Configuring BGP Advanced Settings
This topic describes how to manage advanced Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) settings in the Megaport Cloud Router (MCR):
- An option to override the default autonomous system number (ASN).
- An ASN prepend option to set route advertisement priorities.
- The Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) identifies the preferred VXC used to re-route traffic after a path failure.
- The Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) protocol detects any path failures between BGP neighbors.
Overriding the MCR ASN
The default ASNAutonomous system number.
A collection of connected IP routing prefixes under the control of one or more network operators on behalf of a single administrative entity or domain. assigned to the MCR is 133937. For most configurations, the default ASN is appropriate. Optionally, you can specify another local ASN to override the default ASN on a per-peer basis.
Important
Cloud providers can have restrictions on the ASN value. See the documentation for your cloud provider before overriding the default value.
To override the MCR ASN
-
Select the VXC and select A End or B End.
-
Next to the BGP connection, click Edit.
-
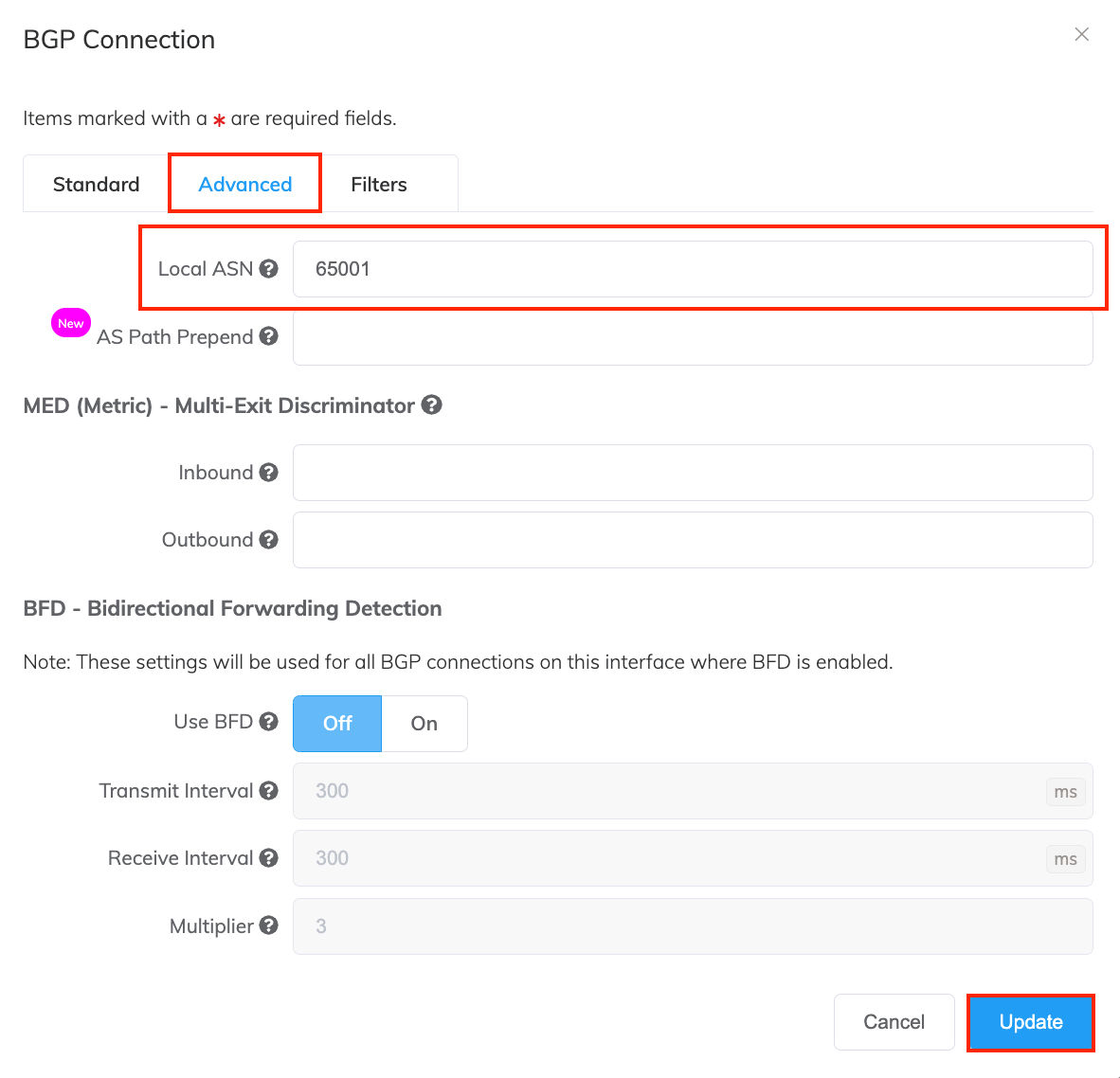
Select the Advanced tab.
-
In the Local ASN field, enter a public or private ASN (for example, enter a number from 64512 to 65534).
The ASN range is from 2 to 4294967294, but the following ASNs are not available:
- 8074, 8075, 12076, 65515 - 65520 (reserved in Azure)
- 23456, 64496-64511, 65535 - 65551 (reserved by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA))
-
Click Update.
Setting the route advertisement priority with ASN prepend
The ASN path length determines the route advertisement priority for outgoing BGP paths. The route with the shortest AS path has the highest preference, and it wins over any longer path advertisements. Longer path lengths have a lower priority. AS path prepending lengthens the path to lower the path priority.
Setting an ASN prepend value is optional.
To set the path advertisement priority on an existing BGP connection
- Select the VXC and select A End or B End.
- Next to the BGP connection, click Edit.
-
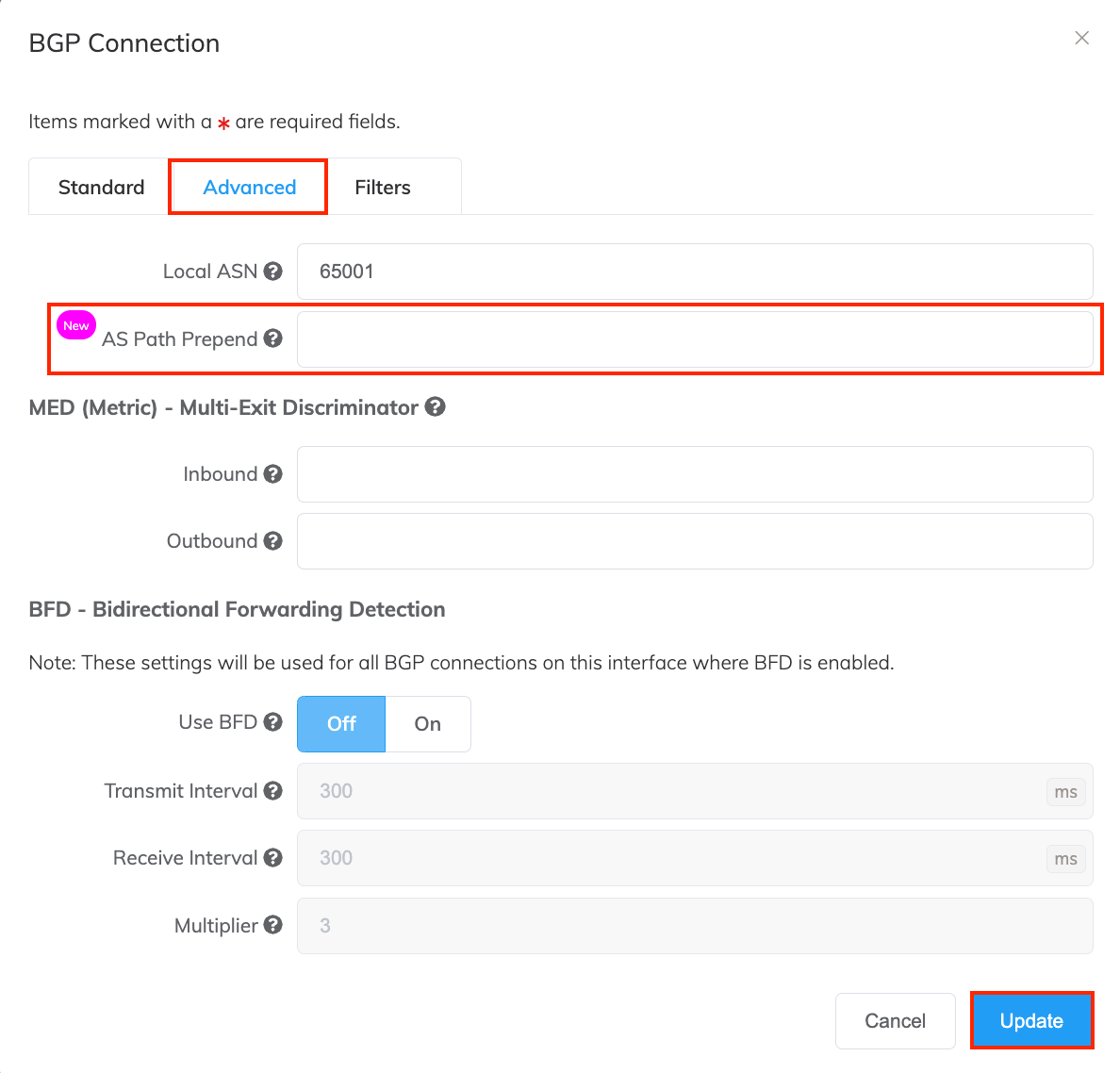
Select the Advanced tab.
-
In the ASN Path Prepend field, enter the number of additional times to add the local ASN to the BGP path. Enter integer(s) within the range of 1 to 10. For example, 2 prepends the ASN to the existing AS path twice, creating an AS path length of 3. Higher numbers deprioritize the path.
- Click Update.
To set the path advertisement priority on a new BGP connection
- Add a new BGP connection.
- Select the Advanced tab.
- In the ASN Path Prepend field, enter the number of additional times to add the local ASN to the BGP path. Enter integer(s) within the range of 1 to 10. For example, 2 prepends the ASN to the existing AS path twice, creating an AS path length of 3. Higher numbers deprioritize the path.
- Click Add.
Configuring the BFD protocol
BGP shares network reachability information with adjacent BGP systems, which are referred to as neighbors or peers. The BFD protocol detects path failure between directly connected BGP neighbors, allowing for a faster BGP routing re-convergence time. Enabling BFD on a VXC connection provides fast link failure detection and failover when connecting to services that support BFD on the remote neighbor. After BFD is enabled, a BGP neighbor relationship can be torn down quickly after notifications from BFD, failing over to another BGP neighbor.
The BFD protocol runs independent of BGP. When BFD is enabled, failover is faster because it occurs before the BGP timer interval elapses. The default setting for the BGP timer is 3 keep-alive window failures of 60 seconds each. When not enabled, failover will only occur after the BGP timer interval elapses.
BFD settings apply to all BGP connections on the interface.
Important
To prevent high CPU utilization, before you enable BFD, disable the sending of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) redirect messages by entering the no ip redirect command.
To configure BFD
-
Select the VXC and select A End or B End.
-
Next to the BGP connection, click Edit.
-
Select the Advanced tab.
-
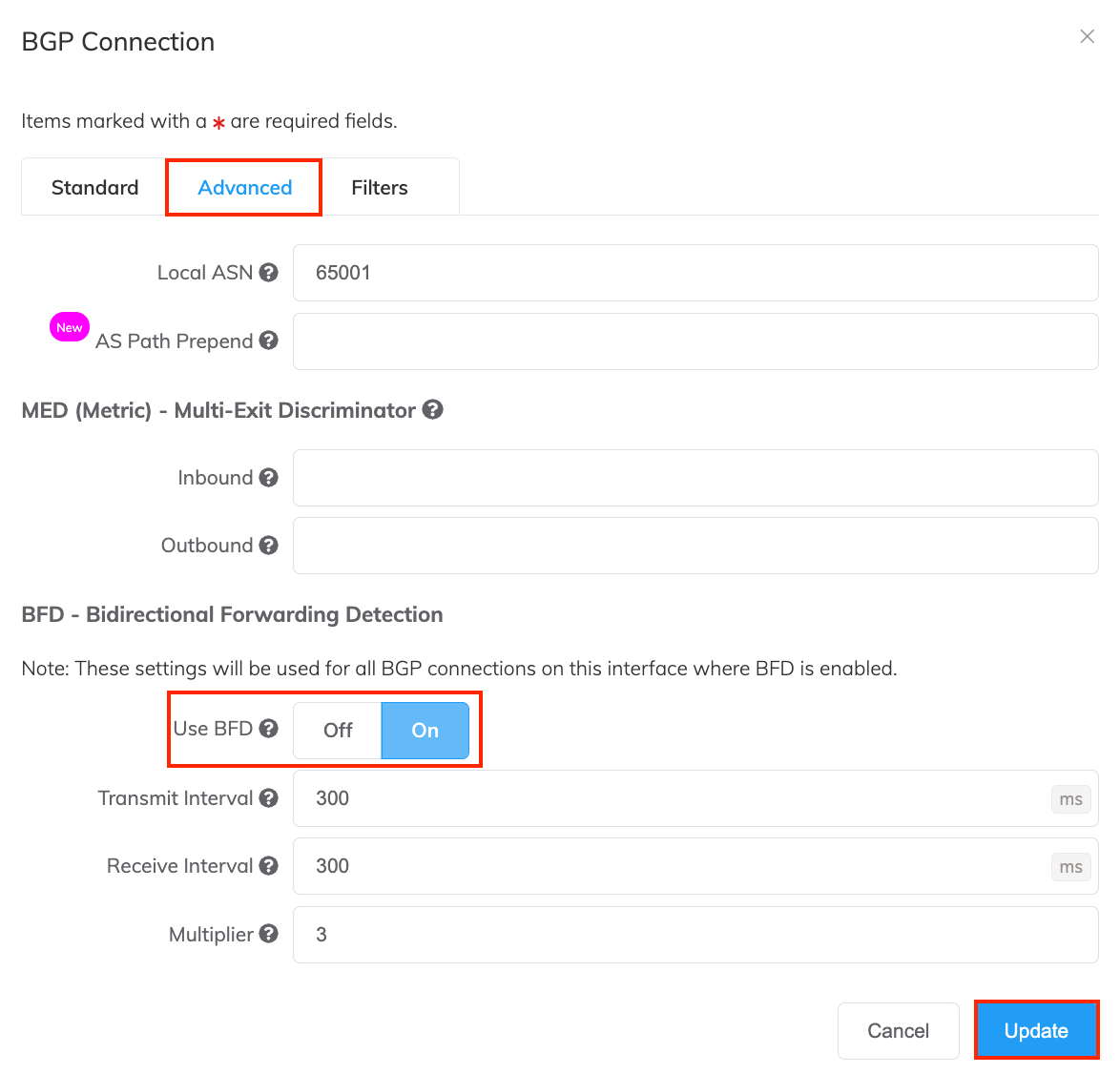
Next to Use BFD, click On.
-
After Transmit Interval, specify the minimum time that the BGP neighbor transmits liveness detection BFD packets to the BGP neighbor. The default is 300 milliseconds. The range is 300 milliseconds to 9000 milliseconds.
-
After Receive Interval, specify the minimum time that the BGP neighbor sends liveness detection BFD packets to this interface. The default is 300 milliseconds. The range is 300 milliseconds to 9000 milliseconds.
-
After Multiplier, specify the minimum number of BFD packets that can be missed before the BGP session is considered down. The default is 3 packets. The range is 3 to 50 packets.
-
Click Update.
Important
You must enable BFD on the BGP neighbor as well.
Default BFD values by cloud service provider
-
AWS Direct Connect – BFD is supported natively by AWS Direct Connect connections. Asynchronous BFD is automatically enabled for AWS Direct Connect virtual interfaces on the CSP side. However, you must configure BFD on MCR VXCs to AWS Direct Connect to enable it for your connection.
By default, the AWS BFD liveness detection minimum interval is 300 milliseconds and the multiplier is 3 packets.
Note
Confirm support for other neighbors with your CSP, as well as specific default values.
-
Azure ExpressRoute – BFD is supported natively by Azure ExpressRoute on private peering. BFD is configured by default under all the newly created ExpressRoute private peering interfaces on the MSEEs. However, you must configure MCR VXCs to Azure ExpressRoute private peering for BFD to enable it for your connection. Between BFD peers, the slowest peer determines the transmission rate.
-
Microsoft Enterprise Edge (MSEE) ExpressRoute routers – BFD transmit and receive intervals are set to 300 milliseconds. In certain scenarios, you can set the intervals to a higher value of 750 milliseconds. You can set higher values to increase the intervals but you can’t configure values lower than 300 milliseconds to decrease them.
-
Google Cloud Services – In late 2021, Google Cloud Partner Interconnect announced support for enhanced features with their Interconnect service. The new features are included in Dataplane V2. BFD is one feature that is now available in V2. BFD was not supported prior to the launch of V2.
Google is in the process of migrating from V1 to V2 with an expected completion date of September 2022. To support the new features, including BFD, the Interconnect Location (Google Edge) and the region where Interconnect connects to Google Cloud Router must both have V2 enabled. For more information on how to confirm your Dataplane version, see Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for Cloud Router.
Important
Before enabling BFD on MCR after May 11, 2022, you need to validate that the Megaport VXC/Google VLAN Attachment with your Partner Interconnect service has enabled V2. For more information on how to validate your Dataplane version, see Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for Cloud Router. If V2 is not enabled, you need to open a Google support case to enable it. In some cases, V2 may not be available. If your VLAN attachment does not use Dataplane V2, do not enable BFD.
MCR automatically operates in BFD single-hop mode for VXCs created after May 11, 2022. VXCs created on MCR prior to May 11, 2022 use BFD multihop and are not compatible with BFD. You need to reorder any VXCs created on MCR to Google prior to May 11, 2022 before you can enable BFD.
Configuring a preferred route
A Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) is a BGP path attribute that can influence a BGP neighbor to take a preferred route when the advertising autonomous system (AS) is the same for candidate routes and there are multiple entry points for that AS. A lower MED metric is preferred over a higher metric. You can use the MED attribute to switch traffic between two VXCs and avoid ECMP (equal-cost multipath) behavior.
Other BGP attributes are taken into account before considering the MED attribute. The MED attribute breaks the tie between two routes when the weight, local preference, AS path, and origin type are the same. The exit point with the lowest MED metric is preferred.
For example, a configuration that consists of a BGP neighbor device, R3, with a MED metric of 20 and another neighbor device, R2, with a MED metric of 10 will cause autonomous system (AS) 123 (of which device R2 and R3 are members) to prefer the path through R2 to reach ASN4.
Adding or changing an MED metric doesn’t disrupt the service.
To configure the MED
-
Select the VXC and select A End or B End.
-
Next to the BGP connection, click Edit.
-
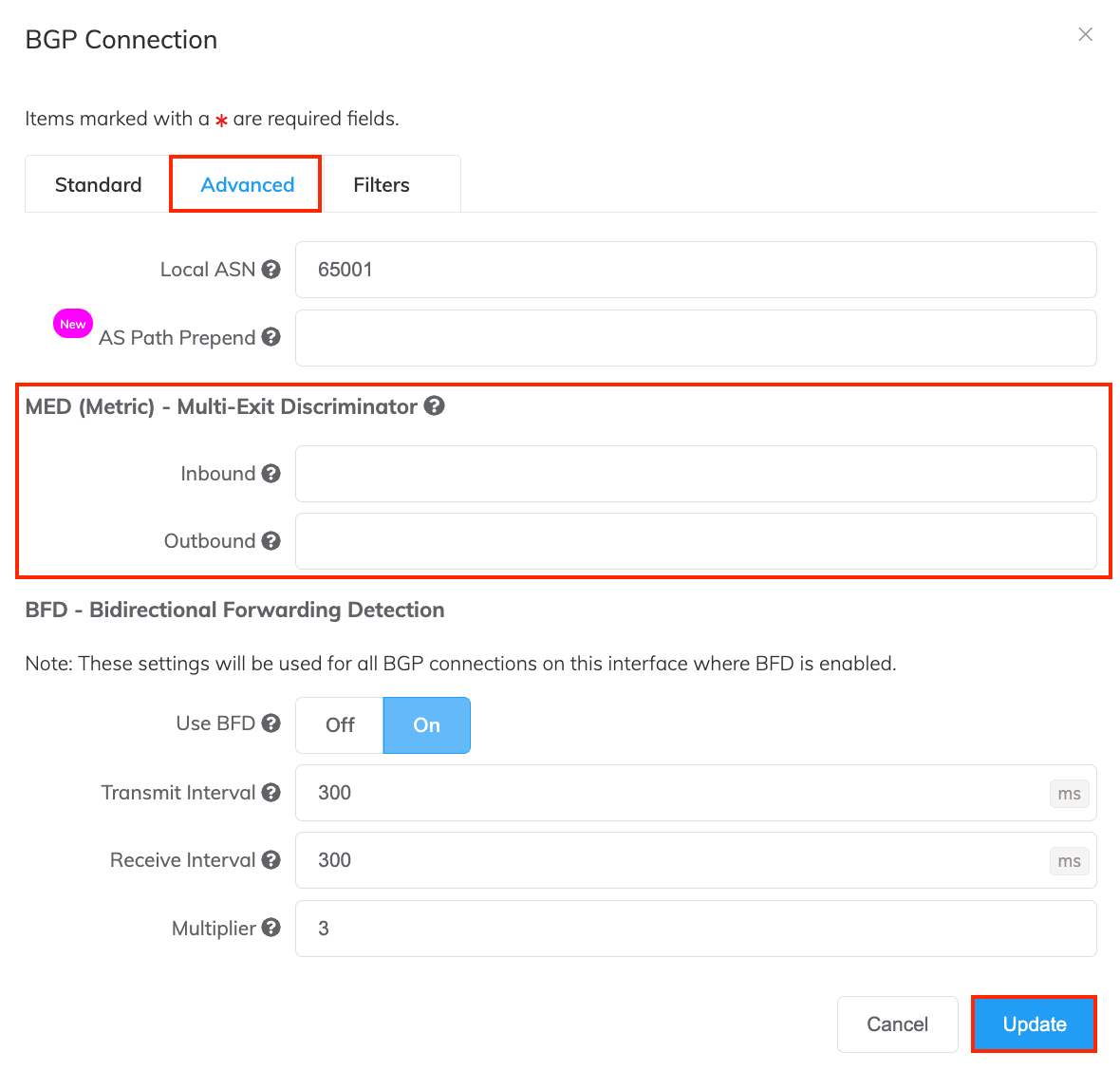
Select the Advanced tab.
-
Next to Inbound, specify a 32-bit integer MED metric to apply to all routes received on this BGP connection. Leave blank to use the value received from the BGP neighbor.
-
Next to Outbound, specify a 32-bit integer MED metric to apply to all routes transmitted by this BGP connection.
-
Click Update.
Using MED with Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform Cloud Router egress is determined by the first condition that is met:
- All egress traffic is sent to the route with the shortest AS path length.
- If routes have the same AS path lengths, all egress traffic is sent to the route with the lowest MED value (the lowest route metric).
- If routes have the same AS path lengths and MED values (the same route metrics), egress traffic is balanced across all routes using equal-cost multipath (ECMP).
Note
Confirm support for other neighbors with your CSP, along with any specific routing metric influences that might have a higher priority than the MED.