Creating an Azure Connection for an MVE with Aruba EdgeConnect SD-WAN
You can create a network connection from an MVE (an Aruba EdgeConnect) to Azure ExpressRoute with Virtual Cross Connects (VXCs). You can create either a private connection or a public (Microsoft) connection.
Important
Before you begin, create an MVE in Aruba Orchestrator. For more information, see Creating an MVE.
There are three parts to adding an ExpressRoute connection to your MVE and Aruba SD-WAN.
-
Set up your ExpressRoute plan and deploy the ExpressRoute circuit in the Azure console. When deployed, you get a service key. For additional details, see the Microsoft ExpressRoute documentation.
-
In the Megaport Portal, create a connection (VXC) from your MVE to your ExpressRoute location.
-
In Aruba Orchestrator, add the ExpressRoute connection details to a LAN interface.
The instructions in this topic describe the second and third parts.
Note
MVE for Aruba SD-WAN requires configuration steps in both Orchestrator and the Megaport Portal for all cloud connections.
Adding the ExpressRoute connection in the Megaport Portal
To set up the ExpressRoute connection, you need to create the connection in the Megaport Portal.
To create a connection to ExpressRoute from the Megaport Portal
-
In the Megaport Portal, go to the Services page and select the MVE you want to use.
-
Click +Connection on the MVE.
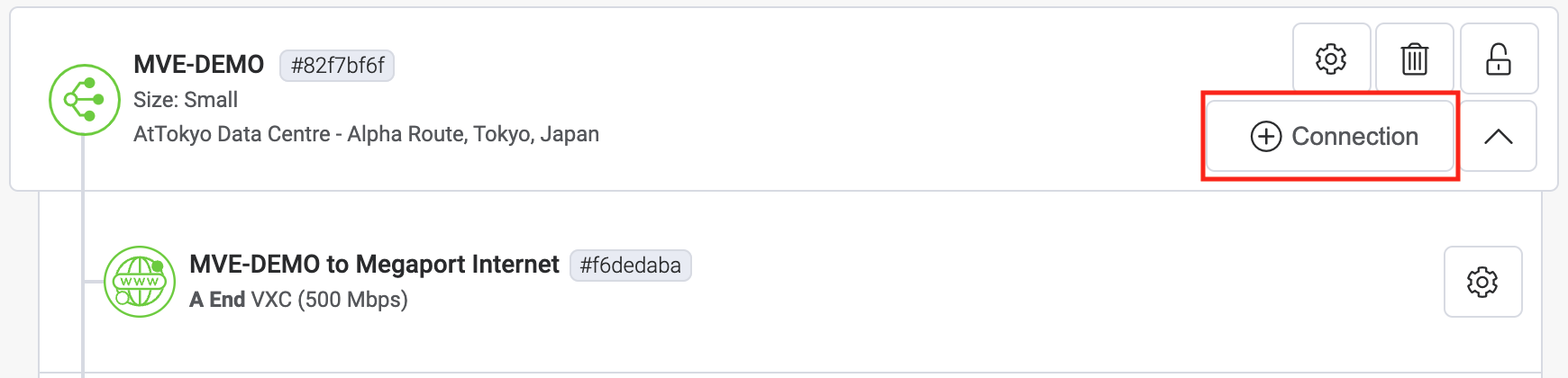
-
Click the Cloud tile.
-
Select Azure ExpressRoute as the provider.
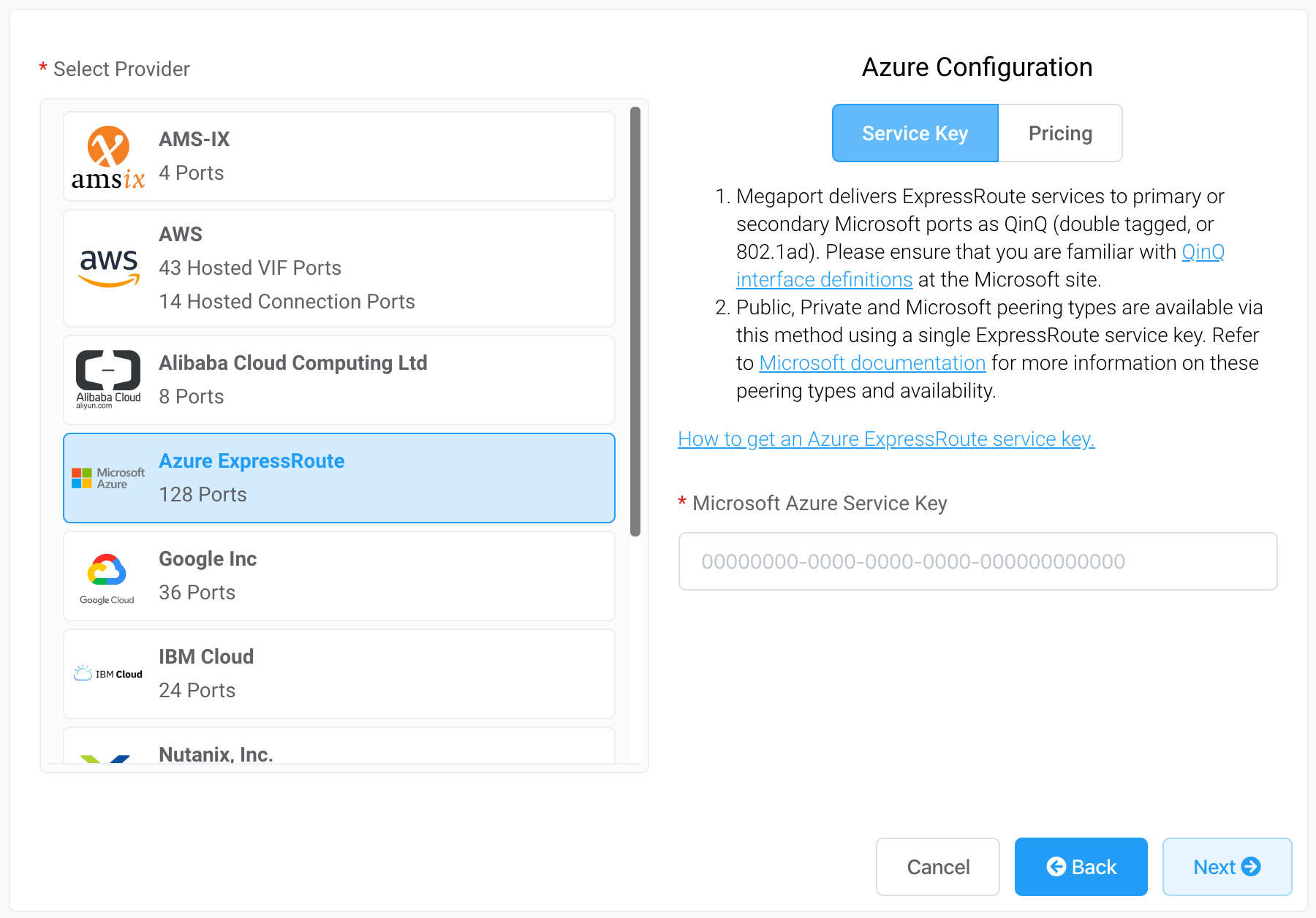
-
Add the ExpressRoute service key into the field in the right hand pane.
The Portal verifies the key and then displays the available port locations based on the ExpressRoute region. For example, if your ExpressRoute service is deployed in the Australia East region in Sydney, you can select the Sydney targets. -
Select the connection point for your first connection.
To deploy a second connection (and this is recommended), you can create a second VXC - enter the same service key and select the other connection target.Some helpful links appear on the configuration screen to resources including the Azure Resource Manager console and some tutorial videos.
-
Specify the connection details:
-
Connection Name – The name of your VXC to be shown in the Megaport Portal.
-
Service Level Reference (optional) – Specify a unique identifying number for the VXC to be used for billing purposes, such as a cost center number or a unique customer ID. The service level reference number appears for each service under the Product section of the invoice. You can also edit this field for an existing service.
Note
Partner-managed accounts can apply a Partner Deal to a service. For more information, see Associating a Deal With a Service.
-
Rate Limit – The speed of your connection in Mbps. The rate limit for the VXC will be capped at the maximum allowable based on the ExpressRoute service key.
-
VXC State – Select Enabled or Shut Down to define the initial state of the connection. For more information, see Shutting Down a VXC for Failover Testing.
Note
If you select Shut Down, traffic will not flow through this service and it will behave as if it was down on the Megaport network. Billing for this service will remain active and you will still be charged for this connection.
-
A-End vNIC – Select an A-End vNIC from the drop-down list. See Creating an MVE in the Megaport Portal for more information about vNICs.
-
Preferred A-End VLAN (optional) – Specify an unused VLAN ID for this connection (for ExpressRoute this is the S-Tag). This must be a unique VLAN ID on this MVE and can range from 2 to 4093. If you specify a VLAN ID that is already in use, the system displays the next available VLAN number. The VLAN ID must be unique to proceed with the order. If you don’t specify a value, Megaport will assign one.
-
Minimum Term – Select No Minimum Term, 12 Months, 24 Months, or 36 Months. Longer terms result in a lower monthly rate. 12 Months is selected by default.
Take note of the information on the screen to avoid early termination fees (ETF). See VXC Pricing and Contract Terms and VXC, Megaport Internet, and IX Billing for more information. -
Configure Single Azure Peering VLAN – By default, this option is enabled for MVE and we strongly recommend keeping it enabled with Aruba SD-WAN.
This option provides a single tag VLAN solution. You configure peering in Azure with the MVE VLAN (A-End) and the peer VLAN set in Azure (B-End). Note, you can have only one peering type (Private or Microsoft) per VXC with this option.Important
If you do not enable this option, the VXC appears active but it does not recognize traffic.
-
Azure Peering VLAN – This value needs to match the A-End VLAN for single tag VLAN peering. A different Azure peering VLAN can also be set, if required.
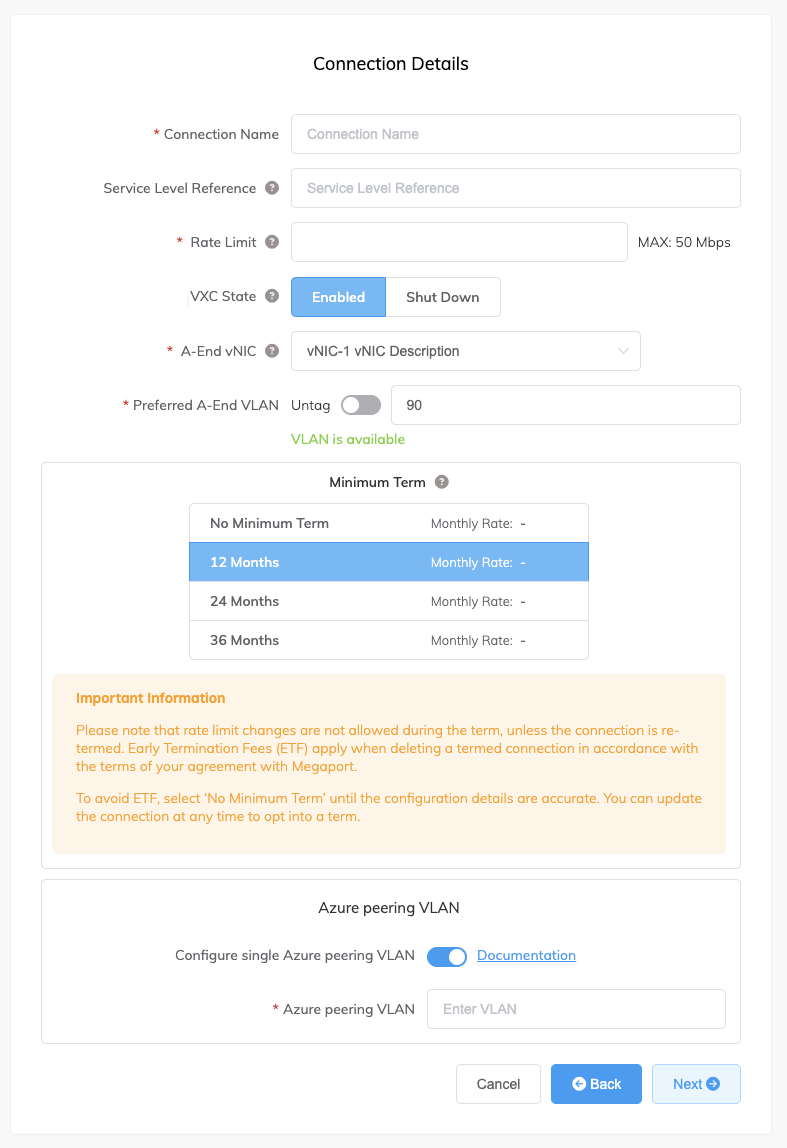
-
-
Click Next and proceed through the ordering process.
When the VXC configuration completes, the VXC icon is green.
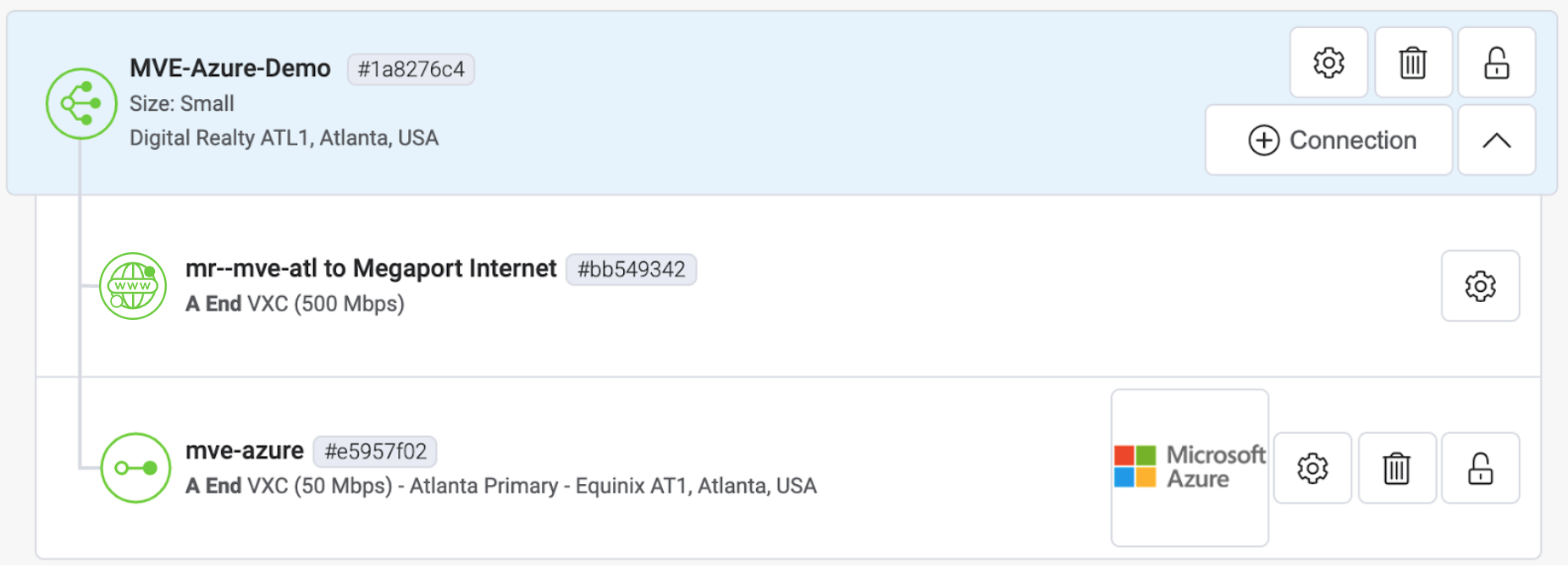
In the Azure Resource Management console, the provider status will be Provisioned.
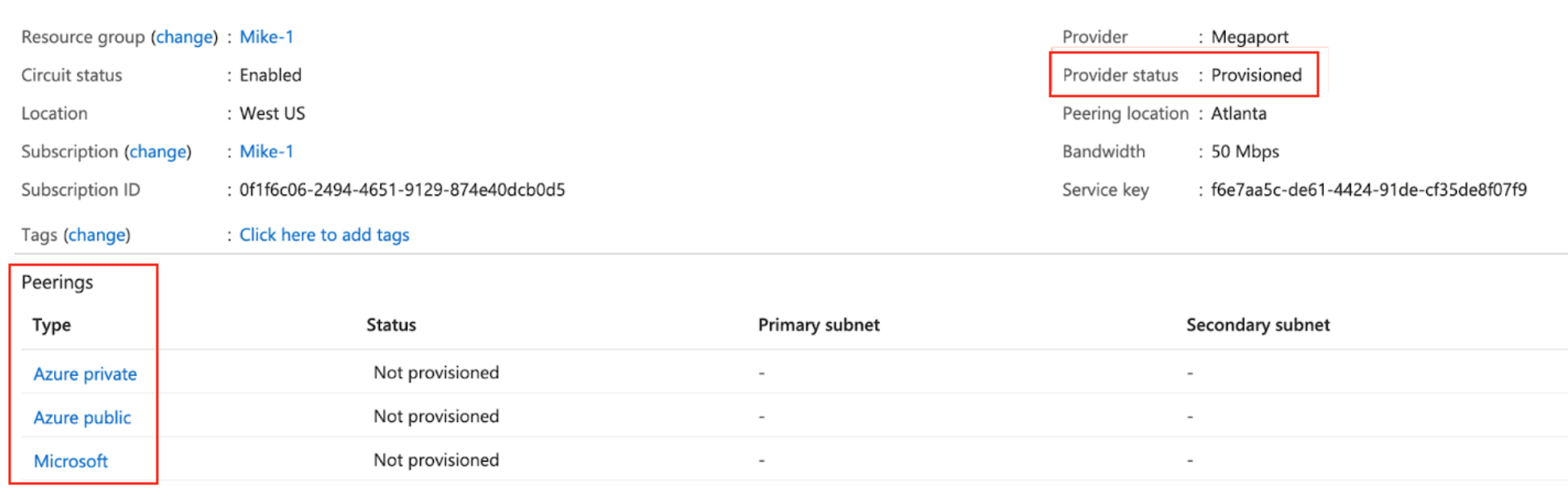
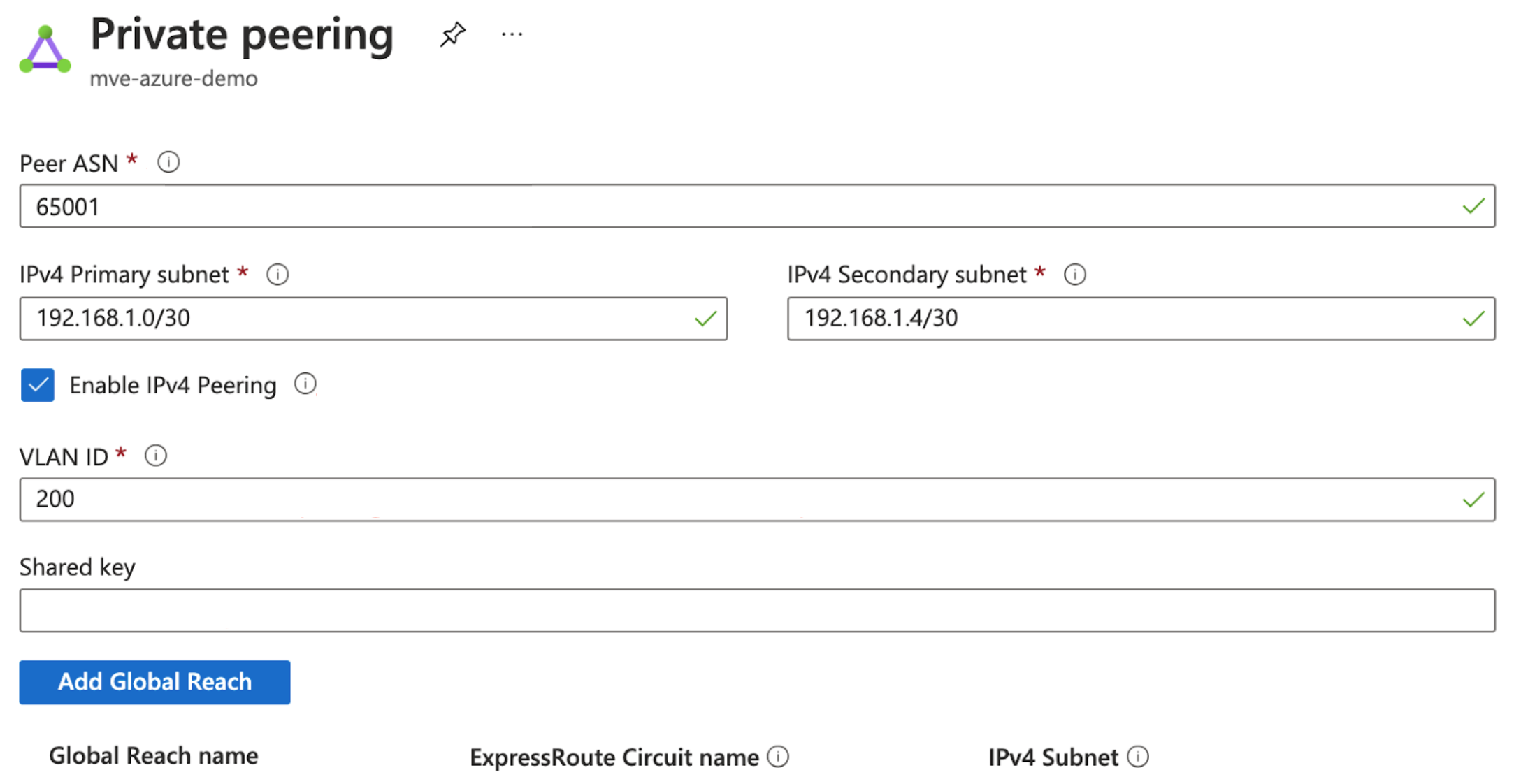
When provisioned, you need to configure peerings. You can configure private and Microsoft peering. Click the peer to configure and provide these details:
- Peer ASN – Enter the ASN for the MVE.
- IPv4 Subnets – From each of these subnets, MVE uses the first usable IP address and Microsoft uses the second usable IP for its router.
- VLAN ID – Enter the A-End VLAN from the MVE. (Note, the VLAN ID in the Azure console can be different from the A-End VLAN.)
- Shared Key (optional) – Enter an MD5 password for BGP.
Adding the ExpressRoute connection to Aruba Orchestrator
After you create the connection from your MVE to Azure and set up the connection in the Azure console, you need to configure it in Aruba Orchestrator. This involves creating a LAN interface and configuring BGP settings, ASNs, VLANs, and MD5 values.
To add the Azure Cloud connection in Aruba Orchestrator
-
Collect the connection details from the Azure console.
Note the values for the Peer ASN, Shared Key, VLAN ID, and IPv4 Primary Subnet. -
Collect the connection details from the Megaport Portal.
Click the gear icon for the Azure connection from your MVE and click the Details view.
Note the value for the A-End VLAN.
for the Azure connection from your MVE and click the Details view.
Note the value for the A-End VLAN. -
Log in to Aruba Orchestrator.
-
Go to Configuration > Networking | Deployment.
-
Locate the appliance by the hostname and click the Edit (pencil) icon.
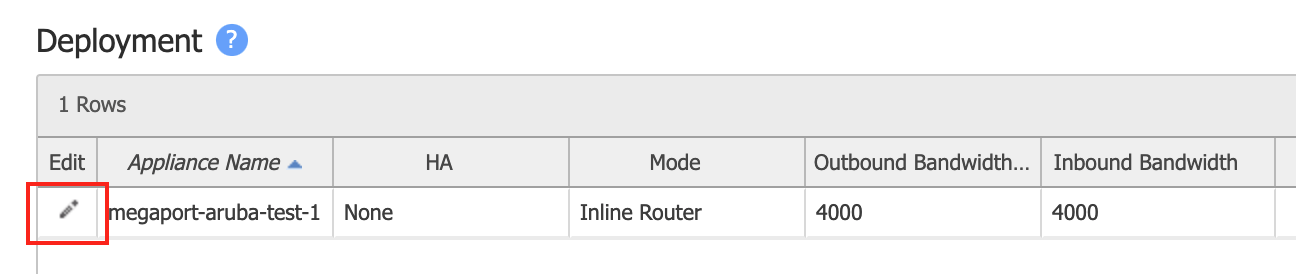
-
If you do not have a wan0 LAN side interface: Click +Add next to LAN Interfaces and in the Interface drop-down menu, choose wan0.
If you already have a wan0 LAN interface, click +IP to add a new configuration.
-
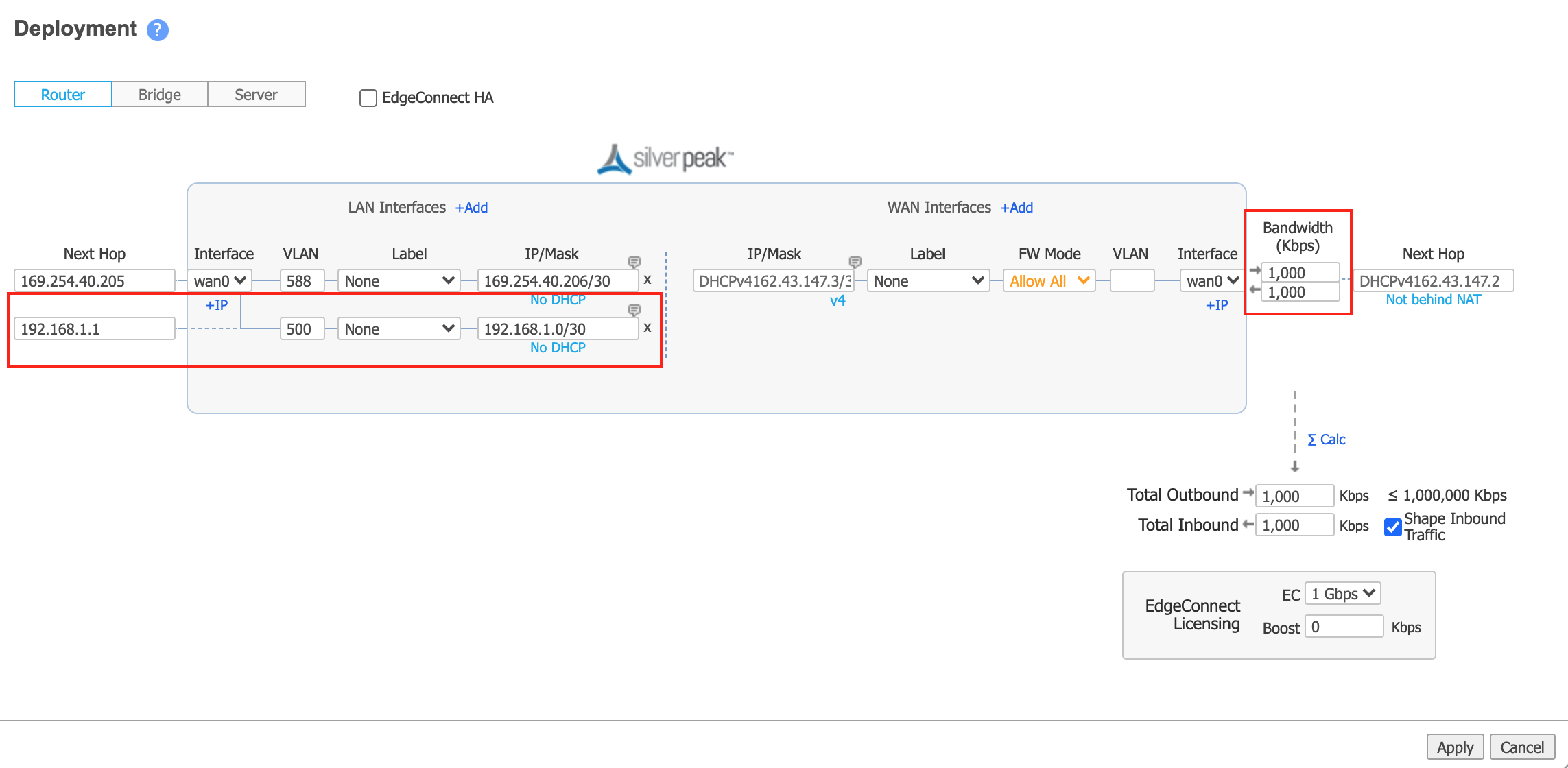
In the VLAN field, enter the A-End VLAN for the Azure connection (found in the Megaport Portal in Step 2).
- Optionally, select a preconfigured Label or select None.
-
In the IP/Mask field, enter the IP address and mask for the MVE side of the Azure connection.
This value is available in the Azure console. The IP addresses and CIDR appear in the IPv4 Primary Subnet field; MVE uses the first usable IP address and Azure uses the second usable IP for its router. For this field, enter the MVE (first usable) IP address.
-
For the Next Hop, enter the IP address for the Azure side of the connection.
From the IPv4 Primary Subnet field in the Azure console, use the second usable IP for the Azure router.
-
Specify in and out bandwidth values.
The bandwidth must be equal to or less than the MVE bandwidth limit.
This image shows sample configuration values (in this example, the Azure interface is added by clicking the +IP link).
-
Click Apply.
-
If prompted, reboot the appliance.
A reboot is required only when adding the first LAN interface, as the system switches the appliance from server mode to router mode.
Once the device is reachable from Orchestrator, you can configure a BGP session.
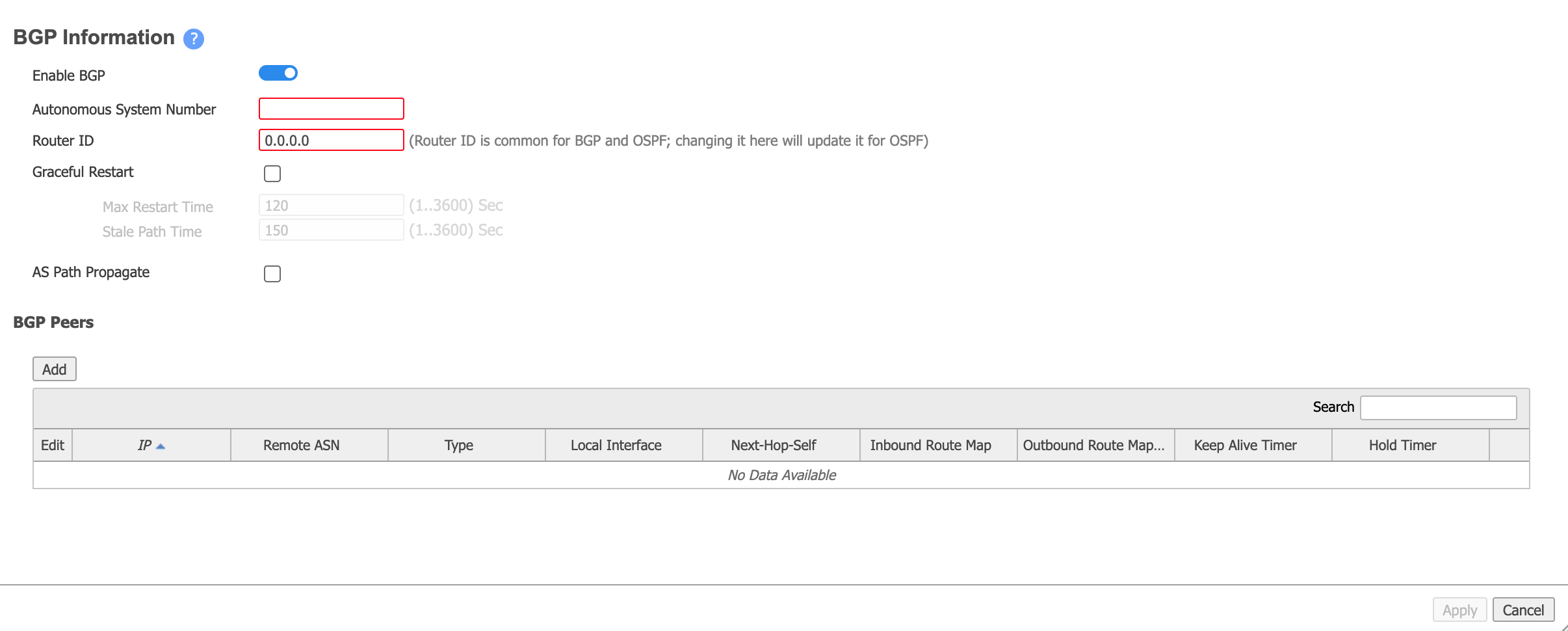
- In Orchestrator, go to Configuration > Networking | Routing | BGP.
- Click the Edit (pencil) icon for the appliance.
- Move the slider to Enable BGP.
-
Provide the Autonomous System Number.
This is the Peer ASN (for the MVE), collected in Step 1.
-
In the Router ID field, enter a system IP as required by your network design.
You can use any IP address on the MVE, such as the loopback 0 IP specified during the initial acceptance of the appliance, the interface IP on the MVE side of the VXC, or the transit IP address.
-
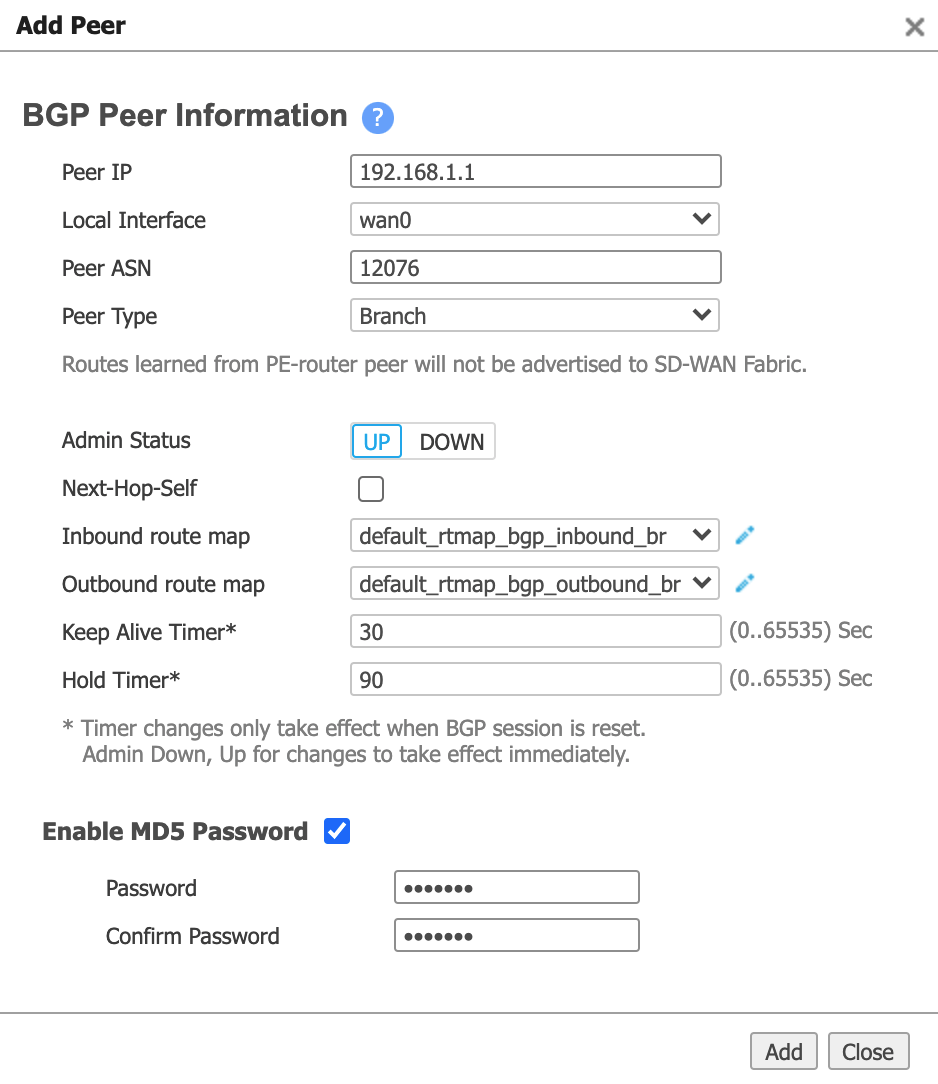
In the BGP Peers section, click Add and provide the following information:
- Peer IP – This is the Azure IP address. From the IPv4 Primary Subnet field in the Azure console, use the second usable IP for the Azure router.
- Local Interface – Choose the associated LAN interface (the interface is in the format wan0+VLAN).
- Peer ASN. Enter the Azure-side ASN of 12076. This is a fixed value, and appears in the connection details on the Azure console.
- Peer Type - Choose Branch.
- Enable MD5 Password - If required, select this and then enter and confirm your MD5 password.
-
Click Add.
- Click Apply.
It takes several seconds for the configuration to be pushed to the appliance. Click the refresh icon to update the data from the appliance.
When successful, the Peer State indicates Established:
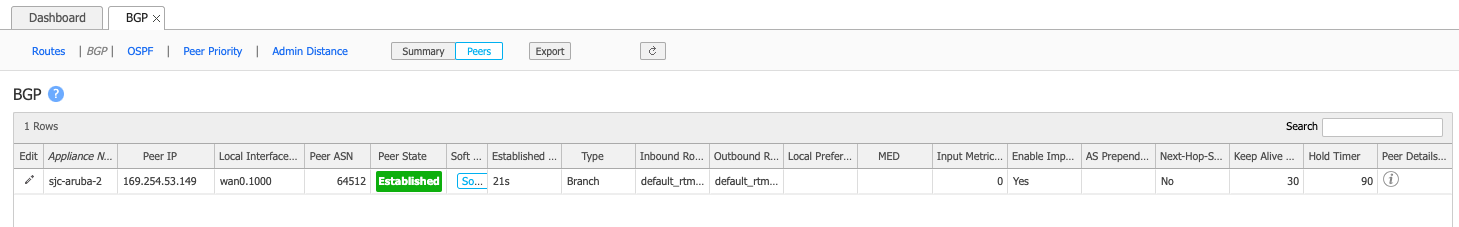
You can also check the BGP status for the connection in the Azure console and verify the BGP session is up.
Validating your Azure connection
You can review connection details, including the connection state, from the CLI with these commands:
show interface wan0.<subinterface id>– Displays configuration details and current status for the appliances.show bgp neighborsorshow bgp summary– Displays configuration details and current status for the BGP neighbors.
To start a CLI session from Orchestrator
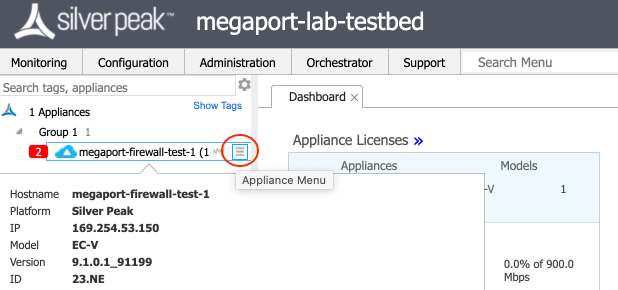
-
In Orchestrator, use the mouse to hover over the appliance and click the Appliance Menu icon to the right of the appliance name.
-
Choose CLI Session from the menu.
-
Enter enable mode to use the recommended CLI commands to display configuration details.