resolves an IP address from a domain name. A PTR record type is used to store reverse DNS entries.When editing an IX, the Reverse DNS field shows the default configured value assigned from the PTR record when the IX service was set up. You can change this field to a non *.megaport.com value in order to define a custom hostname for your IP address. If later you want to revert to the default value, simply clear the field.
The reverse DNS can include any of these characters:
a-z
A-Z
0-9
-
-
Click Save.
Shutting down an IX for failover testing
Once you have joined an IX on the Megaport network, you can temporarily shut down the IX for failover testing, redundancy, or network design testing purposes.
When an IX has been shut down, you can view the IX service that has been shut down, and re-enable the IX service.
For more information about shutting down a Megaport service, see Shutting Down a VXC for Failover Testing.
Tip
You can also decide whether to set the initial state of the connection to enabled (default) or shut down when creating the IX service. For more information, see Joining an IX.
To shut down an IX
-
In the Megaport Portal, go to the Services page and locate the IX.
-
Click the gear icon next to the IX to make changes.

The Connection Configuration page appears.
-
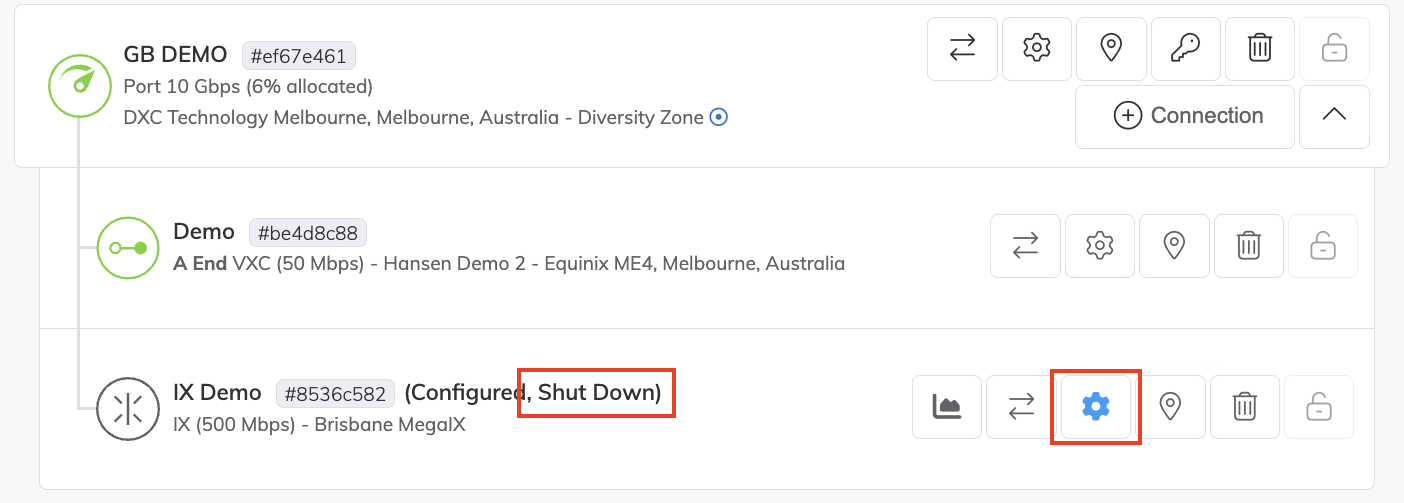
In the IX State field, click Shut Down.
A prompt appears, asking you to confirm the action.
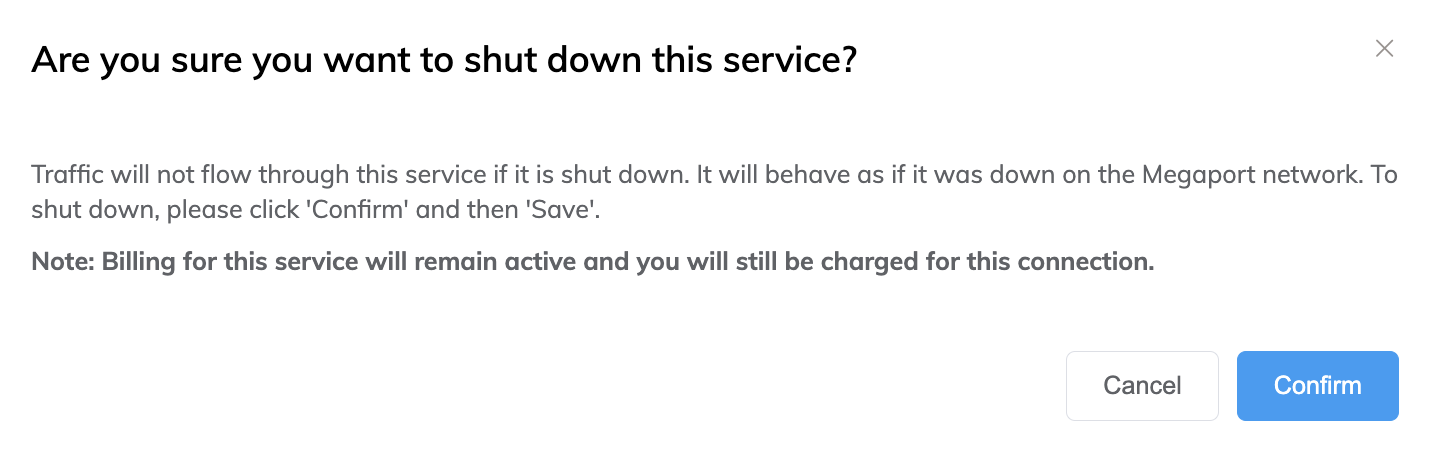
-
Read the prompt then click Confirm and Save.
The IX is shut down. This can take up to two minutes to take effect and be updated in the Megaport Portal.
To re-enable an IX
-
In the Megaport Portal, go to the Services page and locate the IX that is shut down.
-
Click the gear icon next to the IX.

-
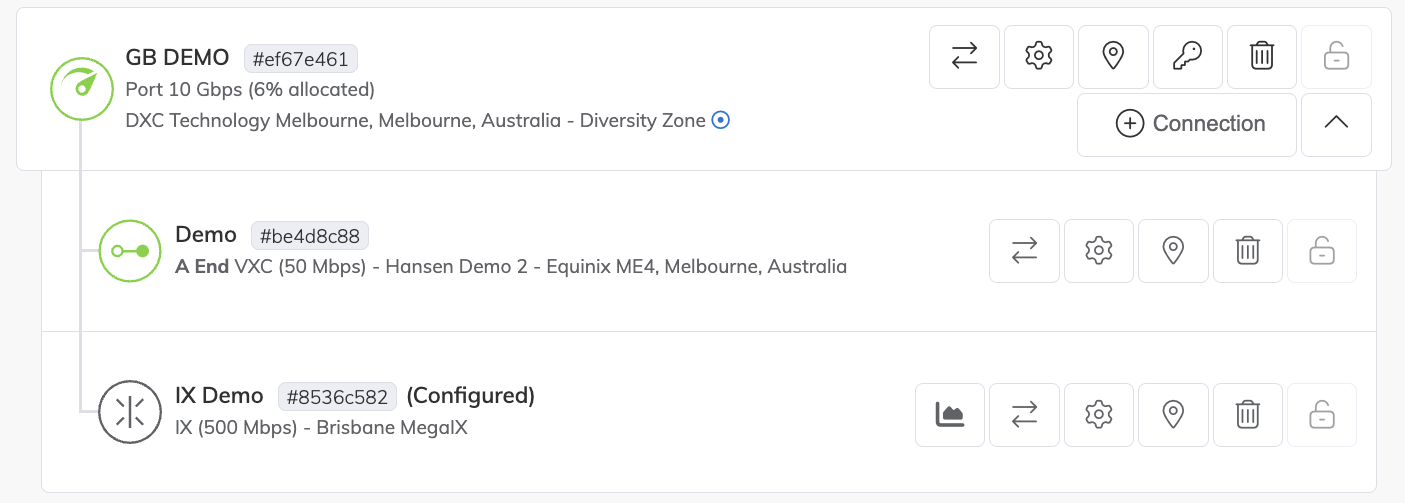
In the IX State field, click Enabled.
-
Click Save.
The IX is now enabled. This can take up to two minutes to take effect and be updated in the Megaport Portal.
Terminating an IX
You can terminate an IX directly from the Megaport Portal.
IXs can be individually terminated or are terminated as part of terminating the attached Port. IXs attached to Ports that are set to terminate in 30 days are terminated when the Port is terminated.
To terminate an IX
-
In the Megaport Portal, go to the Services page.
-
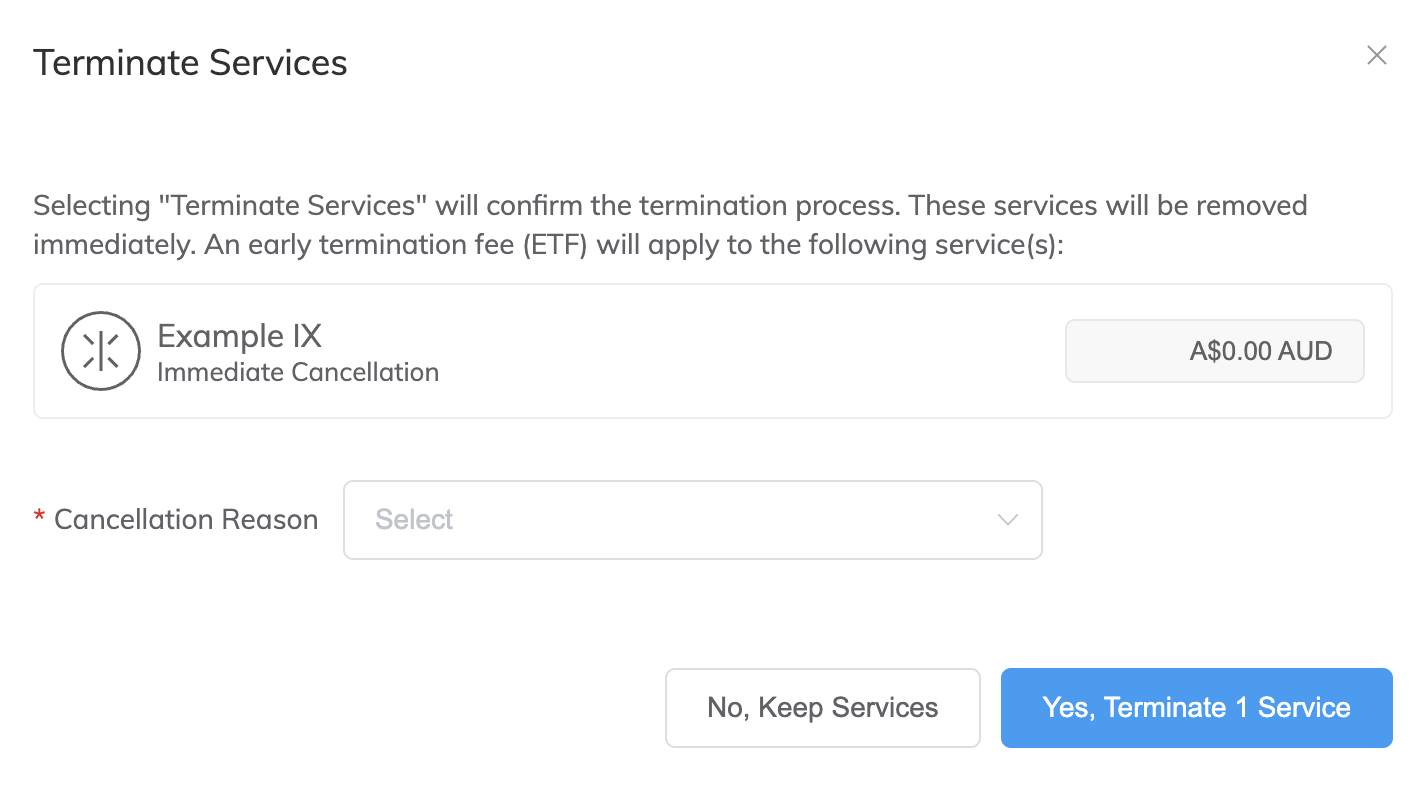
Click the trash icon next to the IX you want to terminate.

The Terminate Services window appears. Early termination fees will be shown here, if applicable.
-
In the Cancellation Reason drop-down list, select the reason that you are terminating the IX. We use this information to help us improve your customer experience.
These options are available:- Moved out of Data Center
- Ordered in Error or Reordering
- Proof of Concept / test
- Project Ended
- Moving to a Cloud-Native Solution
- Switching to Alternative Provider
- Pricing
- Product Performance
- Reason Not Listed
Note
- Ordered in Error or Reordering should be selected if you have upgraded or downgraded the service speed and re-ordered.
- Reason Not Listed provides an optional free text field that allows you to specify a different reason to those listed. This field has a maximum of 400 characters.
-
Click Yes - Terminate Service to confirm the IX termination, or click No, Keep Services to cancel.
The IX is deleted from the Megaport network.
MegaIX Looking Glass
Megaport operates a public, web accessible MegaIX Looking Glass for peers and network operators to investigate the current routing state. You can query both the primary and redundant route servers for live BGP data.
The MegaIX Looking Glass is available at https://lg.megaport.com.
IX Telemetry
IX Flow Telemetry is a generic industry term used for technology that allows measurement of network traffic between peers by user. The IX Telemetry feature in Megaport allows you to see the peering rates of any IX connections your company has deployed.
You can use IX Telemetry to view and analyze your network traffic flow statistics, check whether a peer is using a lot of network traffic, and diagnose and troubleshoot any configuration or networking issues.
To view IX Telemetry in the Megaport Portal, select Tools > IX Telemetry.
Megaport also offers a public API that you can use to access the services available through IX Telemetry. You can use the GET IX Telemetry API to return telemetry details for a specified IX. For more information, see Megaport API.
IX pricing estimates
Remote (non same metro) IX pricing is the same as VXC. An IX in the same metro as a Port is no charge, an IX in a different metro to a Port is charged at VXC rates. In the Megaport Portal, you can test different IX configurations without any obligation, to obtain a price estimate.
For more information, see VXC Pricing and Contract Terms.