Configuring and Maintaining AWS Hosted VIFs
To deploy an AWS Hosted VIF, you need your AWS Account number and the details of the VPC environment.
Note
You can deploy multiple VXCs to the same VPC (for redundancy); however, you cannot deploy a single VXC to multiple VPCs. You need a separate VXC to connect to each AWS VPC.
![]() Watch a
16-minute video for the Hosted VIF setup process.
Watch a
16-minute video for the Hosted VIF setup process.
To create a Hosted VIF connection
- In the Megaport Portal, go to the Services page and select the Port you want to use.
If you haven’t already created a Port, see Creating a Port. -
Add an AWS connection for the Port.
If this is the first connection for the Port, click the AWS tile. The tile is a shortcut to the configuration page. Alternatively, click +Connection, click Cloud, and click AWS.

-
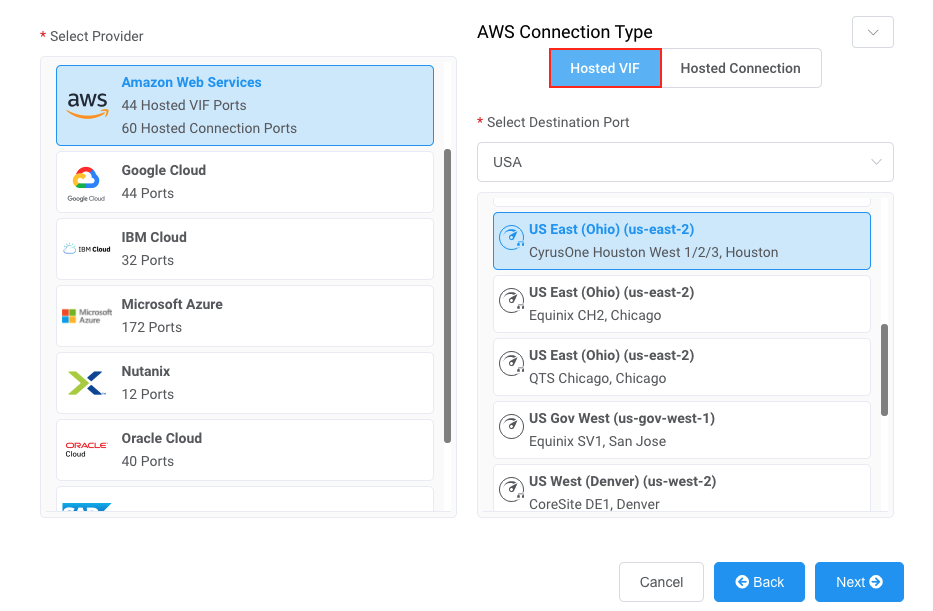
For Provider click AWS and for AWS Connection Type click Hosted VIF.
-
In the Select Destination Port list, select the AWS region and the interconnection point for your connection and click Next.
You can use the Search field to find the Port name, Country, Metro City, or address of your destination Port. -
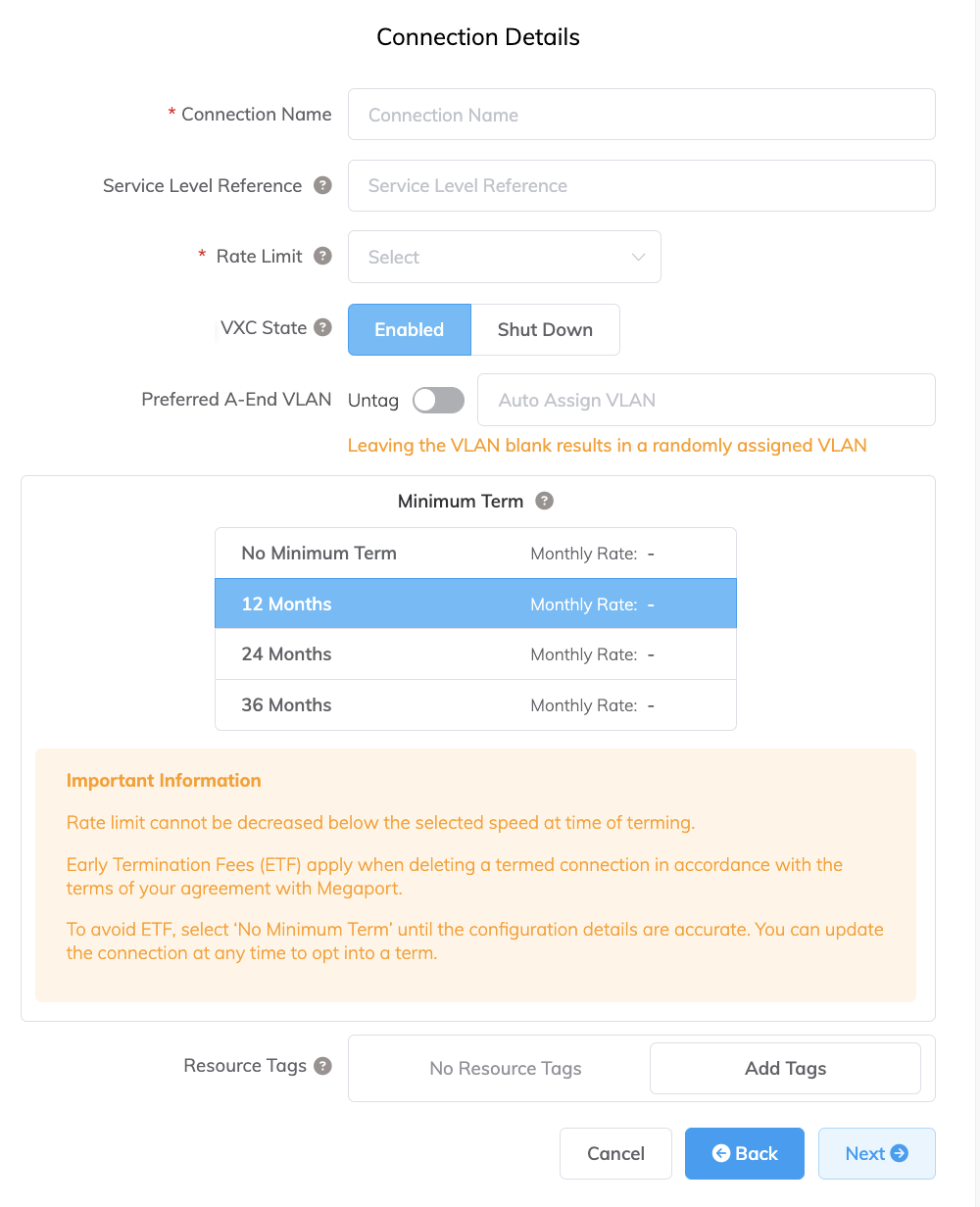
Specify the connection details:
-
Connection Name – The name of your VXC to be shown in the Megaport Portal.
Tip
Match this to the VXC name on the next screen for easy mapping.
-
Service Level Reference (optional) – Specify a unique identifying number for the VXC to be used for billing purposes, such as a cost center number or a unique customer ID. The service level reference number appears for each service under the Product section of the invoice. You can also edit this field for an existing service.
-
Rate Limit – The speed of your connection in Mbps. Accepted values range from 1 Mbps to 5 Gbps in 1 Mbps increments. Note the sum of all hosted virtual VXCs to a service can exceed the Port capacity (1 or 10 Gbps, or 100 Gbps in some locations) but the total aggregate will never burst beyond the Port capacity.
-
VXC State – Select Enabled or Shut Down to define the initial state of the connection. For more information, see Shutting Down a VXC for Failover Testing.
Note
If you select Shut Down, traffic will not flow through this service and it will behave as if it was down on the Megaport network. Billing for this service will remain active and you will still be charged for this connection.
-
Preferred A-End VLAN (optional) – Specify an unused VLAN ID for this connection. This must be a unique VLAN ID on this Port and can range from 2 to 4093. If you specify a VLAN ID that is already in use, the system displays the next available VLAN number. The VLAN ID must be unique to proceed with the order. If you don’t specify a value, Megaport will assign one.
Alternatively, you can click Untag to remove the VLAN tagging for this connection. The untagged option limits you to only one VXC deployed on this Port. The VLAN for the AWS side termination will be automatically allocated and will not impact your Megaport details. You must use untagged VLANs if you are creating a MACsec connection.
-
Minimum Term – Select No Minimum Term, 12 Months, 24 Months, or 36 Months. Longer terms result in a lower monthly rate. 12 Months is selected by default.
Take note of the information on the screen to avoid early termination fees (ETF). For more information, see VXC Pricing and Contract Terms and VXC, Megaport Internet, and IX Billing. -
Resource Tags – You can use resource tags to add your own reference metadata to a Megaport service.
To add a tag:- Click Add Tags.
- Click Add New Tag.
- Enter details into the fields:
- Key - string maximum length 128. Valid values are a-z 0-9 _ : . / \ -
- Value - string maximum length 256. Valid values are a-z A-Z 0-9 _ : . @ / + \ - (space)
- Click Save.
If you already have resource tags for that service, you can manage them by clicking Manage Tags.
Warning
Never include sensitive information in a resource tag. Sensitive information includes commands that return existing tag definitions and information that will identify a person or company.
-
-
Click Next.
-
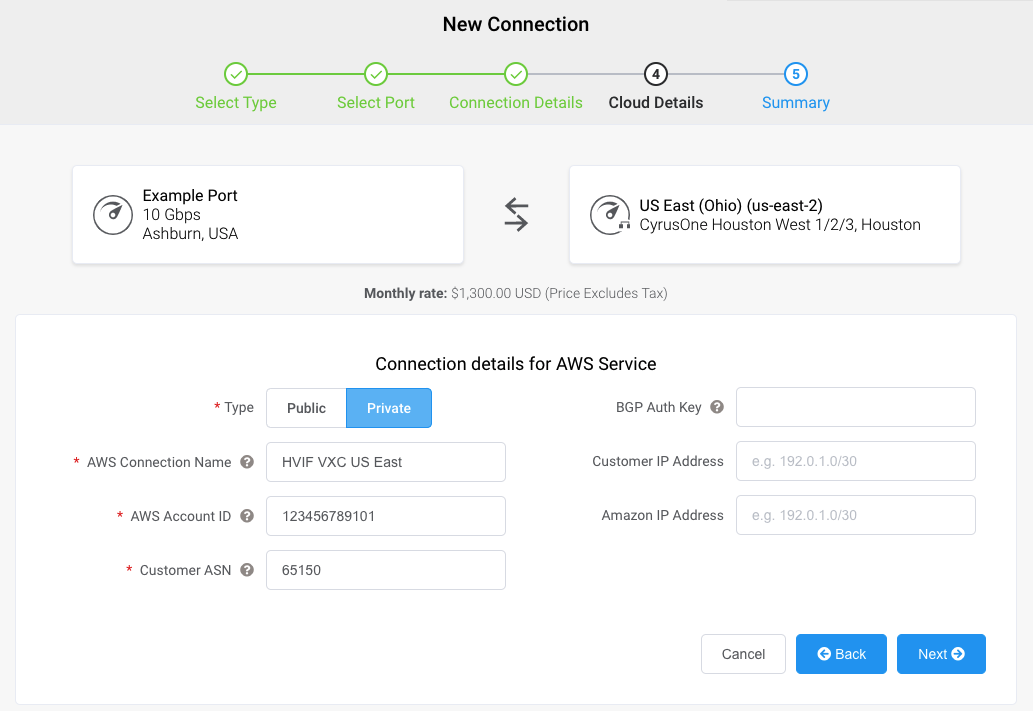
Specify the cloud details.
-
Select Public or Private.
- Private – Access private AWS services such as a VPC, EC2 instances, load balancers, RDS DB instances, on private IP address space.
-
Public – Access public AWS services such as Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), DynamoDB, CloudFront, and Glacier. You’ll also receive Amazon’s global IP prefixes (approximately 2,000 prefixes).
Note
Public VIFs require manual intervention from Amazon and could take up to 72 hours. For more information, see Configuring Public AWS Connections with IP Addresses Provided by AWS.
-
AWS Connection Name – This is a text field and will be the name of your virtual interface that appears in the AWS console. For easy mapping, use the same name for this field as you did for the VXC name on the previous screen.
-
AWS Account ID – This is the ID of the account you want to connect. You can find this value in the management section of your AWS console.
-
Customer ASN – Your networks Autonomous System Number. For Private Direct Connects, this must be a private ASN and the supported private ASN range is 64512 - 65535. For public Direct Connects, this can be either a private or public ASN. If using a Public, you must own the public ASN.
-
BGP Auth Key (optional) – Specify the BGP MD5Sometimes known as an MD5 hash or BGP key. The message-digest (MD5) algorithm is a widely used cryptographic function producing a string of 32 hexadecimal digits. This is used as a password or key between routers exchanging BGP information.
key. If you leave this blank, Megaport negotiates a key automatically for you with AWS which will be displayed in the Megaport Portal. The key is not displayed in the AWS console.Note
The BGP Auth Key is generated during the ordering process when this field is left blank. It will not be displayed on the Summary page when ordering. To see the key, view the Connection Settings after the service has been deployed and is live.
-
Customer IP Address – The IP Address space (in CIDR format) you will use on your network for peering. For private connections, this field is optional and if left blank, Megaport assigns a private /30 address. For public connections, this field is required and needs public IPs (/30) allocated by you for BGP connectivity. You must own the public IPs.
-
Amazon IP Address – The IP address space in CIDR format assigned in the AWS VPC network for peering. For private connections, this field is optional and if left blank, Megaport automatically assigns a private /30 address. For public connections, this field is required and needs public IPs (/30) allocated by you for BGP connectivity. You must own the public IPs.
-
Prefixes – For Public connections only - IP Prefixes to announce to AWS. RIR-assigned IPv4 addresses only. Specify the prefixes you will advertise when deploying a Public Direct Connect.
Once you configure Prefixes for a Public connection, you cannot change them and the field is grayed out. To change this value, create a support ticket with AWS so they can make this change a non-impacting way. Or you can cancel the Hosted VIF and reorder. In both cases, you need to wait for AWS to manually approve the request.
-
-
Click Next.
A summary page appears that includes the monthly cost. Click Back to make changes or click Add VXC to move this configuration to your cart. Once you have finished this configuration, you can configure additional VXCs or proceed through the checkout process.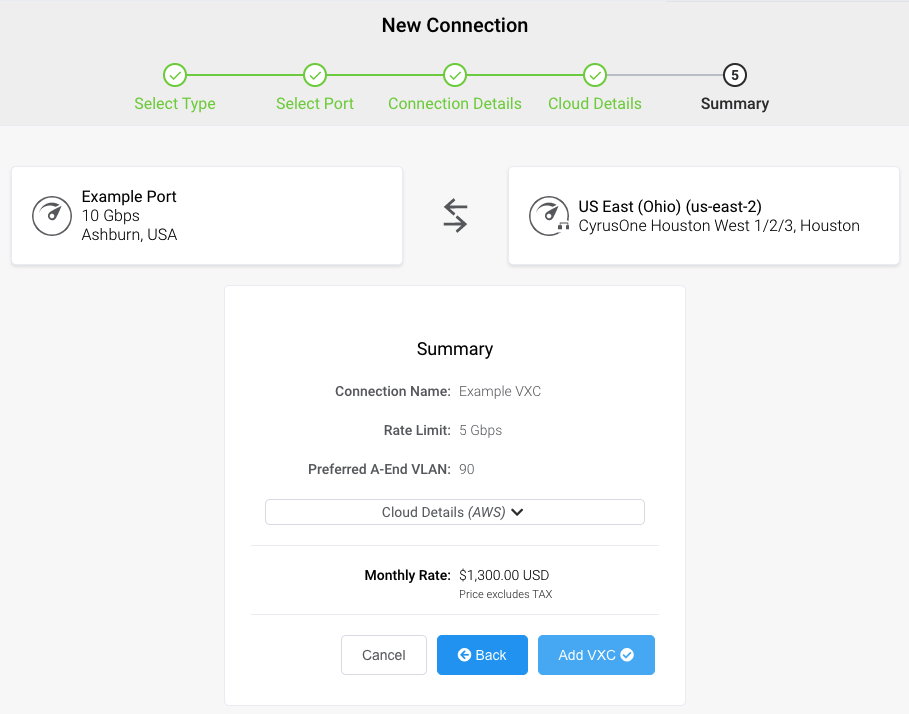
-
Click Order and complete the ordering process to deploy the VXC.
Megaport will deploy the connection. The deployment can take several minutes. - Accept the virtual interface in AWS.
To review and accept in the AWS console, go to Services > AWS Direct Connect for the Direct Connect dashboard. For a private virtual interface, you must also have an existing virtual private gateway or Direct Connect gateway. For more information, see the AWS documentation.
Once you accept the hosted VIF in AWS, the VXC state changes to configured in the Megaport Portal. You can review the configuration details to get the A-End VLAN ID, BGP Auth Key, and IP addresses that you need to configure your router.
To edit a Hosted Virtual Interface
-
Click the gear icon next to the connection in the Megaport Portal to make changes.

If you have permissions to edit VXCs, you can modify the details on the Megaport side including the connection name, VLAN ID, Service Level Reference, and rate limit.
If this is a termed connection, you cannot reduce the term.
Once submitted, those changes take effect in a few minutes.You can also make changes to the AWS details of a VXC. When you change the AWS details, the service will be rebuilt and you need to accept changes to the connection in AWS.
To delete a Hosted Virtual Interface
-
Click the trash icon next to the connection in the Megaport Portal.

For more information, see Terminating a VXC.