Creating an MCR VXC
With a Megaport Cloud Router (MCR) configured, you can add a Virtual Cross Connect (VXC) to a CSP, a local port, or a third-party network. You can optionally connect a physical Port to the MCR via a private VXC or connect to a service provider in the Megaport Marketplace.
A VXC is a point-to-point Layer 2 circuit between two endpoints that is mapped with a VLAN ID on each end. You can order VXCs to reach any destination in the Megaport network just like the VXCs used with the physical Ports. You can connect up to 25 VXCs per MCR.
Note
The VXC target destination type determines the peering type. The peering type determines which routes are advertised. For more information, see MCR Route Advertisement.
- Log in to the Megaport Portal, select
Services and select the MCR.
If you haven’t already created an MCR, see Creating an MCR. -
If this is the first connection for the MCR, click the tile that matches the VXC type. The tile is a shortcut to the configuration page. Alternatively, click +Connection and select a destination type:
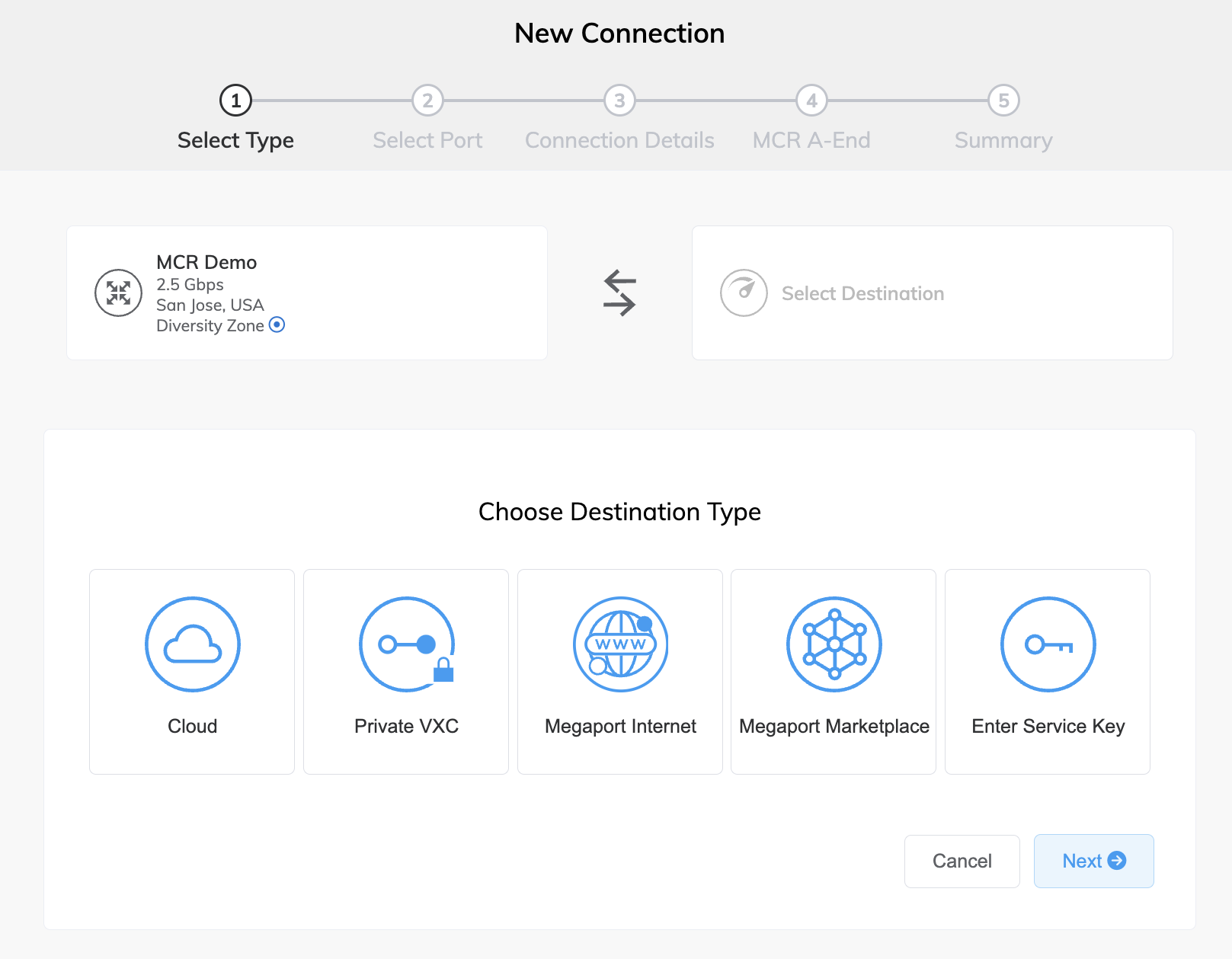
-
Cloud – Provision a dedicated interconnect to a public cloud service provider. After selecting Cloud, select a provider. Some providers require a service key.
For specific CSP configuration details:
- 3DS Outscale – See Creating MCR Connections to 3DS Outscale.
- Alibaba – See Creating MCR Connections to Alibaba Express.
- AWS – See Creating MCR Connections to AWS.
- Azure – See Creating MCR Connections to Azure using ExpressRoute.
- Google – See Creating MCR Connections to Google Cloud Services.
- IBM – See Creating MCR Connections to IBM Cloud Direct Link.
- Oracle – See Creating MCR Connections to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
- OVHcloud – See Creating MCR Connections to OVHcloud Connect.
- Salesforce – See Creating MCR Connections to Salesforce Express Connect.
- SAP – See Creating MCR Connections to SAP HANA Enterprise Cloud.
-
Private VXC – Connect to other Ports local to the current company account. After selecting Private VXC, select a destination Port. For more information, see Creating a Private VXC.
- Megaport Internet – Connect to the internet. After selecting Megaport Internet, select a destination Port (internet router). For more information, see Creating a Megaport Internet Connection for an MCR.
- Megaport Marketplace – Connect to any service provider present in the Megaport Marketplace. After selecting Megaport Marketplace, select a provider. For more information, see Megaport Marketplace.
- Enter Service Key – Connect to a third party on the Megaport network that isn’t publicly listed in the Megaport Marketplace. Select this destination if you have been given a service key, and enter the service key.
-
-
Click Next.
-
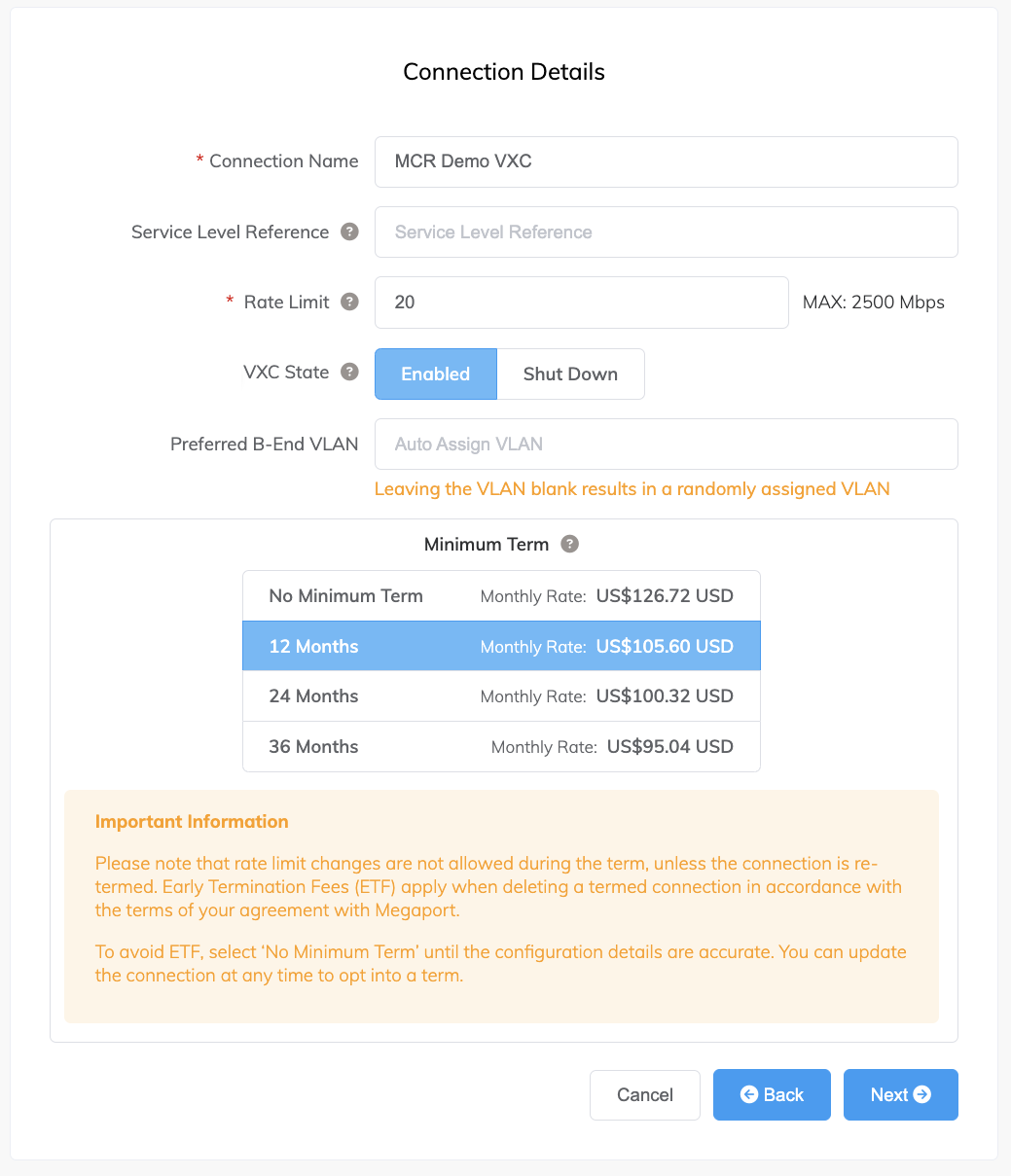
Specify the connection details:
-
Connection Name – The name of your VXC to be shown in the Megaport Portal.
-
Service Level Reference (optional) – Specify a unique identifying number for the VXC to use for billing purposes, such as a cost center number or a unique customer ID. The service level reference number appears for each service under the Product section of the invoice. You can also edit this field for an existing service.
-
Rate Limit – The speed of your connection in Mbps. Specify a rate limit that doesn’t exceed the total rate limit for the MCR. Allow enough bandwidth for any connections that you might add later.
-
VXC State – Select Enabled or Shut Down to define the initial state of the connection. For more information, see Shutting Down a VXC for Failover Testing.
Note
If you select Shut Down, traffic will not flow through this service and it will behave as if it was down on the Megaport network. Billing for this service will remain active and you will still be charged for this connection.
-
Preferred B-End VLAN – Specify the 802.1q VLAN tag for this connection that you will receive through the B-End VLAN. This field will show if the configuration requires this information.
-
Minimum Term – Select No Minimum Term, 12 Months, 24 Months, or 36 Months. Longer terms result in a lower monthly rate. 12 Months is selected by default.
Take note of the information on the screen to avoid early termination fees (ETF). For more information, see VXC Pricing and Contract Terms and VXC, Megaport Internet, and IX Billing. -
Resource Tags – You can use resource tags to add your own reference metadata to a Megaport service.
To add a tag:- Click Add Tags.
- Click Add New Tag.
- Enter details into the fields:
- Key - string maximum length 128. Valid values are a-z 0-9 _ : . / \ -
- Value - string maximum length 256. Valid values are a-z A-Z 0-9 _ : . @ / + \ - (space)
- Click Save.
If you already have resource tags for that service, you can manage them by clicking Manage Tags.
Warning
Never include sensitive information in a resource tag. Sensitive information includes commands that return existing tag definitions and information that will identify a person or company.
-
-
Click Next.
The MCR Connection detail page appears. For each VXC connected to an MCR you can configure one or more interfaces, IP addresses, BGP connections, or static routes. Most VXCs will use one interface. However, you can configure multiple interfaces enabling a Q-in-Q connection and specifying an inner VLAN tag for each interface. Each VLAN ID must be unique. You can add up to five VLAN IDs.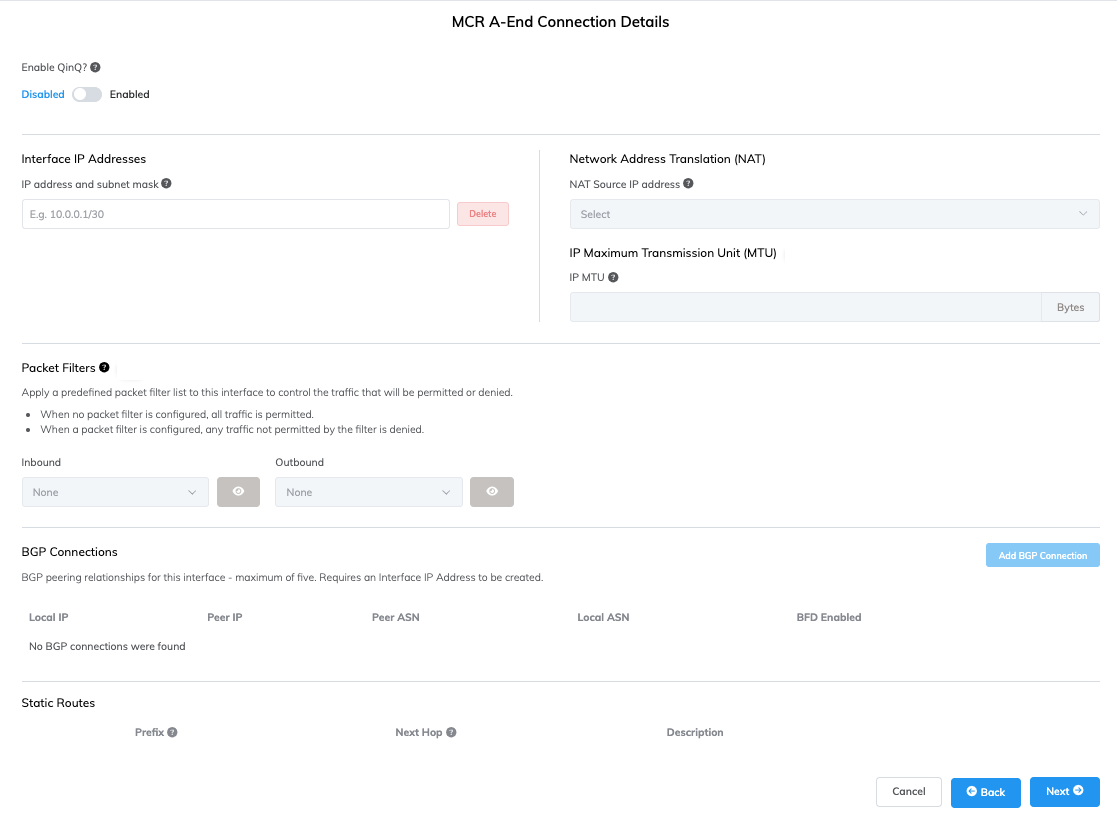
-
Enable or disable the Q-in-Q VLAN option:
- Disabled allows a single VLAN tag (802.1q). This is the default setting. In most cases, you use a single VLAN that is exposed on the destination physical port as a trunked port instance, allowing the port to contain multiple VXCs to destinations other than the MCR you are configuring. Some use cases might require multiple inner VLANs exposed to this port through Q-in-Q.
- Enabled allows the VLAN to carry multiple or dual-stacked VLANs (802.1ad).
After enabling Q-in-Q, accept the default VLAN ID or specify the VLAN ID for the connection.
The tag protocol identifier (TPID) will be set to 0x8100.
For more information, see Understanding Q-in-Q with Megaport VXCs.
-
If you have enabled Q-in-Q, click Add VLAN to enter the preferred VLAN ID for the B-End of the connection. Megaport automatically assigns an available VLAN to the B-End. If you enter a VLAN ID, Megaport verifies that the VLAN ID is available.
-
Enter one or more IP addresses and subnet mask to configure on the A-End interface.
-
(Optional) Select a NAT source IPv4 address from the Network Address Translation drop-down list. All packets leaving this interface will have their source NAT rewritten to this address.
Network Address Translation (NAT)Network Address Translation (NAT) is the process that translates the unregistered private IP addresses used for an organization’s private inner network into a single registered public IP address before packets are sent to an external network. NAT allows private IP networks to use the internet and cloud.
allows flexibility in designing a scalable and secure multi-vendor, multicloud, or hybrid cloud scenario. Source NAT translates the source IP address of a packet leaving the MCR. When you assign a NAT IP address in MCR, all packets leaving the interface use that IP address as their source IP address. Enable this feature when NAT is required for a connection, for example, when you need to translate several private IP addresses into a single public IP address to meet cloud service provider requirements.For more information on how MCR performs NAT to support public peering types to cloud service providers, see How MCR performs NAT.
-
Enter any details specific to the VXC type.
- For more information on adding a BGP connection, see Configuring an MCR.
- For more information on enabling Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) settings, see Enabling the BFD protocol.
- For more information on adding a static route, see Configuring static routes.
-
Click Next.
-
Configure the B-End.
-
Click Next.
The Summary page appears.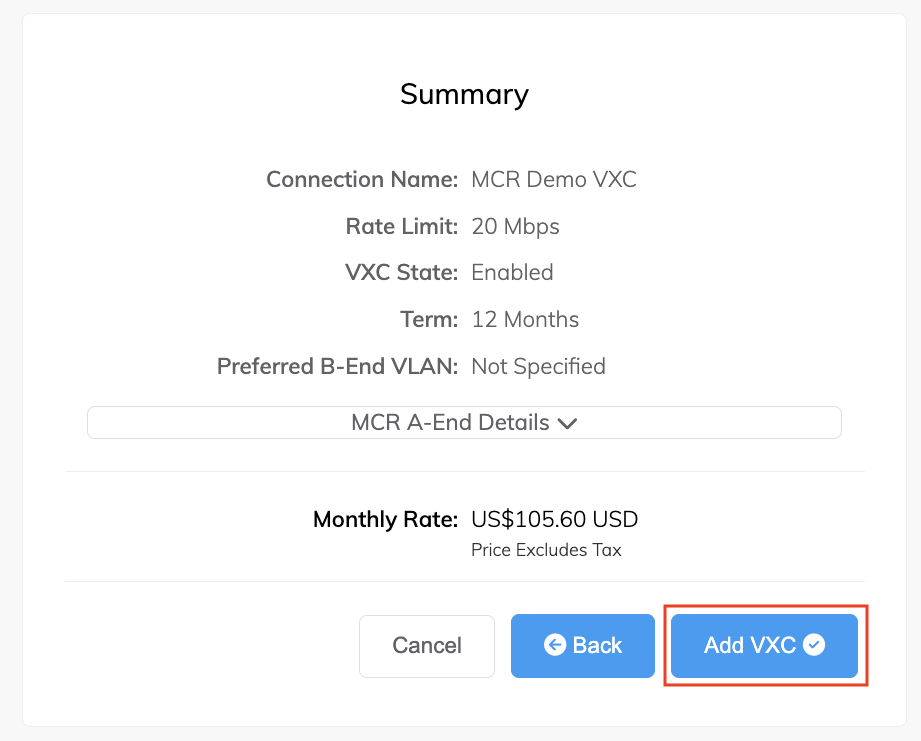
-
Review the Summary details.
Click each down arrow to view A-End and B-End configuration details. -
Click Add VXC.
-
Click Order.
-
Click Order Now.