Planning Your Fortinet Secure SD-WAN Deployment
This topic provides an overview of the provisioning process and describes deployment considerations for the Megaport Virtual Edge (MVE).
| You Provide | Megaport Provides |
|---|---|
| Internet connection from branch | Platform to host virtual SD-WAN appliances |
| SD-WAN vendor enabled at branch | Complete connection from a branch to any destination on the Megaport network and interoperation with other Megaport products and services |
| Customer premises equipment (CPE) installed in branch | Megaport Internet connection to terminate the tunnel between MVE and CPE at branch via internet |
| SD-WAN software license to use on Megaport SDN | Access to the Megaport ecosystem |
Deployment considerations
This section provides an overview of the MVE deployment options and features.
Fortinet Secure SD-WAN uses virtual FortiGate appliances or physical FortiGate appliances much like many other SD-WAN vendors. However, with Fortinet, you can configure the appliances for several different uses. For example, you can configure a Fortinet appliance for use:
-
Strictly as a next-generation firewall (NGFW) for remote offices with local configuration and local logging only.
-
As central management with central logging, or as central management without central logging.
-
In a traditional SD-WAN style overlay network.
For more information, see the Fortinet Documentation Library.
Fortinet Secure SD-WAN features
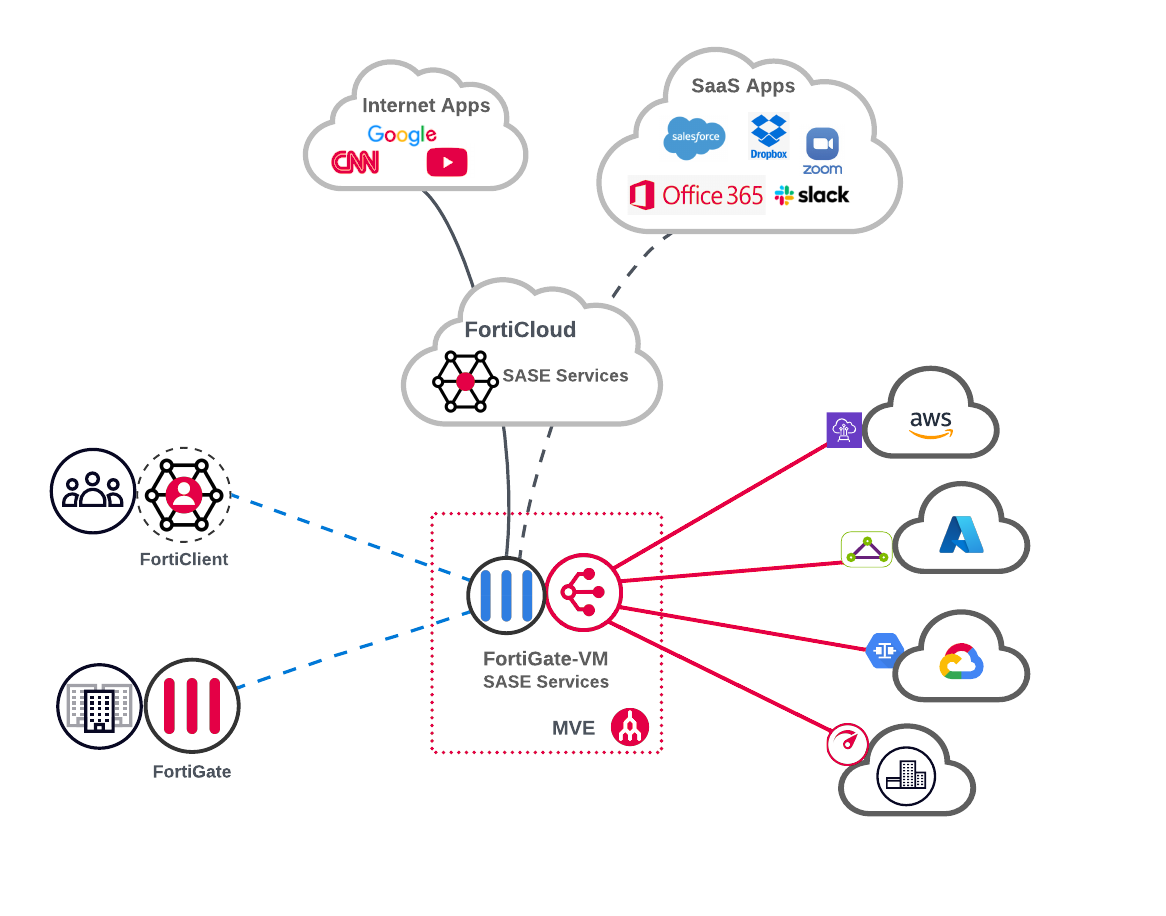
The FortiGate-VM delivers both NGFW and SD-WAN services on a single virtual machine. Hosting the FortiGate-VM on MVE not only optimizes edge-to-cloud network connectivity, but also enforces advanced security services and policies across the Megaport backbone segments.
Embedding the FortiGate-VM into Megaport’s NaaS platform extends the following core Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) elements between the edge and cloud network fabric:
-
Next-generation firewall (NGFW), including stateful firewall policies, network address translation (NAT), intrusion protection services, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) inspection, and threat intelligence.
-
Secure web gateway (SWG) services protect devices from malicious internet destinations using web content filtering and malware scanning.
-
Zero trust network access (ZTNA), which controls access to applications by verifying users and devices before every application session and confirms that they meet the organization’s policy to access that application.
The FortiGate-VM also supports remote user integration with Fortinet SASE solutions using their FortiClient endpoint security agent. The FortiClient enables the device to connect securely to the security fabric over either VPN (SSL or IPsec) or ZTNA tunnels.
The FortiSASE solution allows both the FortiGate and FortiCloud services to be used in a blended design as well. For example, internet and select SaaS applications may be protected using both SWG and a cloud access security broker (CASB) through FortiCloud, while private Megaport connections are protected using FortiGate security services.
Note
If you have already deployed a Fortinet firewall, you can connect it to an MVE so that your headquarters or branches can access cloud services over private interconnects.
For more information on these features, see:
SD-WAN vendors
MVE is integrated with Fortinet SD-WAN, which uses Fortinet’s FortiManager console to create the private overlay network.
Additional SD-WAN providers include Aruba SD-WAN, Cisco SD-WAN, Versa Secure SD-WAN, and VMware SD-WAN.
MVE locations
For a list of global locations where you can connect to an MVE, see Megaport Virtual Edge Locations.
Sizing your MVE instance
The instance size determines the MVE capabilities, such as how many concurrent connections it can support. The MVE instances are consolidated into these sizes:
| Package Size | vCPUs | DRAM | Storage | Megaport Internet Speed * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVE 2/8 | 2 | 8 GB | 8 GB | Adjustable from 20 Mbps to 10 Gbps |
| MVE 4/16 | 4 | 16 GB | 8 GB | Adjustable from 20 Mbps to 10 Gbps |
| MVE 8/32 | 8 | 32 GB | 8 GB | Adjustable from 20 Mbps to 10 Gbps |
| MVE 12/48 | 12 | 48 GB | 8 GB | Adjustable from 20 Mbps to 10 Gbps |
* Megaport Internet access is symmetric, redundant, and diverse. Megaport Internet access is adjustable through the Megaport Internet connection that you attach to the MVE.
These performance and capacity metrics are estimates and your speeds will vary. When choosing an MVE instance size, keep in mind these items:
-
Any increase on the network data stream load can degrade performance. For example, establishing secure tunnels with IPsec, adding traffic path steering, or using deep packet inspection (DPI) can impact the maximum throughput speed.
-
Future plans to scale the network.
What if I need more MVE capacity in the future?
You have a couple of options:
-
You can provision another MVE instance, add it to your SD-WAN overlay network, and split the workload between the two MVEs.
-
You can provision a larger MVE instance, add it to your SD-WAN overlay network, migrate connections from the old MVE to the new larger MVE, and then retire the old MVE.
You can adjust the Megaport Internet bandwidth at any time without having to tear down the virtual machine.
Security
MVE provides capacity to and from your internet-enabled branch locations securely, to any endpoint or service provider on the Megaport SDN. CSP-hosted instances of partner SD-WAN products route critical traffic across the Megaport SDN, reducing internet dependence. Traffic remains encrypted and under your policy control while traveling across the Megaport SDN, to or from, MVE.
Fortinet Secure SD-WAN includes access to a comprehensive security feature: Secure Access Service Edge (SASE). Fortinet on MVE natively supports SASE and SD-WAN services. For more information, see Securing the Network with SASE.
Licensing
You bring your own Fortinet (FortiGate) SD-WAN license for use with MVE. It is your responsibility to have the appropriate licenses for the SD-WAN endpoints created on the Megaport network.
VLAN tagging
Megaport uses Q-in-Q to differentiate VXCs and MVEs on a host hardware system. The tenant MVE receives untagged traffic for the internet-facing link, and single-tagged 802.1Q traffic for VXCs toward other destinations on the Megaport network (such as CSP on-ramps or other MVEs).
vNICs
Each MVE can have up to 5 vNICs. An MVE is created with 1 vNIC by default. You can add up to 4 more, making a total of 5.
Before specifying the number of vNICs on your MVE:
-
Be aware that the number of vNICs can’t be changed after an MVE has been ordered. Decide in advance how many vNICs to specify when you create the MVE.
-
Consult your service provider to make sure that functionality won’t be affected if you add a vNIC.
Note
If you need to change the number of vNICs after an MVE has been ordered, you will have to cancel and re-order the MVE.